Aluminum anodizing is a widely used process for surface finishing of aluminum and its alloys. This oxide layer not only improves the surface hardness and wear resistance of aluminum materials, but also improves its corrosion resistance and aesthetics. The purpose of this paper is to deeply explore the principle of aluminum anodizing process and its working mechanism, in order to provide a clear understanding and guidance for researchers in engineering and manufacturing fields.
What is Aluminium Anodizing?
The so-called anodizing of aluminum is an electrolytic oxidation process. The process of forming an oxide film on aluminum products (anodes) under the action of an applied current in the corresponding electrolyte and specific process conditions.
Therefore, if there is no specific indication for anodic oxidation, generally speaking, the anode is made of aluminum or aluminum alloy, while the cathode is made of lead plate. The aluminum and lead plates are placed together in an aqueous solution, which contains sulfuric acid, oxalic acid, chromic acid, etc., for electrolysis to form an oxide film on the surface of the aluminum and lead plates.
The objects of anodizing treatment can be aluminum and aluminum alloys, magnesium alloys, titanium and titanium alloys, etc. The most widely used and rapidly developing in the market is anodizing of aluminum and aluminum alloys.
Aluminum anodizing process
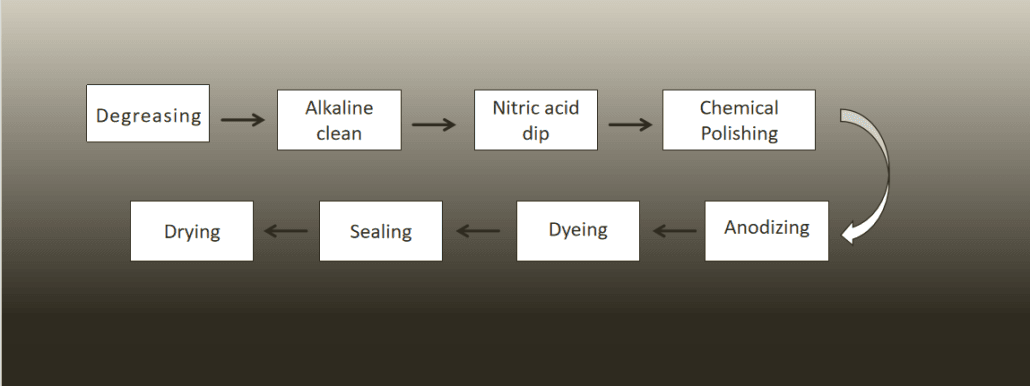
1.Degreasing
Step: At an operating temperature of 50 ℃, gently place the workpiece into the degreasing tank, turn on the timer, and be careful not to collide with the barrel groove. When the time is up, gently remove the workpiece and move it to the next step
Purpose: To remove oil stains from the surface of the workpiece.
2.Alkaline clean
Step: Use a degreaser at an operating temperature of 50 ℃, gently place the workpiece into the alkaline washing tank, turn on the timer, and be careful not to collide with the barrel groove. When the time is up, gently remove the workpiece and move it to the next step
Purpose: Remove the oxide layer on the surface of aluminum parts to expose the pure metal body.
3.Nitric acid dip
Step: Using nitric acid at room temperature, gently place the aluminum parts into the pickling tank, turn on the timer, and be careful not to collide with the barrel slot. When the time is up, gently remove the workpiece and move it to the next step.
Purpose: To remove dirt from the surface of aluminum parts.
4.Chemical Polishing
Steps: Use phosphoric acid, operating temperature 92℃, gently put the aluminum parts into the chemical casting tank, turn on the timer and do left and right rotation, be careful not to collide with the tank, the aluminum parts gently removed to the next step when the time is up.
Purpose: To enhance the luster of aluminum parts by chemical polishing.
