Roughing is a service in manufacturing that involves the removal of waste material from a workpiece to form a rough shape or form. This process is usually done using a cutting tool, such as a milling machine or lathe, and is often the first step in the manufacturing process. It is important because it helps reduce the amount of material that needs to be added in subsequent operations, saving time and money. In this blog, we will explore the necessity, parameters, advantages and considerations during machining of CNC rough machining in manufacturing.
What Is Rough Machining?
The rough machining process in mechanical processing is mainly used to quickly remove large pieces of material and rough process the workpiece into the desired shape, so as to make the subsequent processing more convenient and efficient. The purpose of rough machining is to quickly remove the blank allowance. Generally, large feed and cutting depth are selected to remove as much chips as possible in a short time. Therefore, rough machined products often have low precision, rough surface and high productivity. Rough machining is often the preparation for semi finishing and finishing, which cannot provide good surface finish and tight tolerance.

Advantages of rough machining in machining
- Improve production efficiency: Roughing focuses on removing excess material and leaving enough margin for finishing, taking into account dimensions and tolerances. This can effectively utilize different types of machine tools and improve cutting efficiency.
- Shorten production time: Quickly shorten the time from “raw material size” to “meeting drawing size requirements”.
- Save on tool costs: During roughing, tools that have been retired from precision machining can be used. Because these tools typically have less cutting edge wear and can be repaired or refurbished, they can continue to be used for roughing operations where surface requirements are less stringent.
- Increase the life of machine tools: roughing uses high-power, high-rigidity, low-precision machine tools, while finishing requires high-precision machine tools. The cooperation and combination of roughing and finishing helps maintain the accuracy of machine tools for a long time.
- Reduce the purchase cost of high-precision lathes: Rough machining can be completed with general low-precision machine tools, without the need to purchase expensive high-precision machine tools, thus saving costs.
- Good production line layout: Roughing helps optimize the layout of the production line, taking into account the specific requirements and processes involved.
Process parameters in roughing: feed rate, depth of cut and cutting speed
1.feed rate
Feed rate is the speed at which the workpiece moves in the feed direction relative to the cutting tool. Factors that generally affect feed speed include cutting depth, workpiece material, machine tool performance, etc.
2.depth of cut
Depth of cut is the thickness of workpiece material removed by the cutting tool during each cut. Factors that generally affect cutting depth include workpiece material, tool material, machine tool stiffness, etc.
3.cutting speed
Cutting speed is the linear speed at which the cutting tool moves relative to the workpiece per unit time. Factors that generally affect cutting speed include the hardness of the cutting material, tool material, machine tool performance, etc.
What are the types of rough machining on CNC machine tools?
rough turning
Rough turning is a rough machining process that removes excess material from the surface of the workpiece through cutting. It is generally used to process products with low requirements on size and surface roughness. The main purpose of rough turning is to remove most of the machining allowance on the surface. It is advisable to choose a larger cutting depth and feed rate within the allowable range, and the cutting speed is correspondingly low. The machining accuracy that can be achieved by rough turning is about IT12 to IT11, and the surface roughness is Ra50 to 12.5μm.
rough planing
When the machine tool is roughing, the processing speed is fast, the feed of the workpiece is large, and the cutting allowance is large, so the processing accuracy is low and the surface roughness is large. The processing accuracy of the planer is low, generally around IT13~IT11, the surface roughness is about 25μm, and the knife marks are obvious.
rough milling
Rough milling is the process of removing large amounts of material using a milling cutter. When using a milling machine to rough mill a workpiece, the metal machining allowance is large. Using larger feed rates and milling depths, the machining accuracy is approximately IT13 to IT11 and the surface roughness is 50-12.5 μm.
rough diamond
The machining accuracy that the drilling machine can achieve when drilling is about IT13 to IT11, and the surface roughness is Ra80 to Ra20; when enlarging, the accuracy can reach IT10, and the surface roughness is Ra10 to Ra5; when reaming, the accuracy can reach IT7, and the surface roughness is is Ra5 to Ra1.25.
rasp
When using files to process workpieces, the machining allowance is large, friction heat is obvious, the machining accuracy is very low, generally around IT13 to IT12, and the surface roughness is IT13 to IT12.
