As we all know, injection molding is one of the most widely used manufacturing processes in the world today. It has revolutionized the way we design and produce thousands of daily products and is widely used in various industries including aerospace, food and health, medical electronics, and more. However, like any manufacturing process, injection molding has its unique challenges, one of the most significant being calculating molding shrinkage.
In this guide, we’ll provide you with a comprehensive, informative, and persuasive overview of how to calculate injection molding shrinkage. We’ll cover everything from shrinkage basics and different types of materials to the formula of calculating shrinkage and the various methods and tools available. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or new to injection molding, this guide will give you the knowledge and skills you need to succeed. So, without further ado, let’s get started!

The importance of calculating molding shrinkage
Friends who are familiar with the injection molding industry know that during the CNC injection molding process, when the plastic part is taken out of the mold and cooled to room temperature, its room temperature size has a certain reduction ratio compared to the original uncooled size. This ratio is called the molding shrinkage – a key parameter that determines the accuracy of the final product. This parameter is critical, as even small changes can cause part dimensions to be incorrect and even lead to issues such as warping, sink marks, and voids, affecting the performance and aesthetics of the final product, ultimately affecting product quality and profitability.
Fortunately, with the correct knowledge and tools, you can master the technology of calculating the injection molding rate and improve your manufacturing process to a higher level.

What is the molding shrinkage?
Molding shrinkage is defined as the: the error percentage between the size of a plastic product after it is cooled and solidified and demoulded and formed, and the size of the original mold.
In the cooling and curing stage, plastic gradually solidifies due to the decrease in temperature, and the arrangement of plastic molecules during solidification will change. This arrangement changes can cause the distance between plastic molecules to shrink, which causes the overall volume to shrink.
Since shrinkage is not only the thermal expansion and shrinkage of the resin itself, but also related to various forming factors, the shrinkage of the plastic part after molding should be called the molding shrinkage. This concept is commonly used in polymers.
What factors affect shrinkage?
Shrinkage depends largely on:
| Factor | Example |
| Polymer composition and material properties | PVT, thermal properties |
| Applicable processing conditions | Temperature, pressure, flow, etc. |
| Part design and geometry | Wall thickness, gate location, mold constraints |
types & characteristics of molding materials
Different materials have different shrinkage, and manufacturers must consider them when calculating the shrinkage. For example, because thermoplastic plastic has high molecular liquidity and does not have chemical cross -linking, thermoplastic plastic is usually higher than thermosetry plastic. Additionally, highly crystalline materials such as polyoxymethylene (POM) shrink less than amorphous materials such as polycarbonate (PC).

The surface temperature of the cavity
The molding rate varies depending on the surface temperature of the cavity at the time of injection. Under normal circumstances, the contraction rate will increase when the temperature is high.
Specification pressure × pressure time pressure time
The molding rate changes according to the pressure maintained after plastic injection and the time to maintain the pressure. Under normal circumstances, when the pressure of high pressure and long pressure time, the shrinkage coefficients have become smaller.
Wall thicknes
Wall thickness is a factor of shrinkage, because it affects the crystallinity in the material, and then affects the total potential shrinkage. The uneven wall thickness can lead to different cooling rates of the entire part. The thinner the wall, the faster the cooling, the lower the crystallization and shrinkage. The thicker the wall, the slower the cooling, the higher the crystallization and shrinkage. In non -crystal materials, increased wall thickness often reduces the orientation effect. Keeping uniform wall thickness helps to avoid shrinkage changes that may lead to warp.

