Both CNC machining and 3D printing have significantly changed the manufacturing landscape through the use of computers to guide processes. The fundamental difference, however, is the way they process materials—CNC machining removes material, while 3D printing adds material. In this guide, we’ll provide a comprehensive comparison between CNC machining and 3D printing to help you choose the best method for manufacturing your parts.

What Is CNC Machining?
CNC machining is a producing process through which pre-programmed pc software program directs the motion of manufacturing unit instruments and equipment. CNC stands for “Pc Numerical management,” and this machining permits a wide range of complicated machines, akin to milling machines, lathes, laser cutters, and water knives, to routinely carry out detailed slicing duties. This expertise improves on historically manually managed processes by growing accuracy, complexity and repeatability whereas lowering human error.
CNC machines can be utilized to chop steel, plastic, wooden, glass, foam and composite materials in a variety of purposes from automotive manufacturing to aerospace, development and electronics. Designs are created utilizing CAD (computer-aided design) software program after which transformed into applications particular to CNC machines that may exactly manufacture parts and parts in accordance with preset parameters and designs.
How CNC Machining Works?
The working principle of CNC machining is relatively simple. The process begins with creating a digital model of the part or component using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The digital model is then converted into a set of instructions, commonly known as G-code, which the CNC machine reads and executes.
The CNC machine then uses these instructions to carve the part from a block of material. The machine’s cutting tools move along three axes (X, Y, and Z), and in some cases, a fourth or fifth axis, to create the desired shape. The process is incredibly precise, with many CNC machines capable of producing parts with tolerances of just a few thousandths of an inch.
Types Of CNC Machining
CNC milling is the process of turning materials into art. With our 4-axis and 5-axis CNC milling services, you will carve various shapes with absolute precision, allowing you to achieve extremely high precision parts with a tolerance of 0.005mm (+/-0.0002 in.).
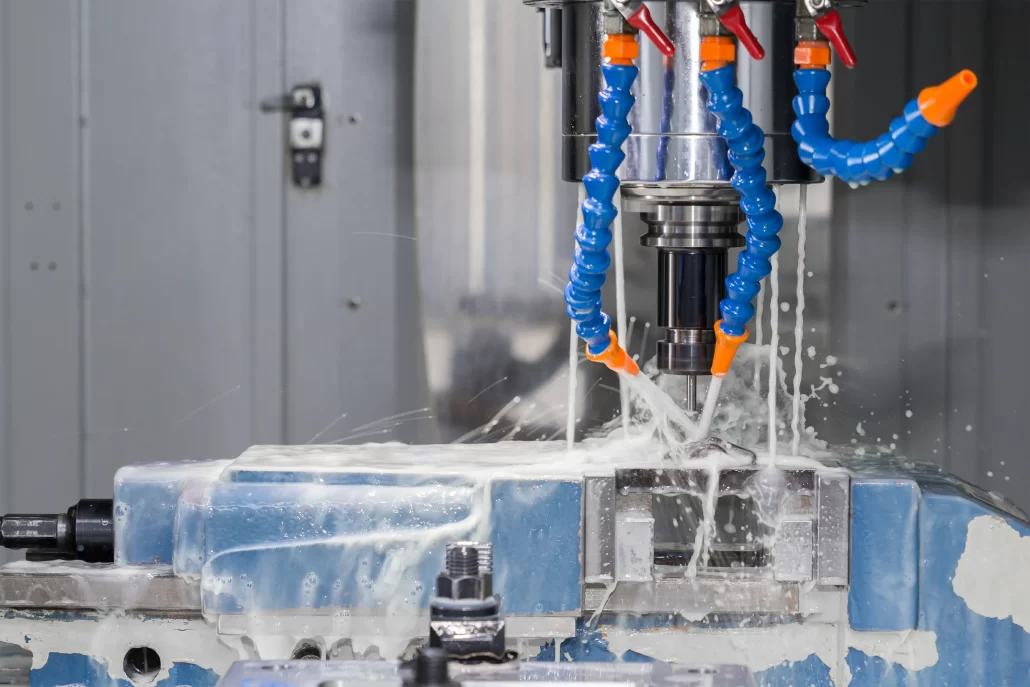

CNC turning is a production process for creating high-precision circular or cylindrical turning parts. When you need high precision and reliability, trust Longsheng’s CNC turning service, and we will transform your creativity into precise reality.