What are the requirements for rough machining of CNC machine tools?
Roughing does not require high surface quality and is generally used as a preparatory step for semi-finishing and finishing. Due to the large machining allowance, fast processing speed, and high processing heat of rough machining, the requirements for processing tools are relatively high, and high-hardness alloy materials are generally used as tool materials.
In addition, the heat generated by the tool during rough machining has a great impact on tool life. Therefore, we must use artificial methods such as using oil, cutting fluid or air cooling to extend the life of the tool.
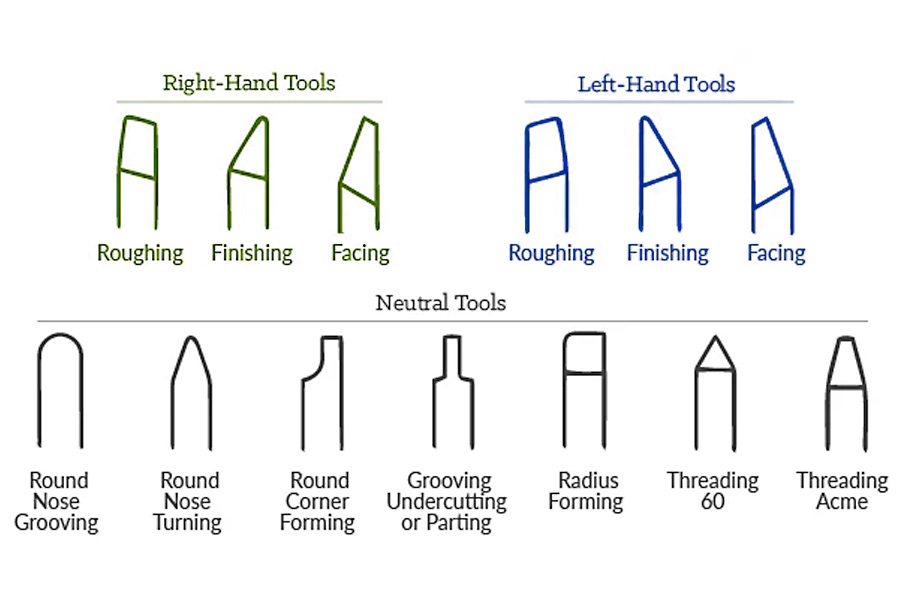
Tips for Effective Roughing in CNC Machining
- Choose the right tool material and geometry: use complex tools, such as carbide or high-speed steel end mills, for roughing because they allow for efficient cutting. It is crucial to look at the flute count and helix angle as they determine the chip removal rate and the efficiency of the cutting tool.
- Optimize cutting parameters:one of the key strategies to follow during roughing is to adjust speed and feed rate. The optimal value must be the one that achieves the highest level of feed rate without affecting tool wear or tool vibration.
- Implement an effective chip evacuation strategy:reduce chip recutting and heat build-up by using proper chip removal methods such as peck drilling or chip breaking during programming. Choose a tool with an optimal number of flutes to enhance the chip removal process.
- Adopt efficient processing technology:discuss some modern methods such as trochoidal milling and high-speed machining to improve roughing rates. These methods help minimize the load on the tool, enhance the cutting process, and increase tool durability.
- Manage heat and tool wear:use coolant when machining, or move to dry machining if heat from rough machining is a problem. It is also important to monitor tool wear and replace tools early to increase efficiency.
- Make sure the setup is rigid:a stable workpiece clamping device is used to ensure the rigidity of the machine and tools to cope with the huge cutting force during rough machining. The table or workpiece should not be vibrated or moved as this may cause surface finish and tool wear problems.
