With the development of global manufacturing, the application of plastics in product design and manufacturing is showing a continuous growth trend. Plastics have advantages such as lightweight, corrosion resistance, and insulation performance, which can meet the diverse requirements of different industries for material performance and product requirements
Meanwhile, the plasticity of plastics makes innovative design and the realization of complex shapes possible. And molding technology is the key process for converting plastic materials into various shapes. In molding technology, compression molding and injection molding are two common and important methods
Through reading this article, you will have a more comprehensive understanding of compression molding and injection molding, providing valuable references for future project selection and technical decision-making. Next, let’s explore the differences and comparisons between compression molding and injection molding, further expanding our understanding of molding technology.
Compression molding technology
Compression molding is a technique that involves placing raw materials in molds and applying pressure to process them into the desired shape. This method is applicable to various materials, including plastics, rubber, composite materials, etc
Principle of compression molding
Compression molding is a molding technique that processes raw materials into the desired shape by applying pressure. The following is a detailed explanation of the principle of compression molding:
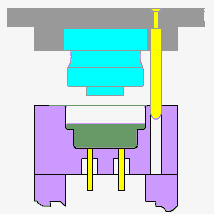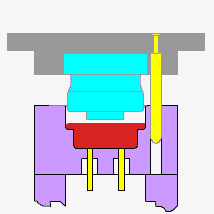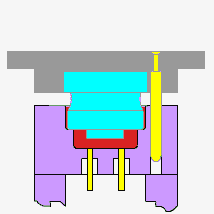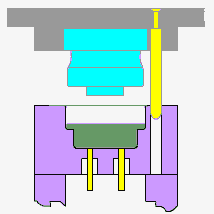
1.Material characteristics
In compression molding, materials are usually used in the form of particles, sheets, or prefabricated billets. The material characteristics have a significant impact on the forming process and the performance of the final product. Key material properties include melting temperature, thermal stability, flowability, and strength. Different materials need to determine process parameters such as pressing temperature, pressure, and time based on their characteristics.
2.Mold design
A mold usually consists of two or more parts, including an upper mold and a lower mold. During the molding process, the upper and lower molds come into contact with each other through pressure, allowing the material to solidify in shape within the mold cavity
3.Process parameters
The process parameters of compression molding include temperature, pressure, and time. An appropriate temperature can bring the material to a molten state, which is beneficial for filling the mold cavity. The application of pressure ensures that the material fully fills the mold cavity and achieves the desired shape. The time parameter controls the duration of the pressing and cooling process, which has an impact on the molding effect and shrinkage rate of the product.
Compression molding process flow
In the process of compression molding, the key steps include preheating, charging, pressurization, pressure holding and cooling. By correctly controlling each step, high quality compression molding products can be obtained. The following is a detailed description of the typical process flow of compression molding:
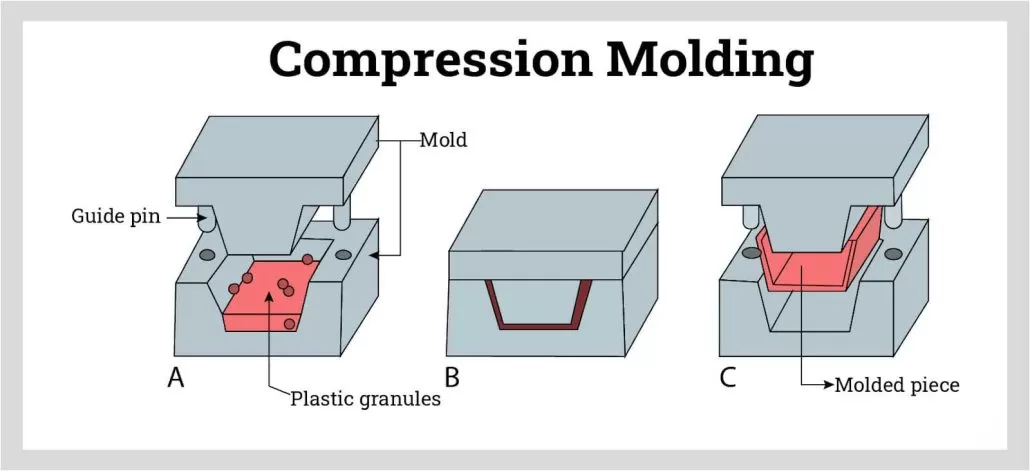
1.preheat
Before compression molding, the mold and raw materials need to be preheated to a suitable temperature. The purpose of preheating is to improve the fluidity of the material and reduce the cooling time during the molding process. The preheating temperature of molds and materials is usually adjusted according to the material characteristics and molding requirements.
