Surface finishing in the manufacturing industry improves a product’s functionality and aesthetics and enhances other attributes. For example, it is suitable for protecting products from corrosion, abrasion, etc. Among the several processes used by different manufacturers, alodine finish has unique properties as the surface finishing option boasts incredible productivity, ease of operation, longevity, etc.
Here, we’ll be able to introduce you to everything you need about Alodine finishing. This will include the principle, applications, design considerations, and other things that make it one of your product’s best surface finishing options.
What is Alodine?

Alodine is a trademarked name for proprietary chromate conversion baths that passivate aluminum and other metals. The term has become synonymous with chromate conversion and is used interchangeably across most industries. It is a chemical film that forms a protective layer on the surface of metals, most typically aluminum, to prevent corrosion and enhance paint adhesion.
Principle of the Alodine finish?
The principle of the Alodine finish, also known as a chromate conversion coating, involves using a chemical substance dissolved in aqueous solutions to produce a gel that is applied to metals such as aluminum alloys. This forms a coating that protects the metals from corrosion and enhances their aesthetic appeal. Unlike anodizing, which uses electrical currents, the Alodine coating process relies on a simple chemical coating procedure. The Alodine finish benefits applications like parts for the electronics industry due to its ability to prevent corrosion while allowing electrical conductivity through the aluminum. It can also act as a base for painting and priming.
Alodine coating types
Alodine coating, or chromate conversion coating, is used to passivate various metals, including steel, aluminum, zinc, cadmium, copper, silver, titanium, magnesium, and tin alloys. It serves as a corrosion inhibitor, a primer to improve the adherence of paints and adhesives, a decorative finish, or to preserve electrical conductivity.
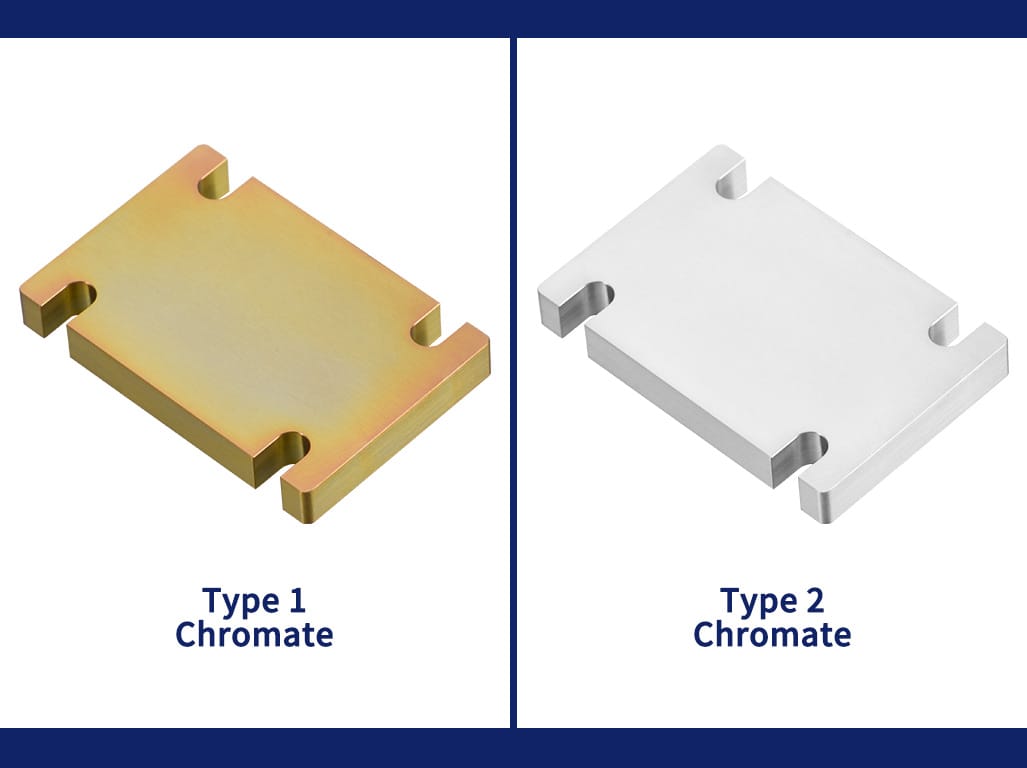
There are several types of Alodine coatings, including:
- Alodine 1200S, Alodine 1201, Alocrom 1200 (U.K.), Alodine 1132 pen, and Alodine 600 are chromate conversion aluminum coatings containing hexavalent chromium. The resulting color is iridescent gold or yellow to tan, also known as yellow chromate.