- Adapt to material properties:make sure that the roughing procedure used is appropriate for the material being machined. This article is designed to give you an understanding of how materials behave under roughing forces so you can get the most out of your cutting tools.
- Leverage software and simulation tools:modern woodworking CNC software has simulation tools that can simulate roughing paths and parameters. These tools can help predict problems that may occur and manage processing to make efficient use of time and resources.
- Processing parameters:minimize feed rate, cutting speed and depth for each roughing operation type. The best way is to set customizable parameters. This will make them more efficient and reduce complexity during processing.
- Select machine and control software:when roughing, equipment with high power and strong rigidity should be selected to withstand larger cutting loads, and ensure that the control software can identify the shape and size changes of the roughing task to improve processing accuracy and standardization.
- Manage heat and cutting fluid:there are several ways to address heat issues when machining aluminum alloys during rough machining. It is recommended to use fluids with lubricating and cooling effects. They keep tools and parts cool.
Differences between Roughing and Finishing
| Aspect | Rough Machining | Finish Machining |
| Purpose | Rough machining aims to quickly shape the workpiece by removing excess material. Surface finish is not a primary concern; the goal is efficient material removal. | Finish machining is performed to enhance surface quality, dimensional precision, and feature tolerances. Speed is not the primary focus. |
| Process Parameters and MRR | Rough machining employs higher feed rates and cutting depths, increasing material removal rates (MRR). | Finish machining uses lower feed rates and cutting depths, which reduce MRR but improve surface finish. |
| Surface Finish and Dimensional Accuracy | Rough machining, with its higher feed rates and cutting depths, leaves serrated scallop marks on the surface, leading to a rough finish and lower dimensional accuracy. | Finish machining, with lower feed rates and cutting depths, ensures improved surface finish, higher accuracy, and tighter tolerances. |
| Tools | Rough machining benefits from negative rake inserts that can withstand high cutting forces and attain faster speeds. | Finish machining typically employs front-angle blades to achieve superior surface finish. |
Why are rough machining and finishing machining often separated in CNC machining?
- Separate roughing and finishing can help reduce the impact of thermal deformation and facilitate recovery and stress relief. During rough machining, internal stresses change due to clamping and heating, causing deformation. Relieving stress and allowing the workpiece to cool by separating the processes helps maintain the dimensional and positional tolerances required for the design.
- At the beginning of processing, the workpiece is usually in a blank state. The blank is used as a reference when clamping, which can easily cause deformation of the workpiece and affect product quality.
- In order to ensure the accuracy of the equipment, roughing and finishing processing should be carried out separately. If rough and finish machining are performed simultaneously on the same equipment for a long time, the accuracy of the equipment will decrease, thereby affecting product quality.
- The residual stress of the workpiece after thermal processing is relatively large. Roughing and finishing can be performed separately. Stress relief annealing or other heat treatments can be arranged before finishing to eliminate residual stress and reduce deformation.
- Roughing allows for higher cutting depths and feed rates, optimizing material removal. In contrast, finishing requires smaller depths of cut and slower feed rates to achieve the desired surface quality and accuracy.
- During rough machining, the risk of deformation is greater due to the large cutting allowance. If finishing is performed after other surfaces have been machined, accuracy will be affected and the machined surface may be damaged.
- High utilization rate of machining equipment: Roughing and finishing have different requirements for machining equipment. By dividing the processing sections, the respective characteristics of roughing and finishing equipment can be fully utilized to maximize production efficiency. Rough machining equipment generally has high power, high efficiency and strong rigidity, while finishing equipment has high precision and small errors, which can meet the drawing requirements.
- At the beginning of production, rough machining is usually selected so that any material defects in the workpiece can be discovered in time to avoid potential problems that may occur in subsequent processing. There are many defects in the blank material, such as pores, bubbles or unevenness caused by internal impurities or insufficient machining allowance. Defects can be found after rough machining so that they can be repaired in time or decide whether to scrap, thereby reducing time costs in the production process.
- Arranging rough machining before precision machining and surface finishing can help protect the surface after precision machining and surface finishing processes and minimize wear and damage.