2.charge
After the preheating is completed, the predetermined amount of material is evenly loaded into the mold cavity. The loading process needs to ensure that the material is evenly distributed in the mold cavity and avoid the formation of voids and bubbles. The accuracy of the loading has an important impact on the quality and shape of the final product.
3.pressurization
Once the material is loaded into the mold, the upper and lower die will close and pressure will be applied so that the material begins to fill the mold cavity. The amount of pressure and the way it is applied are determined according to the material characteristics and product requirements. Hydraulic or mechanical forces are usually used to apply pressure.
4.Pressure maintaining
After the material fills the mold cavity, it is necessary to maintain pressure for a certain time. The purpose of holding pressure is to ensure that the material fills the mold adequately and allows it to cure into the desired shape. The length of the holding time depends on the characteristics of the material, mold size and product requirements.
5.cooling
After the pressure holding process is complete, the material needs to be cooled to solidify and stabilize its shape. The cooling time is determined according to the thermal conductivity of the material and the size of the product. Cooling can be accelerated by natural cooling or the use of cooling media.
6.Mold opening and product removal
After the cooling is complete, the mold will be opened and the molded product will be removed. Before removing the product, you need to make sure that the product has cured and reached sufficient strength. Care should be taken to avoid damaging the product.
Application areas of compression molding
The advantage of compression molding is that it can achieve complex shapes and high precision requirements, and it is suitable for a variety of materials to meet the needs of different industries for product performance and quality. The following are some application cases of compression molding in the automotive industry, electronic product manufacturing and other fields.
1.Automobile industry
Auto parts: Compression molding can be used to manufacture various parts inside and outside of the car, such as instrument panels, door panels, central console, seat components, etc. These components typically require high strength, wear resistance and chemical resistance.
Elastic parts and seals: Compression molding can be used to manufacture automotive elastic parts and seals, such as rubber seals, suspension parts, shock absorbers, etc. These components need to have good elasticity and durability.
2.Electronic product manufacturing
Shell and structural parts: Compression molding can be used to manufacture the shell and structural parts of electronic products, such as the shell of mobile phones, tablets, cameras and other devices, as well as computer and server cases. Compression molding enables complex shapes and high precision requirements.
Insulating parts: In electronic products, compression molding can be used to manufacture insulating parts, such as insulation gaskets, insulation seats, etc., to ensure the isolation and safety of the circuit.

3.Medical device
Medical device housing: Compression molding can be used to manufacture housing for medical devices, such as monitors, medical syringes, etc. These enclosures typically require high precision, high strength and protection.
Rubber products: compression molding in the medical field is also widely used in the manufacture of rubber products, such as rubber seals, rubber fittings, etc., for the sealing and connection of medical devices.
4.Industrial equipment and machinery
Wear-resistant parts and high-temperature parts: compression molding can be used to manufacture wear-resistant parts and high-temperature parts of industrial equipment and machinery, such as countertops, wear-resistant blades, etc. These components usually require high hardness, high wear resistance and high temperature resistance.
Insulation parts and seals: In industrial equipment, compression molding can be used to manufacture insulation parts and seals, such as insulation gaskets, seals, etc., to ensure the safety and normal operation of equipment.
Advantages and limitations of compression molding
As a commonly used molding technology, compression molding has some significant advantages, but also has some limitations. The following is an analysis of the advantages and limitations of compression molding:
advantage
1.High quality of molded parts: compression molding can achieve high precision molding, producing molded parts with good surface quality and dimensional accuracy. This makes compression molding an advantage in applications that require a high degree of accuracy.
