Are you eager to use your 3D printer to its full potential and create colorful prints? Don’t hesitate any longer! In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the fascinating world of multi-color 3D printing. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned enthusiast, we’ll provide you with the knowledge and techniques to bring your creations to life in vibrant color. From understanding how 3D printing prints multiple colors on the same layer to common 3D printing multi-color printing techniques for a seamless printing experience, we have you covered. Let’s explore in depth how 3D printing prints multiple colors on the same layer?
What is multi Colour printing?
multi colour printing is a printing technology that uses different color ink superposition, stippling technology, etc. to print multiple colors on substrates. It is widely used in the production of various printed matter.
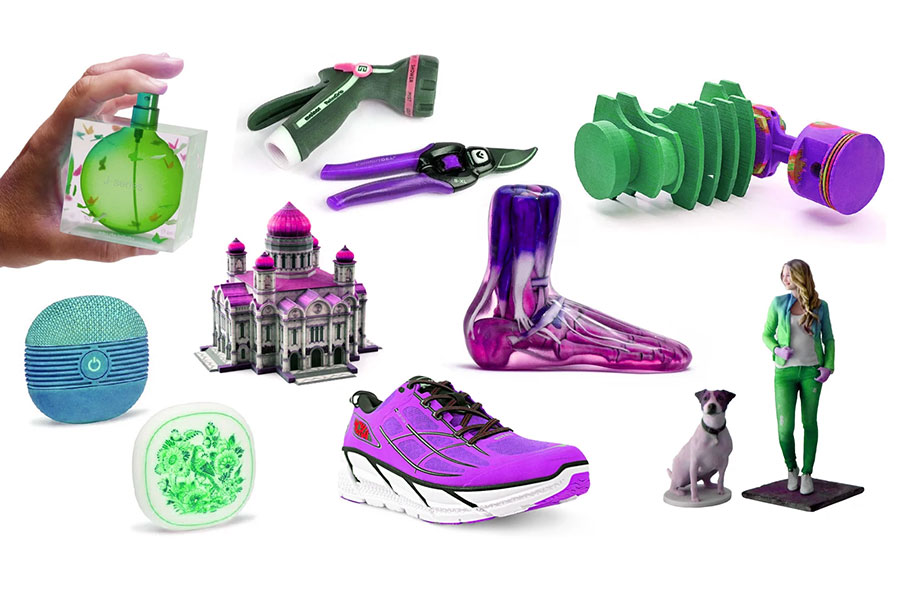

What are the common 3D printing multiple colours printing technologies?
At present, 3D printers mainly use the following technologies to achieve multiple colours printing:
1.FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) multi-nozzle technology
1.1Overview of the technology
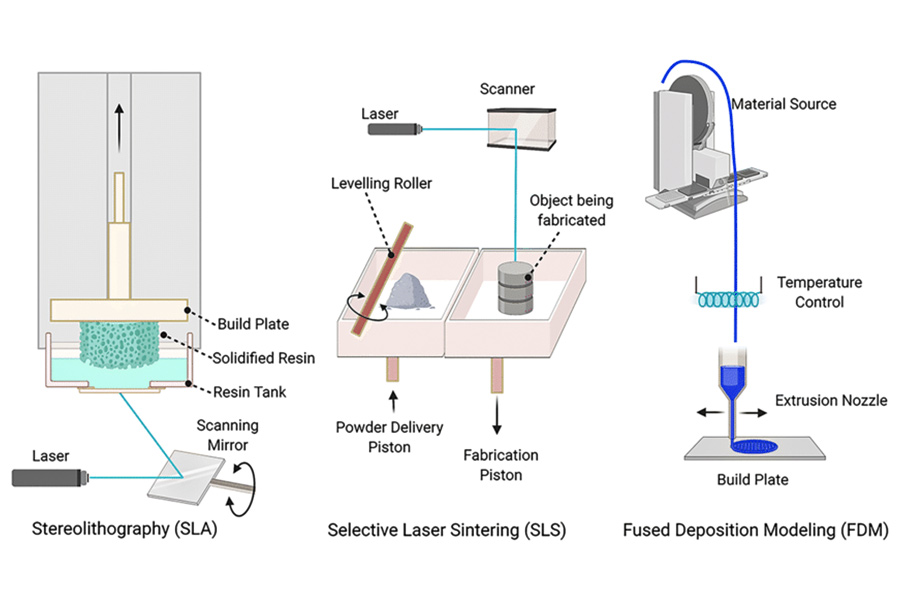
FDM(Fused Deposition Modeling), also known as FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication), is the best-known technology, and a part of the Material Extrusion process. It uses thermoplastic materials, typically in the form of spools of filaments. The heated nozzle of the extruder melts the material which is then deposited onto a substrate. There are several advantages of FDM. The printing process is easy to learn, medium-fast and usually doesn’t require a lot of space. The majority of printers are desktop-sized which makes them ideal for the office. But on the other hand, FDMs are also used as big industrial machines, to support manufacturing processes. In such cases, pellet form of the build material can be used rather than a filament.