5.Anodizing
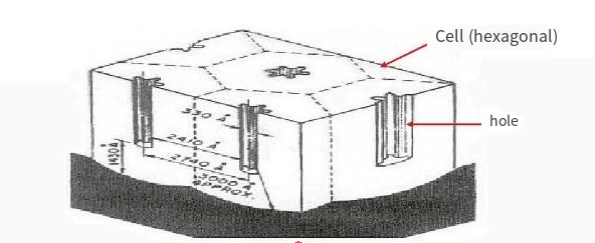
Specific process: When the current passes through, hydrogen gas is released from the cathode, and the oxygen precipitated from the anode is not only molecular oxygen, but also atomic oxygen (o) and ionic oxygen, usually represented as molecular oxygen in the reaction. Aluminum, as an anode, is oxidized by the oxygen precipitated on it, forming an anhydrous aluminum oxide film. The generated oxygen does not fully interact with aluminum, but partially precipitates in a gaseous form.
Principle: The process of placing aluminum or aluminum alloy products as anodes in an electrolyte solution and utilizing electrolysis to form an alumina film on their surface.
Step: Using sulfuric acid at an operating temperature of 21 ℃, move the aluminum parts to the anode tank and place the rack in it. The timer will automatically time. When the timer time is completed, move the aluminum parts to the next tank for operation.
Purpose: To convert the surface of aluminum parts into a layer of oxide film, which has protective decorative properties and some other functional characteristics.
6.Dyeing
Step: Using dye at an operating temperature of 55 ℃, move the aluminum parts to the dyeing tank and place the rack. The timer will automatically time. When the timer time is completed, move the aluminum parts to the next tank for operation.
Purpose: To produce aluminum parts in different colors according to customer color requirements.
Dyeing precautions:
1.The higher the purity of dyes used for dyeing, the better
2.The anodizing treatment conditions for aluminum parts must be consistent, and the dyeing conditions should also be consistent
3.The dye should be completely dissolved, otherwise uneven coloring may lead to dark spots
4.The coloring tank should be made of non active materials to avoid chemical reactions that may cause the dye solution to deteriorate
5.It is strictly prohibited for oil stains to enter the dye solution, otherwise streaks or stains may appear on the colored surface
7.Sealing
Step: Use sealing agent at an operating temperature of 95 ℃, move the aluminum parts to the sealing groove and place the hanger in it. The timer will automatically time. When the timer time is completed, move the aluminum parts to the next barrel groove for operation.
Purpose:To improve the quality of aluminum parts and ensure firm dyeing and coloring, the micro pores of the oxide film layer must be sealed after coloring.
1.Prevent the appearance of the anodic oxide film from deteriorating.
2.Improve the wear resistance of the anodized film.
3.Maximize the corrosion resistance of the anodized film.
4.Minimize the fading of the dyed oxide film.
5.Improve the corrosion resistance of the anodic oxide film.
6.Improve the electrical insulation performance of anodic oxide films, especially in humid environments
Sealing method:
1.Hydration sealing
2.Sealing of pores with inorganic salt solution
3.Sealing holes with transparent organic coating
Factors affecting aluminum sealing:
1.Ni2+content
2.Fluoride content
3.Sealing additive
4.PH value of sealing solution
5.Sealing fluid temperature
6.Impurity ions
7.Sealing time
The sealing materials such as nickel salts, fluoride ions, sealing additives, and their content in the sealing solution determine the sealing quality of aluminum materials
The pH value, temperature, and sealing time of the solution affect the sealing quality of aluminum profiles. Improving the cleanliness of the tank solution and reducing the content of impurities are important guarantees for the sealing quality of aluminum profiles.
8.Drying
Step: At an operating temperature of 50 ℃, move the aluminum parts to the drying tank and place the hanging rack. The timer will automatically time. When the timer time is completed, move the aluminum parts out.
Purpose: To dry the moisture on the surface of aluminum parts.
Anodizing classification
Classification by process
A. Anodizing:
1.Natural color anodizing
2.Black anodizing
3.Other color oxidation (blue oxidation, red oxidation, gold oxidation, etc.)
B. Hard anodizing:
4.Natural hard oxidation (the color of the oxide film varies depending on the material)
5.Black hard oxidation (hard oxidation dyed black)
Classification by substrate
1.Anodizing of extruded aluminum
2.Anodizing of Die Cast Aluminum
Why aluminum needs to be anodizing
Mainly to expand the application range and service life of aluminum.