2.Process flexibility: Compression molding is suitable for a variety of materials, including plastics, rubber and composite materials. It can handle different types and properties of materials and is suitable for the manufacture of products with complex shapes and structures.
3.Suitable for small batch production: Compared with other mass production molding methods, compression molding has advantages in small batch production. It can quickly adjust process parameters and mold design to meet small-scale production needs.
4.High material utilization rate: compression molding can usually achieve a high material utilization rate and reduce material waste. This helps to improve production efficiency and reduce costs.
limitation
1.Longer cycle time: Compared with rapid prototyping methods such as injection molding, compression molding has a longer cycle time. Due to the steps including pressure holding and cooling, the molding cycle is long, which limits the production efficiency and output.
2.Limited scope of application: compression molding has certain limitations in terms of material selection and product shape. Some special materials and complex shapes may not be suitable for compression molding, and other molding methods need to be considered.
3.High equipment and process requirements: In order to achieve high-quality compression molding, advanced equipment and precision mold design are required. This can increase investment costs and place higher demands on process control and operational requirements.
4.Environmental impact: Environmental pollutants such as waste gas and waste water may be generated during the compression molding process, and corresponding environmental protection measures need to be taken to reduce the impact on the environment.
Injection molding technology
Injection molding is often used in the field of plastic product manufacturing, which can efficiently produce a large number of products of the same shape
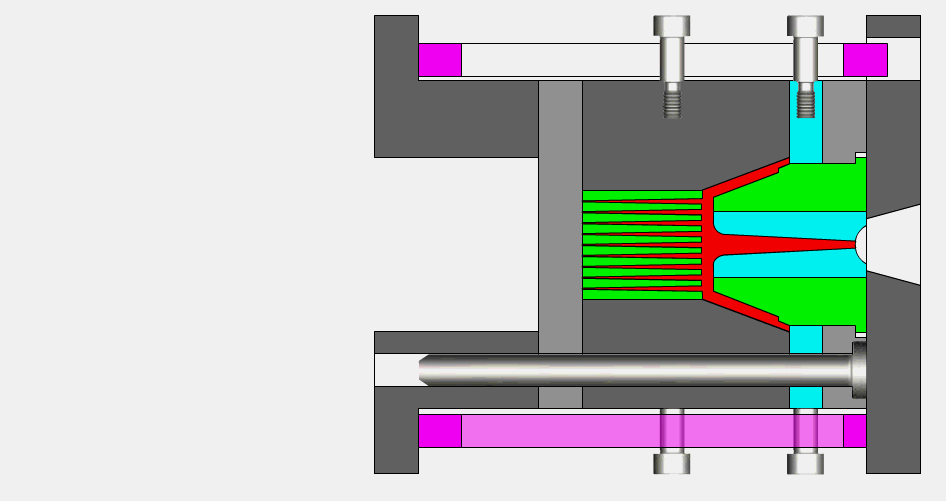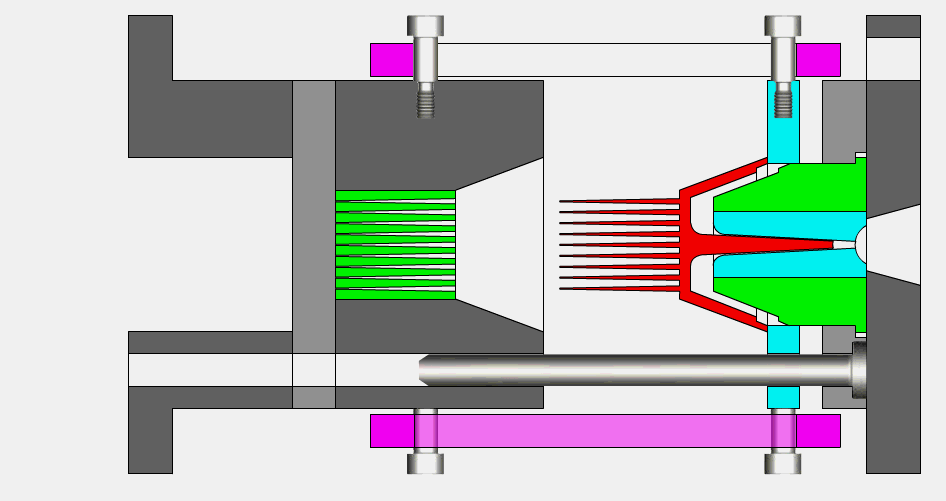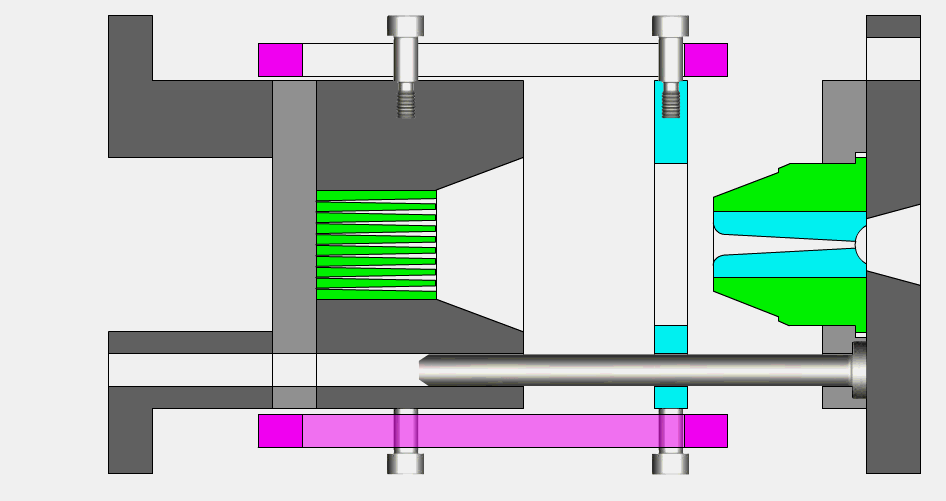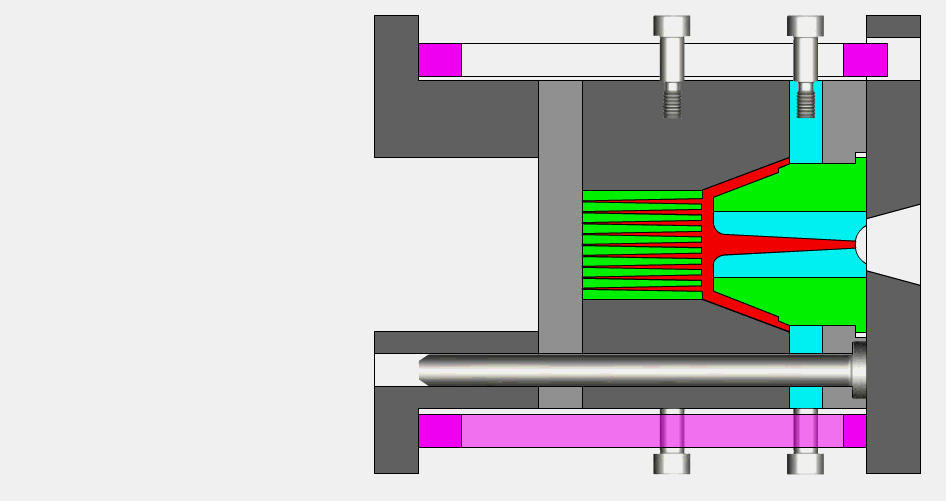
Principle of injection molding
The principle of injection molding is based on the melting and injection, cooling and curing process of plastic materials, which can achieve high-quality injection molding products. The following is a detailed description of the key steps of the principle of injection molding:
1.Material melting
First, the plastic raw material is put into the hopper of the injection molding machine in the form of solid particles or a mixture of particles. The raw material is then heated and melted to form a molten plastic melt. Heating can be done using a heater, heating belt or heating screw to bring the plastic to a melting temperature.
2.Injection
The molten plastic melt is pushed into the injection cylinder by the screw or piston device of the injection machine. In the injection cylinder, the plastic melt is kept at a certain temperature and pressure. When the injection molding machine reaches the set injection conditions, the injection cylinder injects the plastic melt into the injection chamber of the mold.