- Alodine 1000 clear, Alodine 1001 clear, Alodine 1500 clear: These are chromate conversion coatings for aluminum-containing hexavalent chromium. The resulting color is clear, also known as clear chromate.
- Alodine 871 is a non-hexavalent (hex-free) chromium conversion coating for aluminum.
- Alodine 5200 and Alodine 5700 are other alodine coatings types.
In addition, the Alodine process is divided into two stages according to the MIL-DTL-5541 standard:
- Type I: Compositions containing hexavalent chromium.
- Type II: Compositions containing no hexavalent chromium. This Type contains trivalent chromium instead of hexavalent chromium and is often color-clear.
Type 2 Alodine coating, as per the MIL-DTL-5541 standard, has several advantages over Type 1. The primary difference is that Type 2 Alodine coating contains trivalent chromium instead of hexavalent chromium, found in Type 1. This makes Type 2 Alodine coating more environmentally friendly as it is hex chrome-free. Additionally, Type 2 Alodine coatings are usually colorless or similar to the original aluminum surface finish, which can be a desirable aesthetic feature in specific applications. Type 1 and Type 2 Alodine coatings offer the same performance in corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and paint adhesion.
The specific Type of Alodine coating used can depend on the application’s requirements, such as the desired level of corrosion resistance, the Type of metal being coated, and environmental considerations.
Main Characteristics of Alodine Finish
Alodine finish, or Chem Film or chromate conversion coating, is a chemical treatment applied to metals, particularly aluminum and its alloys, to enhance corrosion resistance and provide a conductive surface for further finishing processes like painting and priming.
Corrosion Protection
One of the primary benefits of Alodine finish is its ability to provide excellent corrosion protection. This protection remains effective even if the coating is scratched, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the metal in harsh environments. Applying Alodine involves a chemical reaction that transforms the metal surface into a protective layer, a phenomenon known as passivation.
Conductivity and Paint Adhesion
Alodine coatings maintain electrical conductivity, making them suitable for applications where this property is essential. Additionally, the treated surface becomes an excellent base for paint and primers, ensuring better adhesion and longevity of the applied coatings.
Application Process
Applying Alodine coatings typically involves immersion in a chemical bath containing chromium compounds. This process is fast, can be done at room temperature, and the resulting film is fragile, ranging from 0.25 to 1.0 µm.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency
Compared to other finishing processes like anodizing, Alodine finishes are generally less expensive and do not significantly alter the weight or dimensions of the metal component, preserving its original specifications.
Industrial Applications
Alodine finishing is widely used across various industries, including aerospace, military, and precision machining. It is essential for parts that resist corrosion, such as those used in military and defense applications.
Environmental and Health Considerations
While Alodine solutions are effective, they are also toxic and contain hexavalent chromium, a known carcinogen. This has led to increased regulation and a push for safer alternatives in places like Europe under the RoHS and REACH Directives.
Types of Alodine Coatings
There are different types of Alodine coatings, with MIL-DTL-5541 Type 1 and Type 2 being the most common. Type 1 contains hexavalent chromium, while Type 2 uses trivalent chromium, titanium, or zirconium, which are less harmful to health and the environment.
Visual Appearance
Alodine coatings can vary in appearance, presenting colors like iridescent greenish-gold, yellow, or transparency, depending on the Type of Alodine material used.
Limitations
Despite its many advantages, the Alodine finish is not suitable for decorative purposes due to its appearance and can be irritating to the skin. It is primarily used for its protective qualities rather than aesthetic appeal.
In summary, Alodine finish is a cost-effective and efficient method for protecting metal surfaces, particularly aluminum, from corrosion while maintaining electrical conductivity and serving as a base for further coatings. Its widespread use in critical industries underscores its importance, although environmental and health concerns necessitate careful handling and disposal.
Alodine vs. Anodizing
While both Alodine and anodizing are used to improve the corrosion resistance of metals, particularly aluminum, they are not the same and have vital differences:
- Process: Anodizing is an electrolytic process that applies electrical current to the metal immersed in an electrolyte solution. On the other hand, Alodine is a chemical process that does not use electrical currents.