Aluminum has many advantages, such as low density, high specific strength, good processing performance, high thermal conductivity, good conductivity, and so on. But aluminum itself has many drawbacks:
| Function | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Lattice constant | 4.0496×10`¹ºm (25℃) |
| Density | 2.697-2.699g/cm³ |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | 23×10`³/K (20°C) |
| Thermal conductivity | 2.37W/(cm×K) (25°C) |
| Resistance coefficient | 2.655×10`²Ωm |
| Melting point | 660.5℃ |
| Boiling point | 2477°C |
| Melting heat | 10-147KJ/mol |
1.The hardness is relatively low, while the wear resistance is also poor.
2.Large volume shrinkage during solidification.
3.High expansion coefficient.
4.The melting point is relatively low, and the operating temperature cannot exceed 200 ℃, so high-temperature use is limited.
5.The elastic modulus is only one-third of that of steel.
6.The potential is very negative, so aluminum is prone to severe galvanic corrosion as an anode when in contact with dissimilar metals.

Aluminum cannot improve its mechanical and surface properties through heat treatment like steel. Although aluminum’s strength can be improved through alloying, its surface properties have not been significantly improved, limiting its application as a cosmetic component.
In order to overcome the aforementioned shortcomings of aluminum (mainly the surface properties of aluminum) and expand its application range and service life. This can be achieved by anodizing aluminum.
Anodic oxidation is the process of placing aluminum in an acidic electrolyte solution as the anode, applying high-voltage direct current to move anions towards the anode, and generating new oxygen at the anode to form an oxide film with the aluminum alloy at the anode. Since anodic oxidation needs to be carried out under energized conditions, it is also called electrochemical oxidation.
The purpose of anodizing is fundamentally to form an oxide film on the surface of aluminum and its alloys, improve their protective, decorative, and functional properties, and expand their application range and service life.
advantages of Anodizing Aluminum
Anodizing aluminum oxide alloy has the following advantages:
1.Improving corrosion resistance
Aluminum is a corrosion-resistant metal, as it is very reactive and easily reacts with oxygen in the air to form aluminum oxide.
And the alumina film is transparent, so it is difficult for the human eye to see. This thin alumina film precisely isolates the air and prevents the aluminum substrate from being oxidized. That’s why it has a corrosion-resistant effect.
But everyone probably has a doubt that naturally generated oxide films can have antioxidant effects, why do we still need anodization?
1.The naturally formed oxide film is uneven, resulting in varying shades of color on the surface of aluminum alloy, which is relatively unsightly;
2.The naturally formed oxide film is very thin, easy to scratch, and has weak corrosion resistance. The artificial oxide film generated by anodic oxidation is uniform, dense, and more corrosion-resistant.

2.Improving wear resistance
Aluminum is particularly prone to scratches and wear, and its hardness cannot be compared to steel.
The surface of industrial aluminum profiles that have undergone anodizing is very hard, and the hardness of the oxide film is high. So after anodizing, it is very wear-resistant and not easy to scratch.
3.Improving insulation
Aluminum has excellent conductivity, but it requires insulation in some situations. The anodized aluminum oxide film is non-conductive, so if insulation is needed, anodizing treatment is necessary.
4.Decorative aluminum parts surface coloring
Before anodizing and sealing of aluminum, there will be many and dense pores on the surface, which can easily adsorb some metal salts or dyes, resulting in the formation of rich and colorful colors on the surface of aluminum parts.
5.To lay a foundation for painting
Some aluminum parts require painting treatment on the surface, and the surface voids of anodized aluminum parts have strong adsorption, making the painting more uniform and beautiful.
conclusion
In summary, aluminum anodizing is not only a surface aesthetic treatment process, but also a key method to improve the performance and durability of aluminum products, and can meet the needs of various applications.
At the same time, in order to ensure the successful implementation of aluminum anodizing, it is crucial to choose an experienced service provider. In this regard, Longsheng has extensive experience and professional knowledge. We are not only able to provide high-quality aluminum anodizing processes, but also able to customize solutions according to customers’ specific needs. Whether improving product performance or achieving unique appearance effects, Longsheng is a reliable partner.