3.Filling and sealing
During the injection process, the upper and lower die of the mold are closed to ensure that the injection cavity is filled. The design and shape of the mold determines the shape and size of the final product. Typically, the mold includes one or more chambers, allowing multiple products to be obtained from a single injection.
4.cooling
After the injection is complete, the plastic in the injection chamber begins to cool. During the cooling process, the cooling medium (such as water or oil) in the mold cools the plastic through a cooling channel or nozzle and helps speed up the curing process of the plastic. The cooling time depends on factors such as the type of plastic, thickness and size of the product.
5.solidify
During the cooling process, the plastic gradually solidifies into the desired shape. During curing, the molecules of the plastic rearrange and form a solid structure, which gives the product the required strength and rigidity.
6.Mold opening and release
After the plastic is fully cured, the mold is opened and the molded product is removed from the mold. A thimble, push rod or pneumatic device is usually used to push the product out of the mold cavity. The molded product should have sufficient curing and stiffness to ensure smooth disconnection from the mold and keep its shape and dimension stable.
Injection molding process flow
Injection molding is a commonly used plastic machining technology that involves injecting molten plastic material into a mold, cooling and solidifying it to form the desired product. The following is a typical process flow for injection molding, including mold design, melting and injection, cooling and exhaust stages:
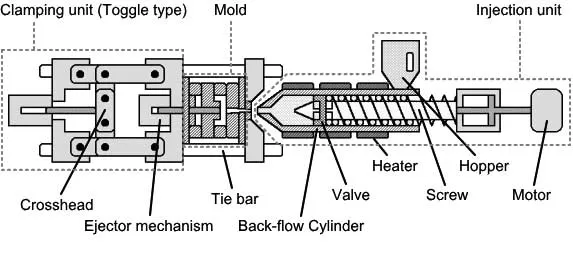
1.mould design
The first step in injection molding is to design the mold. The mold should be designed according to the shape, size, and structural requirements of the product. The mold is usually composed of an upper mold and a lower mold, with an injection cavity, cooling channel, and exhaust system in the middle. The design of the mold should consider the filling performance, cooling effect, and exhaust capacity of the product.
2.Melting and injection
During the injection molding process, plastic raw materials are added to the hopper of the injection molding machine in the form of solid particles or a mixture of particles. Then, the raw materials are heated and melted into a molten state through a heating cylinder and a screw or piston. The molten plastic is pushed into the injection chamber of the mold under high pressure through an injection cylinder. During the injection process, plastic enters the mold through a nozzle and fills the cavity in the mold.
3.Cooling and exhaust
After the injection is completed, the cooling system in the mold begins to cool the injection material. The cooling medium (usually water or oil) in the cooling channel or nozzle absorbs heat from the injection molding material through the mold, allowing it to quickly cool and solidify. At the same time, the exhaust system in the mold helps eliminate gases and air to prevent the formation of bubbles inside the product.
4.Mold opening and demolding
After the plastic cools and solidifies, the mold opens and the formed product is removed from the mold. This usually requires the use of ejector pins, push rods, or pneumatic devices to push the product out of the mold cavity. The formed product should have sufficient curing and stiffness to ensure smooth detachment from the mold and maintain its shape and dimensional stability.
Application Fields of Injection Molding
Injection molding has the characteristics of high efficiency, precision, and reliability. It has important applications in many fields, and the following are some of the widespread applications of injection molding in the fields of household appliances and medical devices:
1.Home appliance industry
Television and computer casings: Injection molding can be used to manufacture casings for equipment such as televisions, computers, and monitors. These shells need to have an elegant appearance, good strength, and durability.
Washing machine and refrigerator components: Injection molding can manufacture components for household appliances such as washing machines and refrigerators, such as control panels, door handles, drawers, and containers.
Air conditioning and heating components: Injection molding is widely used in air conditioning and heating equipment, for manufacturing components such as casings, fan blades, air vents, and drainage pipes.