- By dividing the processing stages, the processing errors caused by factors such as large machining allowance and large cutting force can be gradually corrected, and combined with semi-finishing and finishing to ensure processing quality.
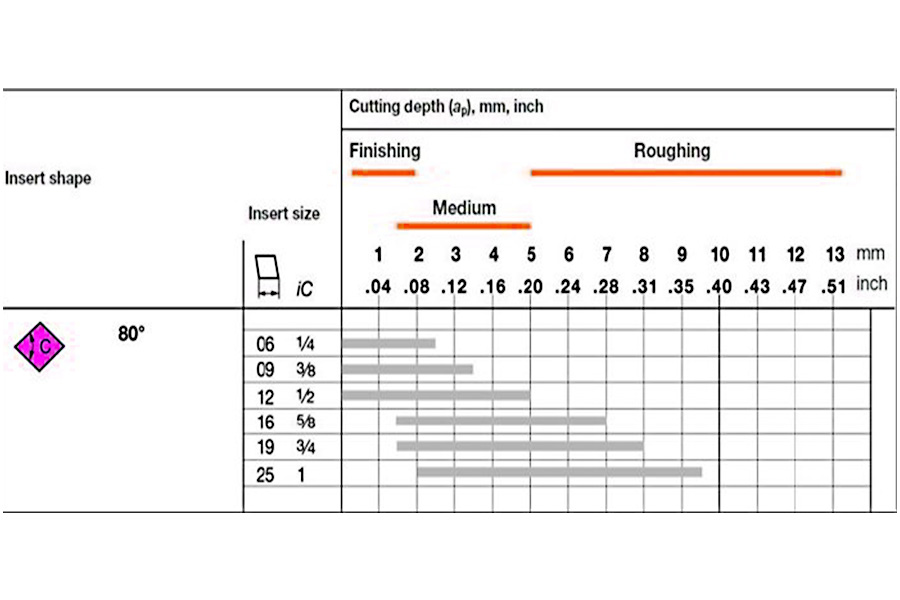
What are the common methods of roughing in CNC machine tool services?
1.Milling
Milling is one of the most common roughing methods used in CNC machine tools. Through the relative motion of the rotating milling cutter and the workpiece, excess material on the workpiece is removed.Various types of milling cutters, such as face milling cutters, end milling cutters, and slot milling cutters, can be used to adapt to different processing needs.
2.drilling
Drilling is the process of making holes in a workpiece with a rotating drill bit. In the roughing stage, drilling is mainly used to make through holes or blind holes in the workpiece.
The speed and depth of drilling can be controlled by the program of the CNC machine tool.
3.Boring
Boring is a processing method that enlarges the diameter of an existing hole. In rough machining, boring is often used to enlarge the rough hole or further correct the position and size of the hole.Boring is usually performed using boring tools or boring bars, which can achieve high machining accuracy.
4.Turning
Turning is mainly used to process rotationally symmetrical workpieces, such as shaft parts. On a lathe, material is removed from the workpiece through the rotation of the spindle and the feed motion of the tool.Turning can quickly remove excess material from the cylindrical surface and end face of the workpiece during the roughing stage.
5.Sawing
Sawing is a method of cutting workpieces by the reciprocating motion of a saw blade or saw blade. In CNC machine tools, sawing is often used to cut off workpieces or remove larger excess parts of workpieces.
6.Planing
Planing is a method of removing material from the surface of a workpiece through linear reciprocating motion of the planer. In CNC machine tools, planing is less used for rough machining, but it is still an effective machining method in certain situations.
7.Rough Grinding
Although rough grinding is usually considered part of semi-finishing or finishing, in some cases rough grinding can also be used to remove large amounts of material from a workpiece. Coarse grinding typically uses coarser abrasives and larger feed rates.
