In the cutting-edge field of 3D printing, the choice of materials undoubtedly plays a decisive role. The choice of material not only determines the physical properties of the finished product, but also has a direct impact on the ease of the printing process and the cost-effectiveness of the final product. Among them, PET (polyethylene terephthalate) filament, as a common 3D printing material, has attracted much attention for its applicability. Next, we will discuss whether PET filament is suitable for 3D printing from multiple dimensions such as its characteristics, 3D printing performance, application scope, and comparison with other materials.
What is PET 3D printing?
PET 3D printing, simply put, is the process of using polyethylene terephthalate (PET) to create three-dimensional parts using additive manufacturing. Due to its robust properties, PET is used in a wide range of applications such as waterproofing, bottling, and food packaging. Due to its excellent chemical resistance, good mechanical properties, and a suitable melting temperature of 260°C, PET has become one of the most popular materials for FDM/FFF 3D printing.
What Makes PET Filament Unique in 3D Printing?
The unique advantages of PET filament yarn in 3D printing are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1.Appearance and transparency
There are two main types of PET filaments: solid and translucent. In particular, translucent PET has a crystal clear appearance, excellent gloss and transparency, and the appearance of the finished product is smooth and translucent. That’s why translucent PET is particularly well used in luminaires, luminous lettering, and other applications where transparency or translucency is required.
2.Outstanding Performance
- High toughness: Objects printed with PET have high tensile and flexural strength. In the process of daily use, it can withstand many bends and impacts, and is not prone to breakage.
- Good heat resistance: PET has a heat deflection temperature of about 75°C, which is the best heat resistance in its class, and PET is more heat-resistant than PLA.
- Chemical resistance: PET has excellent water and chemical resistance, and can maintain a stable state in a humid environment or when exposed to water. This property makes it ideal for making packaging materials, parts for outdoor use, and more.
3.Easy to print
- Moderate printing temperature: Compared with PETG, PET has a relatively low printing temperature, generally in the range of 220 – 250°C. This means that the heating requirements for the printing equipment are not too high.
- Non-stick nozzles: PET prints do not stick to the nozzles easily, which allows users to print faster and reduce stringing, which in turn increases productivity.
- Ease of handling: In terms of printing difficulty, PET material exhibits good ease of use. Especially for those who want a fast, high-quality finished product, beginners are often able to get started with PET printing as well.
4.Environmental & Economic Advantages
- Eco-friendly features: PET does not emit any harmful odors during the 3D printing process, and it is 100% recyclable, which is fully compliant with environmental requirements.
- Affordable: PET has a certain price advantage among general-purpose 3D printing materials. For users with high daily printing needs, this price advantage of PET can significantly reduce printing costs.
How to Optimize PET Filament Printing Temperatures?
When it comes to 3D printing with PET filaments, precise control of the print temperature plays a key role in the print results. Here are a few proven ways to optimize your PET filament printing temperature:
Determine the optimal temperature experimentally
In general, the recommended nozzle temperature range for PET filaments is between 230 – 250°C. In order to find the best temperature for the material and printing equipment you are working with, you can start by printing some small specimens or temperature towers. During the printing process, carefully observe the printing conditions at different temperatures. For example, look at whether the material is extruded smoothly and smoothly, if the extrusion is uneven, it means that the temperature may not be suitable. At the same time, pay attention to the adhesion between layers, as well as the overall appearance quality of the print, whether there are defects, deformation, etc. Through such experimental comparisons, it is possible to filter out a temperature that can make the best printing effect.
Avoid extreme temperatures
If the temperature is too low, the PET material is prone to unevenness when extruded, which will seriously affect the print quality, and the printed object may be incomplete and incomplete. If the temperature is too high, the PET material will degrade, and the printed parts will not only turn yellow, but also lose their strength and become very fragile. Therefore, when setting the temperature, you must avoid these two extremes and try to control the temperature in a reasonable range.
Adjust with bed temperature
Bed temperature has a significant impact on whether the print adheres securely to the hot bed and whether it will warp or not. Typically, the bed temperature can be set at 70 – 85°C when PET filament is printed. Depending on the properties of the printing material you are using and the specific characteristics of your model, you need to flexibly and appropriately adjust the temperature of the hot bed. For example, for some larger models, it may be necessary to increase the bed temperature a little to enhance the adhesion of the print and prevent warping. By adjusting the bed temperature reasonably, the overall printing effect can be greatly improved.