- Effects: Both processes transform the outer layer of the surface of the metal, but they do so in different ways. Anodizing creates a hard, durable layer on the surface that can be dyed for aesthetic purposes. Alodine, on the other hand, makes a thin protective film that prevents corrosion and maintains electrical conductivity.
- Cost and Expertise: Anodizing is generally more expensive than Alodine and requires more excellent technical expertise. Alodine is easier, faster, and more straightforward to apply, making it a more cost-effective option.
- Safety and Environmental Impact: Alodine has a better safety profile and occurs at a lower temperature than anodizing, making it a more environmentally friendly option.
Comparison of Type 1 and Type 2 Alodine Processes
Type 1 and Type 2 Alodine processes both aim to protect metals from corrosion, but they differ in their application methods and effects:
- Application Process: Type 1 Alodine process involves a general washing in a cleaning solution, followed by a rinse and dry. Type 2 Alodine process, on the other hand, consists of cleaning the product using either an acid or an alkaline solution, rinsing it with water, and then applying the Alodine.
- Effects: Both processes create a protective film on the metal surface to prevent corrosion. However, the Type 2 process is more straightforward and faster, making it a more efficient option.
Comparison with Other Coating Methods
Compared to other coating methods, Alodine offers several advantages:
- Corrosion Resistance: Alodine provides excellent corrosion resistance, similar to anodizing and other coating methods.
- Electrical Conductivity: Unlike many other coating methods, Alodine maintains the electrical conductivity of the metal, making it ideal for electronic components.
- Cost-effectiveness: Alodine is generally less expensive and easier to apply than other coating methods, such as anodizing.
- Environmental Impact: Alodine occurs at a lower temperature than many other coating methods, making it a more environmentally friendly option.
In conclusion, while Alodine, anodizing, and other coating methods aim to protect metals from corrosion, they each have unique processes, effects, and considerations. The choice between them depends on the application’s specific requirements, including cost, technical expertise, safety, environmental impact, and the desired properties of the finished product.
Applications of Alodine Finish
Electronics Industry: Alodine is popular in applications like fixed enclosures and cases for the electronics industry. It prevents corrosion, allows easy electrical grounding, and is relatively cost-effective. It is particularly beneficial for parts that need to be electrically grounded and in applications like heat sinks.
CNC Precision Machining Parts: One of the most common applications of Alodine coatings is the surface treatment of CNC precision machined parts. Alodine coatings preserve CNC-fabricated metal parts from corrosion and surface-acting contaminants. What makes Alodine ideal is that there is no significant alteration to the final dimension of the metal parts.
Aerospace Industry: Alodine finish is widely used in the aerospace industry. It improves a product’s functionality by protecting aluminum parts from corrosion, which is crucial for aircraft structures and engine components.
Defense Industry: Alodine finish has wide applications in the defense industry. It is used on various parts like guns, airplane parts, automotive wheels, etc.
Base for Paint Coatings and Priming: Alodine is also helpful for paint coatings and priming. It improves the adherence of these coatings to the metal surface, which is particularly useful in industries where a combination of corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal is required.
Pros and cons
Pros
- Good corrosion protection properties
- It doesn’t significantly alter the weight of the metal
- Useful as a base for paintings and priming
- Good conductive properties
Cons
- It cannot be used for decorative purposes
- Irritating to the skin
Alodine Application Processes
Alodine, or chromate conversion coating, is a chemical treatment that protects metals from corrosion. The application process varies depending on the type of chromatin used. Here are the steps involved in the different kinds of Alodine application processes:
Type 1 Chromating Process
The Type 1 hexavalent chromate conversion coating process includes several steps:
- Clean: A general washing in a cleaning solution is a pre-processing step. This ensures that dirt, oil, and any residue from prior manufacturing or packaging processes are removed before the chromate coating begins. Then, a rinse and dry takes place 1.
Type 2 Chromating Process
The Type 2 chromating process differs from Type 1 and has two types: Acid clean and alkaline clean.
- Acid Clean Process
- Clean the product using acid
- Rinse with water
- Apply the Type 2 Alodine.
- Alkaline Clean Process
- Clean the product using an alkaline solution
- Rinse with water
- Deoxidize to remove oxygen contaminants
- Rinse with water
- Apply the Type 2 Alodine.