1.2Materials
FDM allows the use of a wide variety of thermoplastic materials, such as ABS, PLA, PETG, and TPU as the most common, and more complex materials like composites with carbon fiber, glass fiber, or even graphene for conductivity. These materials offer various mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties, allowing you to choose the most suitable material according to the specific needs of the project.
1.3Advantages of FDM
- Non-toxic, but some filaments like ABS produce toxic fumes. Usually it is environmentally safe process.
- Wide range of colorful printing materials, not so expensive, and with high utilisation.
- Low or moderate costs of equipment.
- Low or moderate post-processing costs (support removal and surface finishing).
- Best for medium-sized elements.
- The porosity of the components is virtually zero.
- High structural stability, chemical, water and temperature resistance properties of materials.
- Rather big build volume comparing to other desktop technologies: 600 x 600 x 500 mm.
1.4 Disadvantages of FDM
- Limited design options. Can’t produce thin walls, acute angles, sharp edges in vertical plane.
- Printed models are the weakest in vertical build direction because of the anisotropy in material properties due to additive layer method.
- Supports are needed.
- Not very accurate, with the tolerance between 0.10 to 0.25 mm.
- Tensile strength is approximately two-thirds of the same material that has been injection-moulded.
- Difficult to control build chamber temperature, which is crucial for best results.
- Problem of “stair-stepping” in vertical build plane.
1.5 Applications
- Low-cost rapid prototyping
- Basic proof-of-concept models
2.SLA (stereolithographic printing) resin coloring technology
2.1 Overview of the technology
A technique known as photopolymerization is used by stereolithography (SLA), a 3D printing method, to produce three-dimensional objects. It was among the earliest methods for additive manufacturing to be created, and it’s still in use today.SLA is commonly used in applications that require high-resolution prototypes, detailed models, jewelry, dental applications, and other industries where accuracy and fine details are crucial.
2.2 Materials
SLA uses photosensitive liquid resins as printing material. These resins are available in a variety of properties, such as stiffness, flexibility, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. Some resins are also designed to mimic specific materials, like ABS, polypropylene (PP), and rubber.
2.3 Advantages of SLA
- Excellent surface finish with layer thickness between 0.05 – 0.15 mm.
- Finished parts can be painted.
- Moderately fast.
- Economical for low production (1-20) parts.
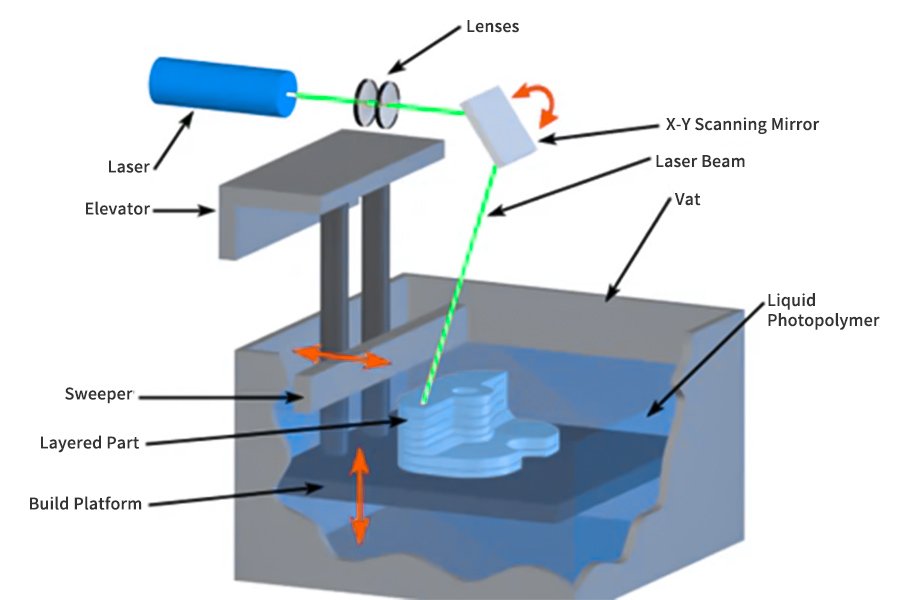
2.4 Disadvantages of SLA
- Expensive materials.