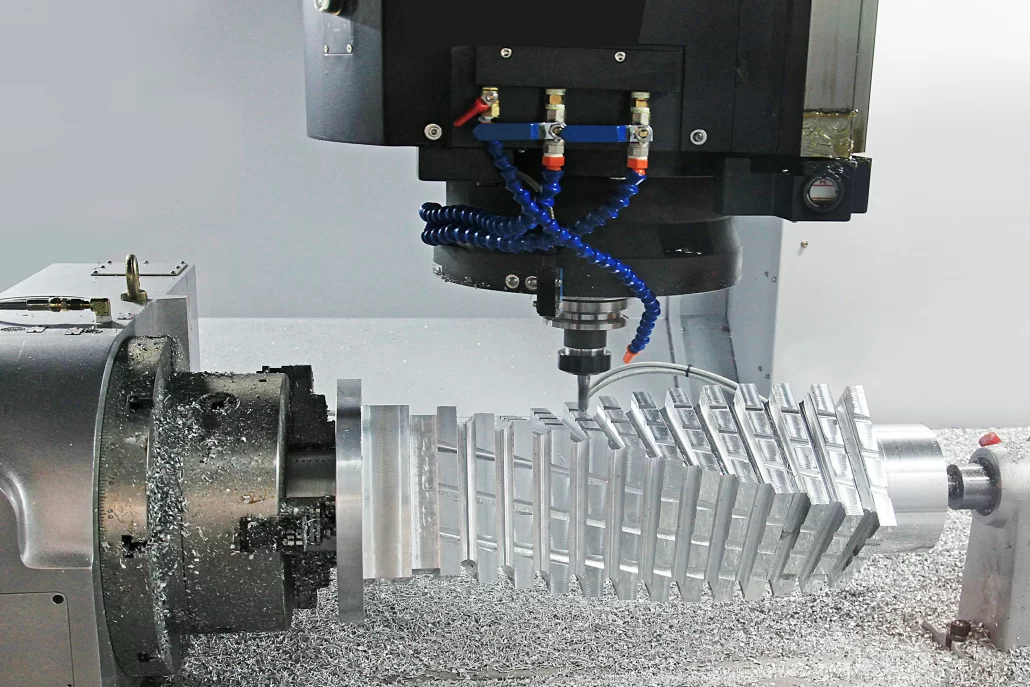
what is The advantage of CNC Machine?
- One of the major CNC machining benefits is accuracy. Because CNC machines receive precise instructions from a computer — and the movements are similarly carried out under computer control — their results will be identical each time and will match the computer model closely. This is a huge advantage when it comes to creating parts with tight tolerances. This capability almost entirely eliminates human error from the equation.
- Another industry-cornering CNC machining benefit is the inherent speed and efficiency of production. CNC machines are capable of producing products much more quickly and efficiently than traditional methods. Many modern units can even load the billet and unload the completed product without human intervention. Naturally, this capability leads to significant cost savings and increased productivity. In addition, this sort of automation makes parts more consistent.
- CNC machining uses less electricity than older processes, thereby reducing energy consumption. In fact, according to the EPA, CNC machining uses about one-seventh of the energy of traditional machining methods. There are multiple reasons; CNC machines not only work quickly but draw less power per minute than most other manufacturing methods.
- A skilled engineer can make the same component many times. However, if each component is carefully studied, each one will vary slightly. A CNC machine will manufacture each component as an exact match.
- CNC machine tools are enclosed to protect operators from flying chips and coolant and keep them away from moving machine components. On manual machines these hazards are smaller because the axes are under machinist control. That’s why manual machines don’t need big guards that restrict access to and visibility of the cutting area.
what is The disadvantage of CNC Machine?
- It is necessary to preset the cutting tool to ensure that the cutting edge is in the desired position of the CNC system. (CNC drives the shaft to the desired position, but does not know where the tool tip is.) Pre setting involves installing each tool in its tool holder to ensure it is in a known position. Alternatively, measure the position of the tool tip in the tool holder and input this value as an offset into the program.
- Programming imposes a delay before machining can start. Plus, to avoid the risk of collisions, it must be proven-out before mounting a workpiece in the machine.
- Many countries no longer teach pupils / students how to use manually operated lathes / milling machines etc… Pupils / students no longer develop the detailed skills required by engineers of the past. These include mathematical and engineering skills.