2.Medical Device Industry
Syringes and syringes: Injection molding can be used to produce various specifications of syringes and syringes, meeting the injection and drug delivery needs of medical devices.
Medical equipment shell: Injection molding can manufacture the shell and panel of medical equipment, such as monitors, surgical instruments, and medical instruments.
Medical equipment and instruments: Injection molding plays an important role in the manufacturing of various medical equipment and instruments, such as injection needles, catheters, masks, and infusion sets.
3.Applications in other fields
Automotive components: Injection molding can be used in the automotive industry to manufacture automotive components such as car lamp housings, instrument panels, door handles, and interior components.
Packaging industry: Injection molding is widely used in the packaging industry, manufacturing plastic bottles, containers, lids, and packaging boxes.
Daily necessities and toys: Injection molding can be used to manufacture various daily necessities and toys, such as combs, toothbrushes, toy cars, and building blocks.
Advantages and limitations of injection molding
Injection molding has some obvious advantages, but also has some limitations. The following is an analysis of the advantages and limitations of injection molding:
advantage
1.High production efficiency: Injection molding can achieve efficient mass production. The automation and high-speed operation of injection molding machines result in short molding cycles and high production efficiency, making them suitable for large-scale production needs.
2.High product accuracy: Injection molding can manufacture precise products with good dimensional accuracy and surface quality. By controlling parameters such as injection pressure, temperature, and injection speed, high-precision and consistent products can be achieved.
3.Large design freedom: Injection molding can manufacture products with complex shapes and structures. From simple components to complex structures, injection molding can meet diverse design requirements and provide a wide range of product design freedom.
4.Wide selection of materials: Injection molding is suitable for various plastic materials, including polypropylene, polyethylene, polyurethane, polycarbonate, etc.
5.Different materials have different physical and chemical properties, which can meet the needs of different products.
Limitations
1.High cost: Injection molding involves mold manufacturing and equipment investment, therefore the initial cost is relatively high. Especially for small batch production or personalized customized products, the cost may not be cost-effective enough.
2.Strict requirements for raw materials: Injection molding requires high quality of raw materials. Impurities, impure substances, and changes in particle size may have a negative impact on product quality. Therefore, the selection and processing of raw materials require special attention.
3.Design limitations: Injection molding has some limitations on product design. For example, factors such as wall thickness uniformity, material fluidity, and shrinkage need to be considered in the design process to ensure the quality and performance of the final product.
4.Environmental impact: During the injection molding process, environmental pollutants such as waste and exhaust gas may be generated. Proper handling and management of these wastes is necessary to reduce negative impacts on the environment.
Compression molding and injection molding: comparison
Compression molding and injection molding both have unique advantages and applicability, but there are also some differences. Understanding and comparing the principles and characteristics of these two forming methods is of great significance for selecting appropriate forming processes, as well as optimizing product quality and production efficiency.
Comparison of forming principles
Compression molding and injection molding There are some differences and similarities in their molding principles. The following is a comparison of the molding principles of compression molding and injection molding, and an analysis of their differences and similarities:
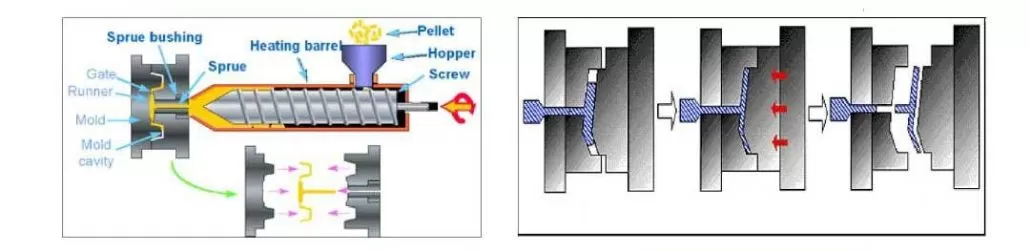
Principle difference
Compression molding: The melted plastic material is filled into the preheated mold cavity by applying pressure and the product is formed during curing.
Injection molding: The molten plastic material is injected into the mold cavity through the pressure of the injection machine, and the product is formed during the cooling and curing process.