Acid Clean Process
The Acid Clean Process is a part of the Type 2 chromating process. It involves cleaning the product using an acid solution, rinsing it with water, and applying the Type 2 Alodine.
Alkaline Clean Process
The Alkaline Clean Process is another part of the Type 2 chromating process. It involves cleaning the product using an alkaline solution, rinsing with water, deoxidizing to remove oxygen contaminants, rinsing again with water, and then applying the Type 2 Alodine.
Steps for Applying Alodine Chemical Conversion Coatings
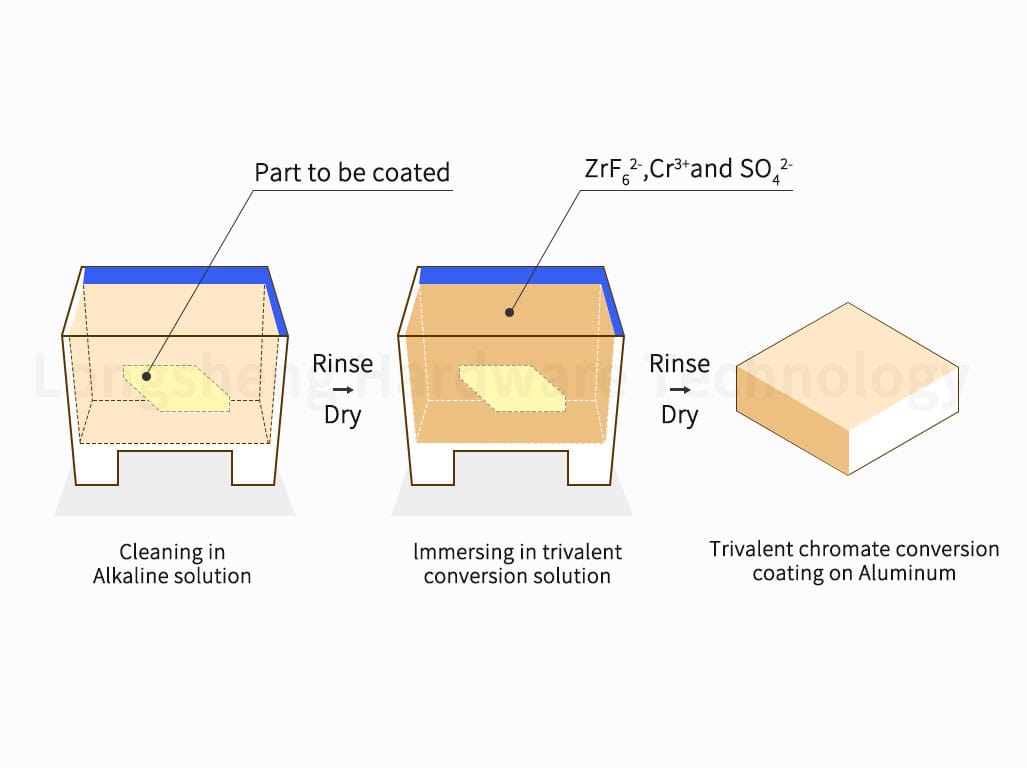
For both Type 1 and Type 2 processes, the steps for applying Alodine chemical conversion coatings are as follows:
- Rinse the metal part at room temperature.
- Clean the metal part using either an acid or alkaline solution depending on the process type.
- Rinse the metal material.
- Immerse the metal part in a trivalent chromium solution according to the part size and time specified.
- After applying the Alodine chemical conversion coatings, rinse with water to remove the excessive coating. Then, rinse with warm water to get a perfect surface finish. Allow the part to dry.
These processes are designed to enhance the corrosion resistance of the treated metal, making it suitable for various applications in the aerospace, electronics, and defense industries.
Technical Aspects of Alodine Coating
Conductive Surface and Applications
Alodine coating is used to maintain the electrical conductivity of the metal surface. This is particularly important in the electronics industry, where it is used for parts that require corrosion protection without compromising electrical grounding. The coating is applied by dipping, brushing, or spraying, and the chromate conversion coating thickness does not change the part’s dimensions.
Thickness of Chromate Conversion Coating
The layer of transformed metal is skinny: Alodine coating thickness is typically only 0.00001-0.00004 inches (0.25-1 µm). Despite its thinness, this coating significantly improves the adhesion of both paint and primer if applied to an aluminum surface before the primer. This makes it ideal for coating precision parts, where maintaining the exact dimensions of the part is crucial.