Use a reasonable cooling strategy
When printing the first layer, it is recommended that you turn off the fan. Because the first layer is in direct contact with the heat bed, turning off the fan allows the material to adhere better to the heat bed, laying a solid foundation for subsequent printing. From the subsequent layers, you can turn on the fan appropriately according to the actual situation. The role of the fan is to balance the cooling and curing rate of the material, making the printing process more stable. However, the wind speed of the fan should not be too large, otherwise it may cause the material to cool too quickly, affecting the interlayer bonding, and it is necessary to find a suitable balance point.
What is the difference between PET and PLA filament?
PET (polyethylene terephthalate) and PLA (polylactic acid) filaments differ significantly in many aspects. Here is a detailed comparison:
| project | PET filament | PLA filament |
|---|---|---|
| raw materials | Petroleum-based materials | Renewable resources (e.g. corn starch, cassava root, sugar cane, etc.) |
| Eco-friendliness | Recyclable, but non-biodegradable | Biodegradable under industrial compost conditions |
| Tensile strength | Taller for applications that require strength | Relatively low and high brittleness |
| heat tolerance | The heat deflection temperature is high and the heat resistance is good | The heat deflection temperature is low and the heat resistance is poor |
| Chemical resistance | Good corrosion resistance | Chemical resistance is average |
| Printing temperature | The nozzle temperature is 220-250°C, and the temperature of the hot bed is adjusted according to the demand | The nozzle temperature is 170-180°C, and there is usually no need to heat the bed |
| Printing difficulty | Moderate, need to pay attention to temperature control to prevent degradation | It is easy to print and suitable for beginners |
| Print effect | The finished product has high gloss and good transparent or translucent effect | The finished product comes in a variety of colors, but it is not as transparent as PET |
| Application scenarios | Packaging materials, outdoor parts, components that require strength and heat resistance | Model making, prototyping, decorations that do not require high strength, etc |
| cost | Depending on market volatility, it may be slightly higher than the PLA | The cost is relatively low, making it suitable for large-scale production |
Which is Stronger: PET vs. PLA Filament?
In the field of 3D printing, PET filament and PLA filament are both commonly used materials, and they have their own characteristics for their robustness.
PET filaments excel in terms of strength. Its tensile strength is quite high, which means that PET filaments are not easy to break when pulled by large external forces. Imagine printing a hook on PET filament that needs to hang a heavy object, and with its high tensile strength, it can withstand the pull of the heavy load. At the same time, the heat deflection temperature of PET filament yarn is also high. For example, in some high-temperature environments, such as those close to 75°C, prints made of PET filament can still maintain stable performance and will not easily deform or be damaged. This gives PET filament a significant advantage in applications where strength and heat resistance are required, such as making parts for outdoor use, industrial molds, etc.
On the other hand, the tensile strength of PLA filament is much lower than that of PET filament, and the brittleness is larger. When subjected to external forces, prints made of PLA filament are more likely to break. For example, a container with a thin-walled structure printed on PLA filament is likely to crack if it is accidentally bumped. In terms of heat resistance, PLA filaments have a lower heat deflection temperature. Once exposed to high temperatures, such as more than 50°C, it is prone to deformation and even damage. This limits the application of PLA filament in high-temperature scenarios, and is more used for printing daily small objects that do not require high strength and heat resistance, such as some decorative ornaments, small stationery models, etc.
Overall, the strength of PET filament is significantly higher than that of PLA filament. Due to its high tensile strength, good abrasion resistance and excellent heat resistance, PET filament yarn can perform well in applications that require certain strength, abrasion resistance or heat resistance. Although PLA filament has a certain strength, it is indeed inferior to PET filament in terms of strength because of its brittleness and poor heat resistance.

When Should You Choose PET Over PETG?
When choosing a material, PET should be chosen over PETG in the following cases:
| Features/Requirements | PET | PETG |
|---|---|---|
| The need for transparency | It can achieve 90% light transmittance | Only 80% light transmittance and high haze |
| Chemical resistance | Resistant to grease, weak acids, suitable for labware | Chemical tolerance may vary depending on the specific formulation |
| Sacrificial layer application | Low temperature water solubility (50°C hot water immersion) | It is not water-soluble at low temperatures |
High transparency requirements
When we need high transparency printing results, PET is a good hand. PET typically achieves a high light transmittance of 90% or more, for example, if you print a lampshade with PET, the light will be as clear as crystal. In contrast, PETG is less transmittance, and the haze may be larger, making it look less clear. Therefore, PET is undoubtedly a better choice for applications that require high clarity, such as optics and display protective films.