Different wall thicknesses, different shrinkage rates – red indicates high shrinkage rate
Gate shape
The contraction coefficient changes according to the shape of the mouth and the mouth. Generally speaking, as the cross -sectional area becomes larger, the shrinkage has become smaller. In addition, compared with the pouring mouth or dive pouring mouth, the shrinkage of the side port has a smaller trend.
Whether there are additive materials in the molding materials
There are many differences between the shrinkage coefficient between natural materials and glass fiber materials. For materials containing glass fibers, the contraction coefficient has a small trend. In fact, the molding shrinkage of mold design is determined by comprehensive research.
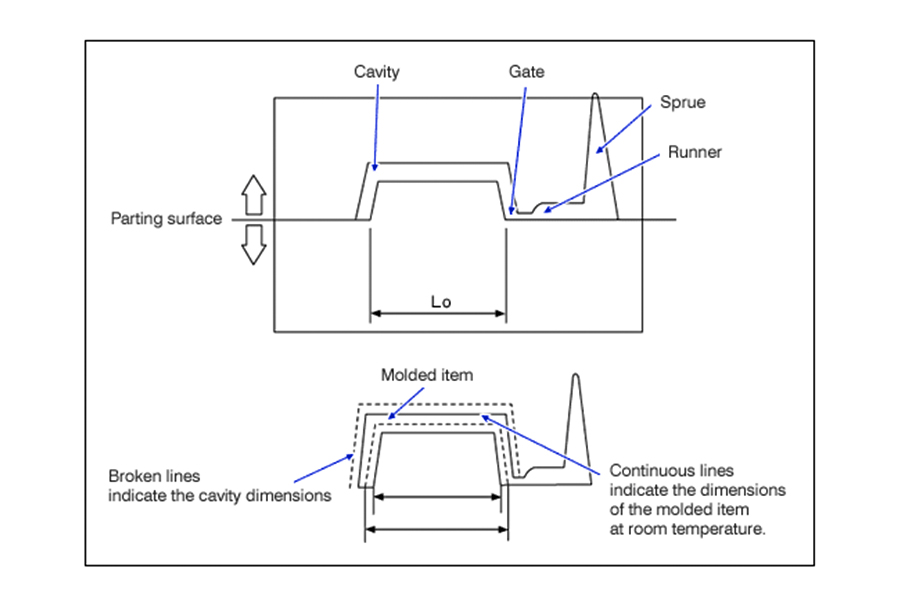
How to calculate shrinkage?
The molding shrinkage can be calculated with the size of the cavity and the final part of the parts, and it is represented by percentage.
S={(D-M)/D}×100%
(S: shrinkage; D: mold size; M: plastic part size)
Suppose the final part size is 1.7in and the cavity size is 1.9in, then the calculation method is:
S={(1.9-1.7)/1.7}×100%
S= 0.00117 in或0. 117%
Which polymers Exhibit low or high shrinkage?
Different polymers have different shrinkage due to the shrinkage and density of the material. The following is a summary of common plastic proportion and shrinkage:
|
Plastic abbreviation |
Proportion |
Shrinkage (%) |
Barrel Temperature |
mold temperature |
|
LDPE |
0.92 |
3 |
220~260 |
20~40 |
|
HDPE |
0.96 |
3 |
190~280 |
30~70 |
|
PP |
0.91 |
2 |
210~280 |
20~50 |
|
PVC |
1.38~1.41 |
1.5 |
170~190 |
20~40 |
|
ABS |
1.05 |
0.6 |
210~260 |
50~80 |
|
AS |
1.07 |
0.6 |
220~270 |
40~80 |
|
BS |
1.01 |
0.5 |
190~230 |
30~50 |
|
GPPS |
1.16 |
0.3~0.6 |
200~250 |
40~60 |
|
HIPS |
1.08 |
0.5 |
210~270 |
20~50 |
|
EVA |
0.95 |
2 |
140~200 |
20~40 |
|
PMMA |
1.18 |
0.6 |
220~240 |
60~80 |
|
PA6 |
1.13 |
0.7-1 |
250~270 |
40~60 |
|
PA66 |
1.13 |
1.3 |
280~300 |
40~60 |
|
PA66+30%GF |
1.39 |
0.3 |
240~270 |
80~90 |
|
POM |
1.42 |
2.1 |
205~225 |
80~100 |
|
PC |
1.2 |
0.5 |
271~293 |
71~93 |
|
PET |
1.33 |
0.4 |
277~293 |
15~30 |
|
PET+30%GF |
1.67 |
0.2 |
265~305 |
95~150 |
|
PETG |
1.27 |
0.2~0.5 |
250~270 |
15~40 |
|
PCTG |
1.23 |
0.2~0.5 |
275~295 |
15~40 |
|
PBT |
1.4 |
1.5~2.2 |
225~245 |
40~80 |
|
PBT+30%GF |
1.61 |
0.4~0.9 |
225~250 |
40~100 |
|
PCT+30%GF |
1.45 |
0.1~0.4 |
295~370 |
105~135 |
|
CA |
1.26 |
0.5 |
160~230 |
40~60 |
|
CAP |
1.2 |
0.5 |
215~240 |
40~75 |
|
CAB |
1.19 |
0.5 |
230~250 |
40~85 |
|
PP(Thermostability) |
1.12 |
0.9~1.1 |
180~220 |
60~80 |
|
PPS+40%GF |
1.67 |
0.25 |
300~340 |
120~150 |
|
PPO |
1.07 |
0.5~0.8 |
270~310 |
70~93 |
|
PSU |
1.24 |
0.5 |
330~360 |
120~160 |
|
PES |
1.37 |
0.68 |
340~380 |
120~160 |
|
LCP |
1.7 |
0.02 |
385~400 |
35~200 |
|
SBS |
0.96~1.1 |
1.5 |
145~160 |
25~30 |
|
SEBS |
0.87~0.91 |
1.6 |
180~220 |
35~65 |
|
TPU |
1.24 |
1.2 |
190~220 |
24~49 |
|
TPV |
0.97 |
1.5~2.5 |
180~190 |
10~80 |
|
TPEE |
1.2 |
1.4 |
220~250 |
45 |
What are the methods for measuring molding shrinkage?
Plastic molding shrinkage is determined by measuring the difference between the dimensions of the plastic product after cooling and solidification and the dimensions of the mold. There are two common testing methods, one is the linear dimension method and the other is the proportional dimension method.
- The linear dimensional method calculates shrinkage by measuring the length, width and thickness of a plastic product. First, prepare a standard mold and measure its dimensions. The molten plastic is then poured into the mold and allowed to cool and solidify. After the plastic has completely solidified, remove the product and use a dimensional measuring instrument to measure its length, width and thickness. Finally, the dimensions of the product are compared with the dimensions of the mold to calculate the shrinkage.
- The proportion size method is calculated by preparing a set of molds of different sizes. First prepare a series of different sizes and measure the size. Then, the melting plastic
Inject it into these molds for cooling and solidification. After the plastic is completely solidified, take out the product and use the size to measure the instrument to measure its size. Finally, the size of the product is compared with the size of the mold to calculate the shrinkage.
The test results of plastic molding shrinkage have important guiding significance for the design and production of plastic products. By understanding the shrinkage of plastic, you can predict the final size of the product after cooling and curing, so as to reasonably design the size of the mold. If the shrinkage is too large, the size of the product may not meet the requirements; if the shrinkage is too small, it may cause the product size to be too large and cannot meet the assembly requirements. Therefore, reasonable control of plastic molding shrinkage is essential to ensure product quality and stability.
Why choose Longsheng?
Dongguan Longsheng is located in a city known as the “World Factory”-China Dongguan. It has a very mature injection molding and CNC processing service experience. If you have this need or have any questions, you can comment and send a quotation. Our professional technicians are waiting for you!