In conclusion, Alodine coating is a versatile and effective method for protecting metals from corrosion, improving the adhesion of paints and adhesives, and preserving electrical conductivity. Its thinness makes it ideal for precision parts, and its different classes allow for a range of applications depending on the level of corrosion resistance required.
Achieving High-Quality Alodine Finish
Achieving a high-quality Alodine finish involves several factors:
- Material Quality: The quality and Type of the material being treated significantly influence the outcome of the Alodine process. Variations in the purity or overall quality of the material will affect the final appearance after the Alodine process steps.
- Preparation Stages: The preparation stages of chromate conversion coatings are crucial. Ineffective rinses can lead to contaminated tanks, which can reduce the quality of the results.
- Deburring: The consistency of the coating can be improved by deburring the surface. Deburring will remove or hide minor machine marks on the parts, making the surface smoother and the finishing of better quality.
- Alodine Material: Using the wrong Alodine finish can also affect the quality of the product. Therefore, ensure you don’t have a nasty can of material. You can ascertain this by asking the manufacturers for the QC sample and checking whether they meet your specifications.
Importance of pH, Temperature, and Material Quality
- pH: Ensuring you use the Alodine finish at the correct pH is crucial. Using it at an incorrect pH could lead to non-adhering coatings.
- Temperature: The temperature at which the Alodine process is carried out can also affect the quality of the finish. Temperatures too high and low can lead to spotty coatings or runs/sagging.
- Material Quality: As mentioned earlier, the quality of the material being treated plays a significant role in the outcome of the Alodine process. High-quality materials will typically yield better results.
In conclusion, achieving a high-quality Alodine finish involves careful consideration of several factors, including the quality and Type of the material, the preparation stages, the pH and temperature at which the process is carried out, and the quality of the Alodine material used. By carefully managing these factors, achieving a high-quality, durable, and aesthetically pleasing Alodine finish is possible.
Cost and Efficiency
The cost of applying Alodine coatings can vary depending on several factors. These include the size and complexity of the parts being treated, the Type of Alodine process used, and the cost of the Alodine solution itself.
In addition, there are also costs associated with the necessary safety measures, such as personal protective equipment and safe disposal of used solutions. The cost of maintaining the equipment used in the Alodine process and the cost of water and energy used in the process must also be considered.
Despite these costs, Alodine coatings can be a cost-effective solution for protecting metals from corrosion, particularly compared to other methods such as anodizing. This is due to the relatively low cost of the Alodine solution and the simplicity and speed of the application process.
Efficiency and Application at Room Temperature
One of the critical advantages of Alodine coatings is their efficiency. The process can be carried out at room temperature, which reduces the energy costs associated with heating or cooling the solution. This also makes the process faster and more straightforward, increasing efficiency.
The efficiency of the Alodine process can also be improved by ensuring that the parts being treated are properly prepared and that the Alodine solution is applied correctly. This includes ensuring that the solution is at the correct pH and temperature and that the parts are thoroughly cleaned and rinsed before the Alodine is used.
In conclusion, while there are costs associated with applying Alodine coatings, they can be a cost-effective and efficient solution for protecting metals from corrosion. By carefully managing the process and taking steps to improve efficiency, achieving a high-quality finish is possible while keeping costs to a minimum.
Advantages and Limitations
Alodine finish, also known as chromate conversion coating, offers several benefits:
- Corrosion Resistance: Alodine finish primarily protects the metal surface from corrosion. This makes it particularly useful in industries such as aerospace and military, where parts are often exposed to harsh environmental conditions that can lead to corrosion.
- Adhesion: Alodine finish improves the adhesion of paints and adhesives to the metal surface. This makes it an excellent base layer for paint, particularly in applications where some areas of the finished product remain paint-free.
- Electrical Conductivity: Unlike many other finishes, Alodine does not compromise the electrical conductivity of the metal. This makes it ideal for electronic components and other electrical grounding applications.
- Precision Fit Applications: Alodine finish is much thinner than other finishes, such as anodizing. This makes it ideal for applications that require precise fits, such as in the aerospace industry.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite its many benefits, there are also some limitations and considerations associated with Alodine finish:
- Toxicity: Alodine solutions, particularly those used in Type 1 chromatin processes, contain hexavalent chromium, a known carcinogen. Therefore, appropriate safety measures must be taken when handling Alodine solutions.