Scenarios where good chemical resistance is required
PET can also play a role in applications where good chemical resistance is required. PET is highly resistant to common chemicals such as greases and weak acids. In the laboratory, for example, utensils made of PET will not be easily corroded, whether they hold grease reagents or contact with weak acid solutions. In the field of food packaging, PET is well insulated from the influence of external chemicals on food. As for PETG, its chemical resistance will vary depending on the specific formulation, and it may not meet all chemical resistance needs like PET.
Sacrificial layer application scenario
In 3D printing, sacrificial layers are sometimes used. PET is particularly suitable for sacrificial layer materials because it has the unique property of being soluble in water at low temperatures. For example, when printing an object with a complex structure, there needs to be a support structure, and this support structure can be printed with PET. When printing is complete, simply soak the whole object in hot water for a while and the PET support layer will dissolve and be easily removed. However, PETG does not have this low-temperature water solubility, so PET is superior in applications that require a sacrificial layer.
How to Solve PET Filament Moisture Absorption?
One of the small troubles of PET filament yarn is that it is easy to absorb moisture. But don’t worry, we have a solution.
- Sealed and dry when stored: We can put the PET filament in a container that is very airtight and then throw in some desiccant, like silicone desiccant. In this way, the moisture in the container is absorbed by the desiccant, creating a low-humidity storage environment for the PET filament, which is as dry as if it were in the desert.
- Dry before printing: Before you are ready to print, you also have to “roast the PET filaments”. You can use the oven to dry it, usually set the temperature at about 50°C, and bake for 4 hours. If the time is tight, you can also increase the temperature to 70°C, but the time must be shortened to about 1 hour, just like cooking, the temperature should be shorter, otherwise it will be “overbaked”.
- Real-time humidity monitoring: In the storage and printing environment, we can install a humidity sensor, which is like a small eye for the environment, staring at the humidity changes in real time. As soon as the humidity exceeds the safe range, let’s say 40%, we act quickly and either add more desiccant or switch to a drier storage place.
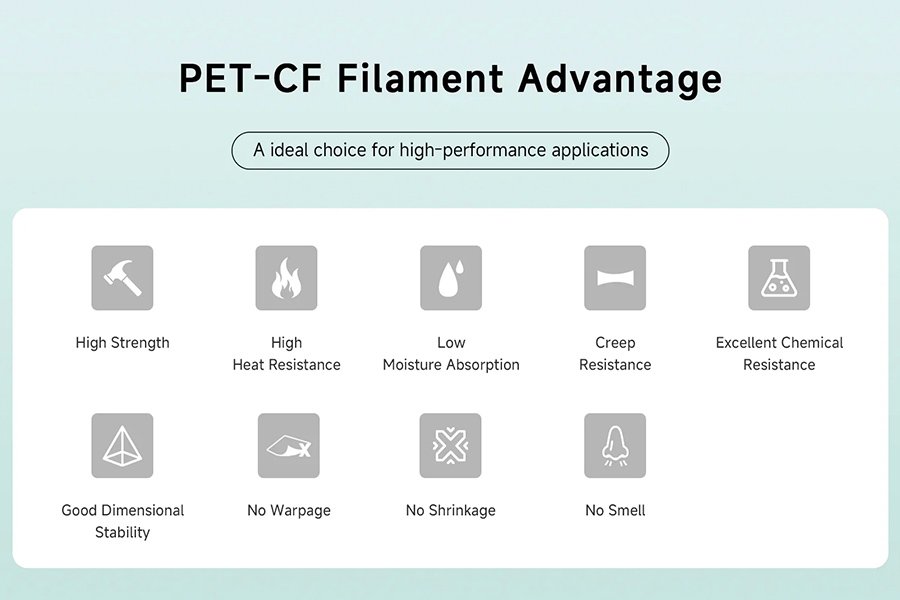
What Are the Best PET-CF Filament Applications?
PET – CF (Carbon Fiber Reinforced PET) filament yarn is the “all-rounder” in the materials industry, and it has excelled in many fields.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry is extremely demanding in terms of materials, but PET-CF filaments are up to the task. It has high strength, light weight and good rigidity, which is especially suitable for manufacturing important components such as drone racks and internal support structures of aerospace vehicles. In the case of drones, a frame printed with PET-CF filament is both sturdy and lightweight, allowing the drone to fly farther and more stable.
automotive
In automotive manufacturing, PET-CF filaments also play a big role. It can be used to make body parts, engine parts, etc. Imagine a body made of PET-CF filament yarn that is lighter, and the fuel efficiency of the car or the range of an electric car can be greatly improved, and the strength will be higher, and the car will be safer and more durable to drive.