Pressure mode
Compression molding: Pressure is usually applied using mechanical force or liquid pressure to fill the mold cavity with plastic.
Injection molding: The pressure of the injection machine is used to inject molten plastic into the mold cavity.
Plastic state
Compression molding: The plastic needs to be pre-melted and kept molten before being filled into the mold cavity.
Injection molding: The plastic is heated and melted by the injection machine and injected into the mold.
Cooling mode
Compression molding: mainly rely on the mold for cooling, through the mold cooling system or external cooling medium to reduce the plastic temperature.
Injection molding: The injection of molten plastic is cooled by a cooling system in the mold.
Product shape
Compression molding: Suitable for a variety of materials and complex shape products, including cavity and thin-walled structure products.
Injection molding: More suitable for mass production and products requiring precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.
Raw material requirement
Compression molding: The requirements for raw materials are relatively low, and various types and shapes of plastic particles can be used.
Injection molding: The requirements for raw materials are relatively high, requiring plastics to have good fluidity and melting characteristics.
Molding accuracy
Compression molding: Due to the influence of the compression and curing process, the molding accuracy is relatively low, and there may be certain size and shape changes.
Injection molding: Injection molding can achieve high precision size and shape control, suitable for products requiring high precision manufacturing.
Comparison of process flow
The following is a comparison of the process flow of compression molding and injection molding, exploring their characteristics and advantages:
| Process Step | Compression Molding | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Preheating | The mold needs to be preheated to the melting temperature. | No preheating of the mold is required. |
| Material Loading | Preheated plastic material is placed in the mold cavity. | Molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity using an injection machine. |
| Applying Pressure | Pressure is applied using mechanical force or hydraulic force to fill the entire mold cavity. | Plastic is injected into the mold cavity using the pressure generated by the injection machine. |
| Holding Pressure | After filling, the mold is kept under pressure for a specific time to ensure proper solidification. | The injection machine maintains pressure during the cooling process to ensure proper solidification. |
| Cooling | The mold is cooled for a certain period to achieve sufficient hardness. | The mold’s cooling system rapidly cools and solidifies the plastic. |
| Mold Release | The mold is opened, and the finished product is removed. | The mold is opened, and the finished product is removed. |
Compression molding features and advantages:
Suitable for the manufacture of various materials and complex shapes.
High quality molding parts, high product density, good surface quality.
Available in a variety of materials, suitable for thermoplastic and thermoset plastics.
Suitable for small batch production and custom product manufacturing.
Features and advantages of injection molding:
High production efficiency, suitable for large-scale continuous production.
High precision size and shape control is possible.
Suitable for a variety of product types, including small parts and large complex structures.
Can meet the needs of a large number of products, suitable for mass production
Comparison of product quality
There are some differences in the quality of molded parts between compression molding and injection molding. The following is a comparison between compression molding and injection molding in terms of appearance quality and dimensional accuracy:
| Quality Aspect | Compression Molding | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Quality | Typically has good surface smoothness and no air bubbles. | Can achieve smooth, flawless, and consistent surface quality. |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Relatively lower dimensional accuracy with possible dimensional deviations and shape variations. | Higher dimensional accuracy, enabling precise control of dimensions and shapes. |
| Surface Finish | Has good surface quality, with smooth and defect-free surfaces. | Can achieve consistent, smooth, and defect-free surface finish. |
| Texture | Limited by mold design and material flow, texture may not be clear. | Can achieve clear and consistent texture. |
| Strength | Generally has higher strength, suitable for demanding applications. | Typically has good strength, meeting the requirements of general applications. |
| Material Selection | Suitable for various thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics. | Suitable for various thermoplastic materials. |
| Surface Gloss | Generally has good surface gloss. | Can achieve very high surface gloss. |
Comparison of production efficiency
The following is a comparison between compression molding and injection molding in terms of production efficiency and cycle time:
| Aspect | Compression Molding | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Production Efficiency | Relatively lower production efficiency, suitable for small-batch production and customized product manufacturing. | Higher production efficiency, suitable for large-scale continuous production. |