As a reliable plastic injection manufacturer with extensive experience and expertise, we offer assistance at every stage of production, including expert advice on the best materials for your application, as well as other factors to consider. Our goal is to help you build a successful plastic mold project. Need professional help with your plastic injection molding project? just contact us today or request a quote.
Conclusion
In short, calculating the mold shrinkage in the injection molding industry is a vital step, which is very critical for production efficiency and the quality of the finished product. Through the above description and explanation, you should have a general understanding of the molding shrinkage. And you can increase your injection molding level to a new level by mastering the calculation of this ratio.
FAQs
How to prevent PP from shrinking?
1. Proper processing temperature: Control the processing temperature to avoid overheating, which can reduce the risk of shrinkage.
2. Good mold design: Ensure that the mold design is reasonable to minimize the stress on the PP during processing.
3. Moisture control: Keep the PP dry to prevent moisture from affecting its properties and causing shrinkage.
4. Post-processing treatment: Some post-processing treatments, such as annealing, can help reduce shrinkage.
How about Longsheng Technology‘s injection molding processing services?
Longsheng Technology’s injection molding processing services are remarkable. They possess advanced technology and professional expertise. Their team is skilled in handling various materials and can ensure high-quality molding results. They pay attention to details, strictly control the processing process, and provide reliable and efficient services. Whether it is in terms of product quality, delivery time, or customer service, Longsheng Technology demonstrates excellent performance, making them a trusted choice in the field of injection molding processing.
Why should we calculate molding shrinkage?
Calculating molding shrinkage is important for several reasons. Firstly, it helps ensure the dimensional accuracy and fit of the final product. Understanding shrinkage allows us to design molds and parts more precisely to meet the required specifications. Secondly, it assists in predicting and controlling potential issues during the manufacturing process, reducing the likelihood of defects and rework. Additionally, it is crucial for optimizing the design and production process to achieve better quality and performance.
What is the formula for calculating plastic molding shrinkage?
Shrinkage = (Dimension after molding – Dimension before molding) / Dimension before molding * 100%.
resource
A Simulation Study of Conformal Cooling Channels in Plastic Injection Molding