- Post-processing is not only required but also multithreaded, messy process. After the print is done, the resin needs to be washed in an ultrasonic bath or by dunking a part in IPA (isopropyl alcohol), then the supports must be removed and after that, the printouts needed to be cured with UV light.
- The resin alone is toxic, but mixed with IPA is even more dangerous. The liquid should be secured and sent for disposal to a specialized company.
- Waste material is not recyclable and is hard to manage
- Supports are needed
- Printouts are the weakest in vertical build direction due to anisotropy in material properties because of the additive layer method.
- Laser needs to be calibrated periodically
- The layer-thickness may vary in different resins
- Photopolymers are toxic, as well as the fumes that are escaping during the process.
2.5 Applications
- Functional prototyping
- Patterns, molds, and tooling
- Dental applications
- Jewelry prototyping and casting
- Modelmaking
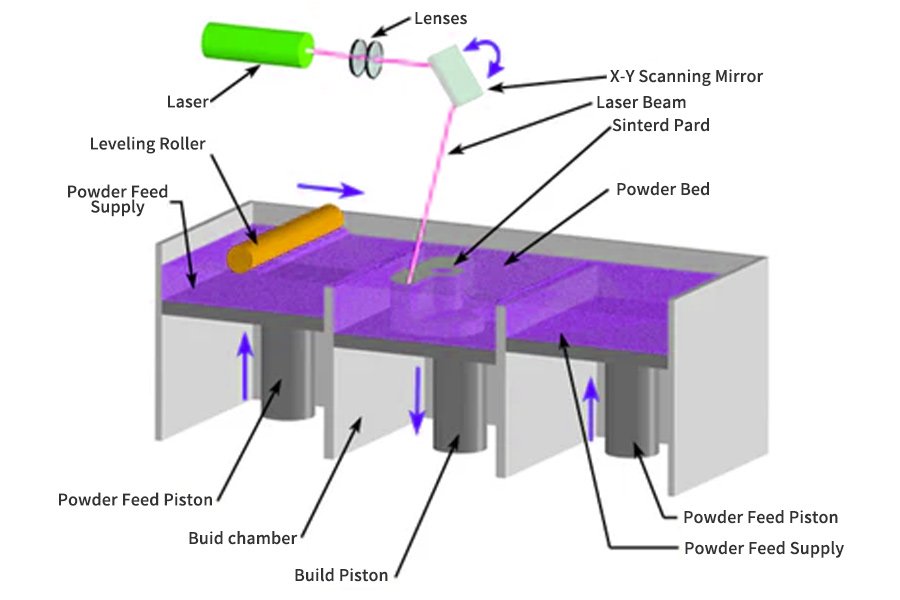
3.SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) powder dye technology
3.1 Overview of the technology
SLS is a 3D printing technology based on the selective fusion of thermoplastic powders using a high-power laser. The machine spreads a thin layer of powder on the build platform, and the laser traces the layer pattern on the powder surface. As the powder fuses, the build platform descends, and the process is repeated for the next layer. SLS is particularly suitable for the production of functional parts and durable prototypes.
3.2Materials
SLS uses thermoplastic powders, such as nylon (PA), polyamide (PA), polystyrene (PS), and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU). These materials offer strong mechanical and thermal properties, making them ideal for functional and high-performance applications.
3.3Advantages of SLS
- No support structures needed.
- Movable parts with complicated inner geometry.
- Smooth surfaces – it is hard to notice the layer.
- Durable printouts.
- Powder is reusable after printing.
- Low to moderate material costs, while using the full working area.
- Desktop SLS 3D printers are inexpensive compared to industrial machines.
- Skilled labour is not required (only desktop SLS 3D printers).
3.4 Disadvantages of SLS
- Industrial machines are expensive.