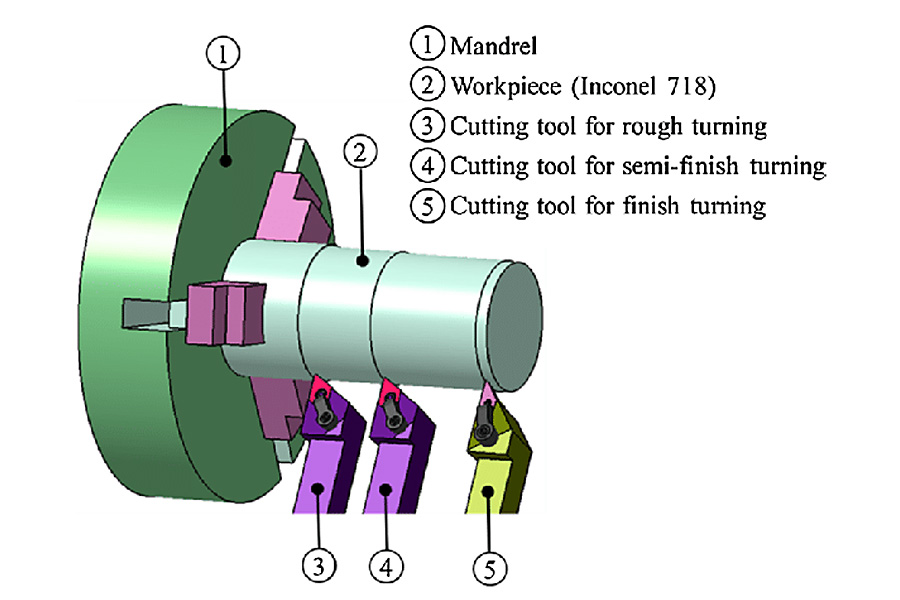
Things to note when roughing machining
There are several important factors to consider when roughing. Roughing is a technique for quickly and efficiently removing large amounts of material to produce the desired shape and size, followed by a finishing procedure. When performing rough machining, the following precautions should be taken:
Material removal rate
The basic goal of roughing is to remove material as quickly as possible. Therefore, it is important to optimize the material removal rate while maintaining process stability. If we need to achieve efficient chip evacuation and reduce cutting time, then we need to choose the right cutting parameters such as cutting speed, feed rate and depth of cut.
Tool selection
Choosing the right cutting tool is crucial for roughing operations. Typically, roughing involves the use of solid carbide or high-speed steel (HSS) end mills, roughing end mills, or indexable mills. The tool should be able to withstand high cutting forces and provide sufficient rigidity and heat resistance.
Cutting parameters
Choosing the right cutting parameters is crucial for successful roughing. Cutting speed, feed rate and depth of cut should be balanced to ensure efficient material removal while avoiding excessive tool wear or breakage. Optimum parameters may vary depending on the material being processed, machine capabilities and equipment.
Chip control
Effective chip control is essential to prevent chip clogging, tool damage and poor surface finish. Proper chip evacuation can be achieved by selecting appropriate cutting parameters, using chip breakers on the cutting tools, using coolant or lubricants, and using chip evacuation methods such as coolant through the tool or chip conveyors.
Tool life and cost
Roughing operations place high demands on cutting tools because of the high material removal rates involved. Balancing tool life and cost is critical. It may be more cost-effective to use cheaper or less durable tools for roughing operations, while reserving high-performance tools for finishing operations where surface finish and dimensional accuracy are critical.
During the machining process, by paying attention to the above matters, manufacturers can optimize the roughing process, reduce processing time, minimize tool wear, and effectively achieve the desired part shape, laying the foundation for subsequent finishing operations.