| Cycle Time | Longer cycle time, influenced by preheating, compression, holding, and cooling steps. | Shorter cycle time, with faster injection and cooling processes. |
| Batch Production | Suitable for small-batch production and customized product manufacturing. | Suitable for large-scale batch production. |
| Automation Level | Can achieve a certain level of automation, but manual intervention is still required. | Can achieve high automation through injection machines and automation systems. |
| Material Loading | Loading process is relatively simple and can be done manually or automatically. | Automatic plastic material loading through injection machines. |
| Mold Preparation Time | Requires mold preheating, resulting in longer mold preparation time. | No mold preheating required, resulting in shorter mold preparation time. |
| Equipment Complexity | Relatively lower equipment complexity and lower equipment cost. | Higher equipment complexity and higher equipment cost. |
Comparison of cost-effectiveness
The following is a cost-benefit analysis comparison between compression molding and injection molding, considering factors such as raw material costs and equipment investment:
| Cost Factor | Compression Molding | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Material Cost | Relatively low, typically $0.8-1.2/kg | Relatively high, typically $1.2-2.0/kg |
| Equipment Investment | Low level, typically $100,000-$500,000 | High level, typically $500,000-$2,000,000 |
| Production Efficiency | Lower, typically 100-500 parts per hour | Higher, typically 500-2,000 parts per hour |
| Cycle Time | Relatively longer, typically 1-10 minutes | Relatively shorter, typically 10-60 seconds |
| Labor Cost | Relatively low, typically $15-$30/hour | Relatively high, typically $25-$50/hour |
| Equipment Maintenance Cost | Relatively low, typically 1-3% of annual equipment investment | Relatively high, typically 3-5% of annual equipment investment |
| Applicable Product Types | Suitable for various shapes and sizes, including large and complex structures | Suitable for various shapes and sizes, including small components and large products |
conclusion
By comparing the differences and similarities between compression molding and injection molding, we can draw the following conclusions:
Differences:
Molding principle: compression molding is through the heat softened material placed in the mold, in the process of pressure and curing to form a product; Injection molding is done by injecting melted plastic into a mold and forming a product during cooling.
Process flow: compression molding requires multiple steps such as preheating, charging, pressurizing, holding pressure and cooling, and the cycle time is long; Injection molding has a simplified process flow and shorter cycle time.
Product quality: Injection molding has higher appearance quality, dimensional accuracy and surface quality control capabilities; The compression molding is relatively low in terms of appearance quality and dimensional accuracy.
Application: Compression molding is suitable for small batch production and custom products, injection molding is suitable for large-scale continuous production and mass production.

Similarities:
Material selection: Compression molding and injection molding are suitable for a variety of thermoplastics.
Molding principle: compression molding and injection molding are plastic products formed through molds.
Application areas: Compression molding and injection molding are widely used in many fields, such as the automotive industry, electronic product manufacturing, home appliance manufacturing and medical devices.
Comprehensive evaluation
Compression molding and injection molding are common plastic molding methods, which differ in forming principle, process flow and product quality. Injection molding has high production efficiency, dimensional accuracy and appearance quality control ability, which is suitable for large-scale continuous production and mass production. Compression molding is suitable for small batch production and custom product manufacturing, with lower cost and flexible process performance. The selection of suitable molding methods should be comprehensively considered according to the comprehensive factors such as product requirements, production scale and cost effectiveness.
Longsheng: Injection molding services
We have a variety of injection molding machines and molds, and whether you need to manufacture prototype samples, small batch production, or large-scale continuous production, we can provide customized injection molding solutions for you. Welcome to contact us, let’s discuss your project requirements together and provide you with high-quality injection molding services.
gloria.wu@longshengmfg.com
FAQ
The cycle time of compression molding is relatively long, usually between a few minutes to several tens of minutes, depending on product size, material characteristics, and process parameters. The cycle time of injection molding is relatively short, usually between a few seconds and a few minutes
If you need to produce small batches or customized products, especially for large or complex structures, compression molding may be more suitable. Injection molding is suitable for large-scale continuous production and mass production, especially for the manufacturing of small and precision parts