Electrical & Electronics
In electronics manufacturing, PET-CF filaments are used to manufacture high-precision, high-strength fixtures, housings and internal support structures. Its excellent rigidity and dimensional stability ensure that electronic components are manufactured and tested without errors, just like putting on a strong and well-fitting “armor” for electronic components.
Industrial Equipment
PET-CF filaments excel in the manufacture of high-performance industrial components such as end-arm actuators, measuring tools and bending dies. The addition of carbon fiber greatly increases the strength and rigidity of the material, while also reducing the weight of the components and making the equipment more efficient.
Sports & Leisure Products: For high-end sporting goods, PET-CF filament yarns are also the best choice. For example, golf clubs, bicycle frames, etc., when made of PET-CF filament, are lightweight and strong, which not only allows athletes to perform better, but also extends the life of the product, so that sports enthusiasts will love it.
How to Reduce Stringing in PET 3D Printing?
Stringing can sometimes be a headache when it comes to PET 3D printing, but we’ve got a trick up our sleeve.
- Adjust the retraction settings: We can increase the retraction distance, just like letting the molten plastic “retract” into the nozzle as soon as the printhead moves, so as to reduce the amount of plastic dripping out. The retraction speed can also be slightly faster, but not too fast, otherwise the plastic inside the nozzle may be broken, which will be troublesome.
- Optimize the print path: Today’s slicing software is very smart, with path optimization features, such as “avoid cross gaps” and “minimize stroke movement”, which we can make good use of. Make the print path more reasonable, reduce unnecessary movement of the print head, and don’t let it “run blind”, so as to reduce the phenomenon of stringing.
- Nozzle maintenance and cleaning: Nozzles are like printed “mouths” that need to be well maintained. We need to clean the nozzle regularly to remove all the carbonization residues, otherwise they will clog the nozzle and affect the plastic discharge. You can use a nylon brush with a suitable detergent to clean up, but you have to be careful not to break the nozzle.
- Adjust the printing parameters: If the nozzle temperature is lowered a little, the fluidity of the plastic will be less strong, and the risk of wire drawing will be reduced. The printing speed can also be adjusted, don’t let the print head stay too long when moving, otherwise the plastic will easily drip out or leak.

Conclusion
PET filaments perform very well in the field of 3D printing. Not only do they have good physical and chemical properties, they are also easy to use during the printing process and produce great printing results. Especially in applications that require transparent or translucent effects, good heat resistance, and chemical resistance, the unique advantages of PET materials are highlighted. So, if you are looking for a cost-effective 3D printing material, PET filaments are definitely worth considering. Maybe it will be your “right-hand man” on the road to printing.

Contact us now to get exclusive CNC machining solutions!


Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. LS makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through LS’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please contact to our for more information.
Team LS
This article was written by various LS contributors. LS is a leading resource on manufacturing with CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, injection molding,metal stamping and more.
FAQs
Is PET filament suitable for 3D printing?
Yes, PET filament is very suitable for 3D printing. It has good melt fluidity and interlayer adhesion, which can ensure that the printed parts have good surface quality and mechanical strength. At the same time, the printing temperature of PET filament is relatively low, which helps to reduce the energy consumption of the printer and extend the life of the equipment.
Can PET plastic be used for 3D printing?
Of course. PET plastic is a thermoplastic that is processable, so it can be made into filaments and used in 3D printing. During the 3D printing process, PET plastic is able to quickly melt and cool and solidify to form a stable print layer, resulting in the construction of three-dimensional objects.
When to use PET filament?
PET filament yarn is suitable for 3D printing projects that require high mechanical strength, chemical resistance and good surface quality. For example, when you need to print parts that need to withstand external shocks or need to resist chemical attack, PET filament yarn is a good choice. In addition, if you want your prints to have a smooth surface and stable dimensions, you can also consider using PET filaments.
Which is stronger PLA or PET?
In general, the strength and toughness of PET filaments are usually higher than those of PLA. PET has better temperature resistance and impact resistance, which gives it an advantage over PLA in some applications. However, it should be noted that there may be differences in the performance of PLA and PET filaments of different brands and models, so the selection needs to be considered comprehensively according to specific needs and printing conditions. At the same time, PLA also has its unique advantages, such as biodegradability, lower printing temperature, etc., so it may be more suitable for some specific applications.