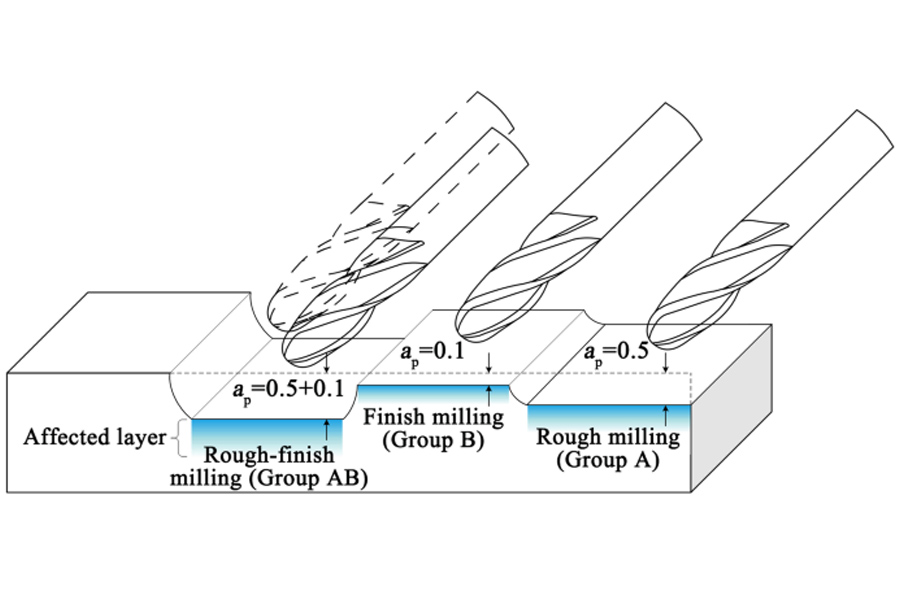
What are the main functions of rough machining?
※Error correction: Roughing is the initial machining stage in a series of workpiece machining stages. Errors can occur when dealing with large machining allowances and high cutting forces. These errors are gradually corrected during semi-finishing and mechanical finishing to ensure the required processing quality.
※Equipment utilization: Different processing stages have different requirements for equipment. Roughing equipment has the characteristics of high power, high efficiency, strong rigidity, etc., which is very suitable for the role of roughing equipment. This stage makes full use of the characteristics of roughing equipment to improve production efficiency. Ensure project requirements are met.
※Defect identification: Rough machining is the precursor to the machining sequence. It can detect defects in the workpiece blank in time. This includes sand holes, porosity, or insufficient machining allowance. Identifying these defects at this stage is valuable as it enables timely repair or the decision to scrap the workpiece, thus avoiding wastage of time and resources in subsequent machining.
※Stress Management: This stage also provides the opportunity to efficiently schedule the cold and heat treatment processes. After thermal processing, the workpiece may have significant residual stress. Separating roughing and finishing and incorporating aging processes to eliminate this stress ensures dimensional stability and quality of the final product.
※Surface Protection: Finally, strategic placement of roughing operations at the beginning of the machining sequence provides protection for surfaces undergoing mechanical finishing and pre-finishing. This reduces wear and maintains the quality of the final product.
Choose Longsheng for your one-stop service
Obtaining high-quality processing services remains an essential goal for rapid production success. At Longsheng, we offer a full range of machining services to meet your machining needs – from initial roughing to final finishing.
With over 15 years of manufacturing experience, we handle CNC parts with tolerances up to 0.005mm, with same-day quotes and 72-hour delivery. We produce over 80.00 parts in various quantities. Our goal is to provide the highest quality and efficient metal parts processing services to prototyping and mass production customers. From raw material control to product inspection, we always adhere to the pursuit of excellent quality to provide you with impeccable results. Longsheng recognizes the importance of production Every detail is important, so we ensure that the products not only meet your expectations but exceed them in terms of quality and visual appeal. When looking for a reliable and professional roughing service provider, consider Longsheng as your trusted partner in achieving efficiency and excellence in your machining processes.