What is 3D Printing?
Its additive manufacturing expertise creates exact and complex practical parts or merchandise by stacking and fusing successive layers of fabric. So, a 3D printer doesn’t use a fabric block to govern the form. As a substitute, the nozzle deposits materials layer by layer from the underside up within the print mattress based on the slice sample of the uploaded design.
In the meantime, slice sample refers back to the person’s horizontal layers into which a CAD mannequin is split. Every slice represents a cross-sectional space of the dummy that the printer follows to deposit the fabric layer.
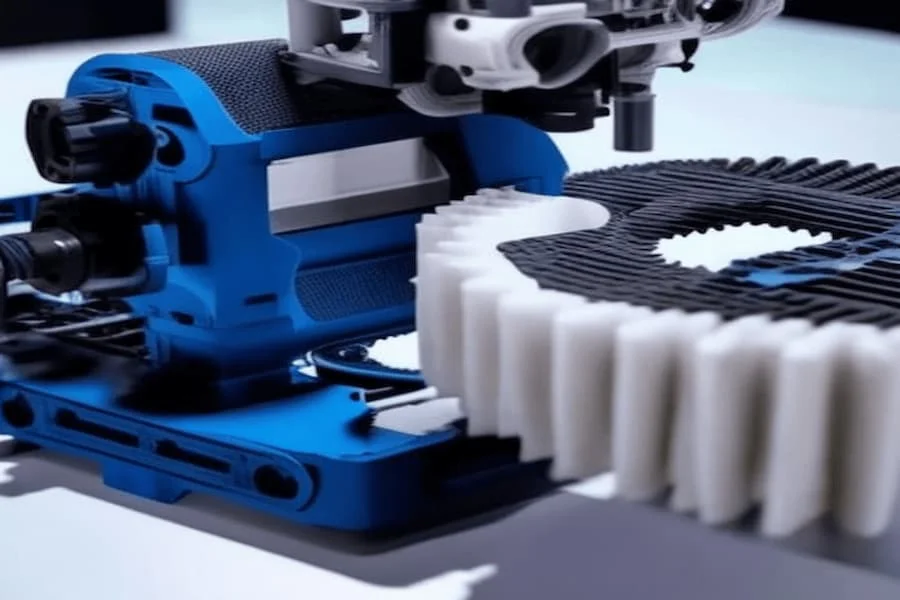

How 3D Printing Works?
- Designing the Model: The process starts with the creation of a digital 3D model using CAD software or by 3D scanning an existing object.
- Slicing the Model: The 3D model is then sliced into thin numerous 2D cross-sectional layers using slicing software, providing instructions for the 3D printer on how to construct each layer.
- Layer-by-Layer Construction: The printer follows the instructions from the sliced model, depositing material layer upon layer, gradually building the object. These layers fuse together to form the final three-dimensional object.
- Post-Processing (Optional): After the printing is complete, some objects may require post-processing to achieve the desired appearance or functionality.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
you might want clarification on several 3D printing technologies. Although they observe identical fundamental precepts, their working mechanism, materials compatibility, and printing capabilities vary. Listed below are the frequent types of 3D Printing technologies.

| Kind | Supplies | Description/Working | Execs | Cons |
| FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) | Thermoplastics (ABS, PLA, Nylon) | It melts and extrudes the fabric filament layer by layer to attain the ultimate form. | Structural stability, low price, numerous supplies | Rougher end and average precision |
| SLA (Stereolithography) | Photopolymer Resin | SLA employs an ultraviolet laser to remedy photopolymer resin in a tank, creating layers. | Excessive precision, easy finishes, and creates detailed fashions and prototypes. | Restricted materials alternative |
| SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) | Polymer Powder(Nylon PA 12, glass-filled Nylon | A laser beam sinters materials powder in a chamber, usually with inert gasoline, to forestall oxidation. | Advanced geometries attainable | Longer lead instances and tough floor texture |
| DMLS (Direct Metallic Laser Sintering) | Metallic Powder (numerous alloys, aluminum, copper, nickel ) | DMLA fuses metallic powder particles layer by layer with a laser. | Prints intricate and robust metallic parts. | Excessive price and restricted materials selections. |
what is the advantage of 3D printing?