- Environmental Impact: Using hexavalent chromium in Alodine finishes has raised environmental concerns. Local regulations must dispose of iodine solutions to prevent environmental contamination.
- Quality of Finish: The quality of the Alodine finish can be affected by several factors, including the quality and type of the material being treated, the preparation stages, and the pH and temperature at which the process is carried out. Therefore, careful management of these factors is required to achieve a high-quality finish.
In conclusion, while Alodine finish offers many benefits, there are also some limitations and considerations that must be taken into account. By carefully managing these factors, maximizing the benefits of Alodine finish while minimizing its limitations is possible.
Expert Services and Support
LongSheng Precision CNC machining services offer a range of surface finishes that can improve a product’s aesthetic and functional design. The surface finish is an integral part of the CNC machining process, and modern industrial designers have the tools and checks to ensure their designs are functional and stand out from the crowd.
Before the main finishing types for CNC machining are applied, pre-finish processes are standard in the industry. These include degreasing and deburring, which can help improve the final finish’s quality. However, it’s important to note that electroplating finishing is a highly complex and precise process that requires significant technical expertise and experience for successful application.
Recommendations for Surface Finishing Needs
When selecting the correct surface finish for your CNC machined parts, there are several factors to consider. These include the desired aesthetic and functional properties of the part, the material it is made from, and the cost and turnaround time of the finishing process.
For example, an as-machined finish will leave small but visible tool marks and blemishes on the part, but it is highly affordable to produce because post-processing isn’t necessary. On the other hand, a polished finish will create a smooth and shiny surface, but it may be more expensive and take longer to produce.
Conclusion
The use and disposal of Alodine solutions come with health, safety, and environmental considerations, mainly due to the presence of hexavalent chromium in some solutions. Thus, it’s vital to follow appropriate safety measures and regulations when handling and disposing of these solutions.
Achieving a high-quality Alodine finish requires careful consideration of several factors, including the quality and Type of the material, the preparation stages, the pH and temperature at which the process is carried out, and the quality of the Alodine material used.
In the context of LongSheng Precision CNC Machining Services, Alodine finish can be a valuable tool when chosen carefully based on the specific requirements of each project. Expert services and support in LongSheng can provide valuable insights and guidance to ensure the successful application of Alodine finishes.
Alodine finishes, though they come with certain limitations, offer many advantages and can be a powerful tool for cost-effectively enhancing the properties and lifespan of metal parts.
FAQs
Can you provide examples of industries that commonly use Alodine finish?
Alodine finish is commonly used in the following industries:
- Aerospace: It is used for aircraft parts due to its corrosion-resistant properties.
- Military and Defense: Alodine finish is used for various equipment and parts.
- Electronics: It is used for parts that require electrical conductivity.
- Maritime: Alodine finish is used for parts and equipment that are exposed to harsh marine conditions.
- CNC Precision Machining: It is used for precision machined parts.
- Medical and Dental Equipment: Alodine finish is used for various medical and dental equipment.
- Sporting Goods Manufacturing: It is used in the manufacturing of various sporting goods.
- Building and Architecture: Alodine finish is used in various building and architectural applications.
What are the common challenges or limitations of using Alodine finishes?
The common challenges or limitations of using Alodine finishes include:
Toxicity: The Alodine solution can be toxic to the skin, requiring operators to handle the process with protection and care.
Durability: A clear Alodine finish is not as durable as other finishes such as powder coating or anodizing. Over time, the Alodine finish can fade.
Aesthetic Limitations: While Alodine can be done in a clear finish, the only other color option for Alodine is a yellow/brown color. This limits its versatility compared to anodizing, which can be dyed nearly any color.
Can Alodine finishes be applied to different types of materials?
Yes, Alodine finishes can be applied to different types of materials. While it is primarily used on aluminum, Alodine finish can also be applied to the following materials:
- Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Titanium
- Zinc
- Cadmium
- Copper
- Silver
- Tin Alloys
The coating serves as a corrosion inhibitor, a primer to improve the adherence of paints and adhesives, and as a decorative finish. However, it’s important to note that while Alodine finish is less costly than anodizing, it is also less durable. Furthermore, the Alodine solution can be toxic to the skin, so care must be taken during application.



I conceive you have mentioned some very interesting details, appreciate it for the post.