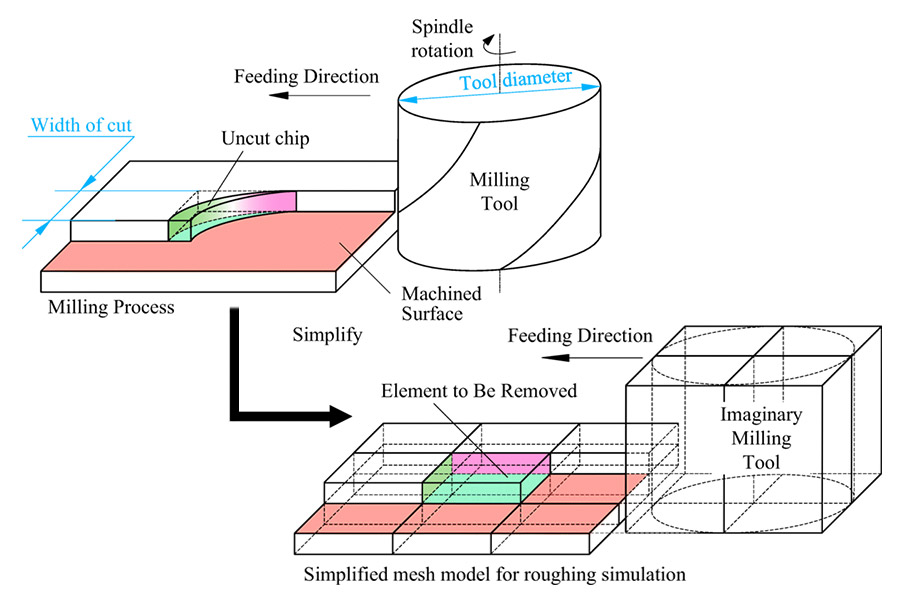
conclusion
Rough machining in CNC machine tool services is an important part of the metal processing process. It provides a stable foundation for subsequent processing by efficiently and quickly removing excess material from the workpiece. In practical applications, it is necessary to select appropriate roughing methods and parameters according to the specific conditions and processing requirements of the workpiece to ensure processing quality and efficiency. Optimizing roughing is a key strategy to simplify part cycle times, improve surface finish, extend roughing cutter life and maximize machine tool efficiency.
FAQs
What is CNC machine tool finishing?
Finishing refers to the final phase of the machining process, where the focus is on achieving the desired surface quality, dimensional accuracy, and overall appearance of the machined part. It involves removing any remaining imperfections such as roughness, burrs, machining marks, and refining surfaces and ensuring the machined part meets the required specifications.Different methods can be employed in machining to achieve the desired finish, depending on the material being machined and the desired outcome. Some standard finishing techniques include surface coating, grinding, deburring, polishing, and CNC precision machining.
What impact does rough machining have on CNC machining?
① Rough machining can quickly remove most of the excess material on the surface of the workpiece, making the shape and size of the workpiece close to the final requirements, thereby significantly shortening the entire processing cycle and improving production efficiency. ② Rough machining can more accurately control the amount of material removal, reduce unnecessary material waste, and reduce production costs. ③Rough machining can eliminate problems such as defects in the blank and insufficient machining allowance, and avoid greater errors and waste in subsequent processing. ④ Through reasonable roughing parameter settings and tool selection, processing errors and surface roughness can be minimized, creating better conditions for subsequent semi-finishing and finishing.
What are the challenges faced during roughing CNC machining?
The challenges faced during rough machining CNC machining mainly include high-precision machining requirements, complex shape machining, material properties and tool selection, machining efficiency and cost, process arrangement and machining sequence, as well as process technology and personnel operations. In order to deal with these challenges, a series of measures need to be taken, such as optimizing tool paths, selecting appropriate tools and process parameters, rationally arranging processes and processing sequences, and strengthening technical training and operating specifications.
Which has a high dimensional accuracy in roughing vs. finishing?
Finishing machining is much higher than rough machining in terms of dimensional accuracy. Rough machining is mainly used to quickly remove irregular skin and most of the machining allowance on the blank to prepare for subsequent finishing; while finishing is used to further improve the machining accuracy and surface finish of the part to meet high-precision requirements. In the actual processing process, it is necessary to select the appropriate processing method according to the specific requirements and processing conditions of the part.