- 3D printing requires a very limited setup to begin printing. The setup process and the 3D printing machine are the same regardless of the type of part being printed. All that is required is to convert the 3D model of the part, usually handled with either OEM or third-party software. After the conversion is complete, the file is loaded into the printer through a USB-A connector, wirelessly, or an SD card.
- 3D printing can be considered eco-friendly due to the use of recyclable materials like metals and thermoplastics. Parts can also be printed exactly where they are needed instead of being shipped from a centralized heavy-manufacturing plant. This eliminates the significant energy costs associated with transport. The additive nature of 3D printing also results in less wastage.
- The low cost and print-on-demand features of 3D printing make it ideally suited to developing prototypes. A 3D printed part can be produced in less than a day. This allows for rapid iteration of new concepts without the up-front tooling cost typical of other common technologies like injection molding.
what is the disadvantage of 3D printing?
- Most 3D printed parts require some form of post-processing. Typically post-processing may include support removal, UV-light curing, sintering in a furnace, polishing, and even machining for high-tolerance features like bearing housings.
- Due to the ease and low cost with which 3D printed objects can be manufactured, it becomes easy to duplicate designs without the original creator’s consent. There are millions of freely available designs on the internet that can be easily downloaded and copied without crediting or compensating the original owner of the intellectual property or them ever being aware of it. 3D scanning has also become more accessible, which means that real-world objects can be scanned and then duplicated.
- Some 3D printing technologies like FDM and SLS produce parts whose properties are anisotropic. This means that the parts’ performance varies depending on the direction of load applied. Typically, the parts will be weakest on the Z-axis, which is defined as the axis that points up from the 3D printer print bed.
- 3D printers have a wide range of build sizes. However, the printers commonly used for production, have build volumes smaller than large-scale manufacturing technologies like: laser cutting, horizontal mills, and metal casting. As such, 3D printing is generally used for small-scale manufacture of complex components. It must be noted that there are exceptions to this rule, as some specialized 3D printers have very large build volumes.
When to use CNC machines?
| Best Use | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Ideal volume: 3+ units | Variety of materials | Requires more pre-production planning |
| Mid-stage prototyping | Functional parts/assemblies that can be tested just like production parts | Is typically more expensive |
| Production models | Strength consistent with end-use requirements | Produces more material waste |
| Environmental resistance (temperature) | Setup + CAM time costs | |
| Tight tolerances (up to 0.005”/0.0127mm) |
When to use 3D Printing?
| Best uses | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Early stage prototyping for fit and form | Fast production times | Part assembly/functionality may not be exactly the same as the final product |
| Pre-manufacturability prototyping | Can quickly incorporate user/engineering feedback | Tight tolerances aren’t always achievable due to 3D print resolution |
| Ideal volume: 1 to 5 units (anything more may become costly) | Makes polished-looking visual models | Not as appropriate for very high strength, functional applications |
| Ability to print complex shapes at a low-cost | ||
cNC machine vs 3D printing:comprehensive comparison
| Attribute | 3D Printing | CNC Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Medium | Expensive |
| Speed of build | low set up time,long build time | long set up time,low build time |
| Strength | 10–20 % of native material | 100 % of native material |
| Precision | 0.016mm~1mm+( Typically around 0.2 mm) | 0.005mm |
| Operator skill | low | Very high |
| Unlimited material availability | No | Yes |
| Part design | Unrestricted | limited |
| Surface finish | Grained, rough, and stepped; features are often blurred | Can deliver very high surface quality by using longer cut times |
What Are the Similarities Between 3D Printing and CNC Machining?
3D printing and CNC machining are similar in that both processes can produce functional products. In terms of processes, however, 3D printing and CNC machining do not have anything in common.
CNC machining and 3D printing can go hand in hand for the quick production of complex parts to be slightly finished on some surfaces. Depending on the material, 3D printed parts can be combined with machining to achieve very low roughness or to meet very low tolerances.
conclusion
3D printing offers advantages in terms of cost and time to build parts. CNC machining, on the other hand, can deliver a close correlation to mass production characteristics whenever the precision of the part is a critical factor.When deciding to use a CNC machine or 3D printing, you should consider what to make and what materials to use. You can refer to our above about materials, accuracy, cost, part design and other factors. Hope this helps. If you still have any questions, you can leave us a message and we will try our best to solve your questions.