- Long lead time.
- Cleaning of the machine must be done precisely when changing material to avoid contamination.
- Long printing time (for larger objects).
- For a powder management during post-processing a vacuum cleaner and compressed air is recommended as it can get dusty.
3.5 Applications
- Functional prototyping
- Short-run, bridge, or custom manufacturing
How the 3D printing and multiple colours printing technology works
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) multi-nozzle technology: It is actually a layer-by-layer printing technology. Literally understood, the materials to be printed are laid out layer by layer on a flat surface, and finally multiple layers are stacked up to form a fixed model style. This process is similar to a baker piping cream on a pastry. Different paths, amounts, and even different speeds will affect the final pattern.
SLA (stereolithographic printing) resin coloring technology: It uses liquid photosensitive resin as the raw material, and irradiates the preset area through the ultraviolet light source under the bottom plate, allowing the photosensitive resin material in the selected area to solidify, so as to achieve point-to-point printing. Line, from line to surface, print out the three-dimensional model layer by layer. Subsequent LCD, DLP, and CLIP are basically innovative technologies based on this prototype. For example, compared to SLA technology, LCD and DLP change from the original laser irradiation point to the irradiation surface, which can speed up the irradiation area per unit time, thus reducing the printing time; while CLIP technology goes one step further and directly irradiates through the bottom light source. During the process, the model is continuously pulled up, and the final solidification is performed at the critical layer where the semi-solid is in contact with the air. This further improves the printing speed based on DLP.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) powder dye technology: It mainly uses nylon powder as the main raw material, and uses high-heat laser to perform high-temperature thermoplastic molding according to pre-selected positions. This type of technology is mainly used for customer groups with special needs for materials in the industrial field. According to reports, SLM technology is similar to this. The main difference between the two is the difference in 3D printing materials. SLM technology uses metal powder materials. The current innovations in 3D printers are mainly the number of laser heads, the power of the laser heads and the metal materials. The number of types is the starting point for continuous upgrading.
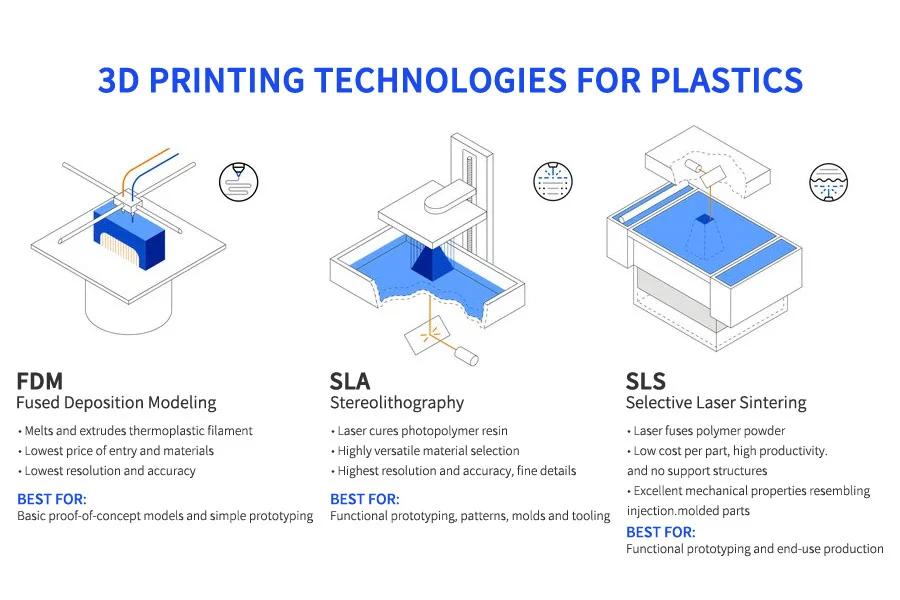
Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing multi colour printing technology
| Parameter | FDM | SLA | SLS |
| Advantages | Low-cost consumer machines and materials Fast and easy for simple, small parts | Great value High accuracy Smooth surface finish Fast printing speeds Range of functional applications | Strong functional parts Design freedom No need for support structures |
| Disadvantages | Low accuracy Low details Limited design compatibility | Sensitive to long exposure to UV light | Rough surface finish Limited material options |
Comparative analysis of 3D printing multi-color printing technology
Decision And Floor End
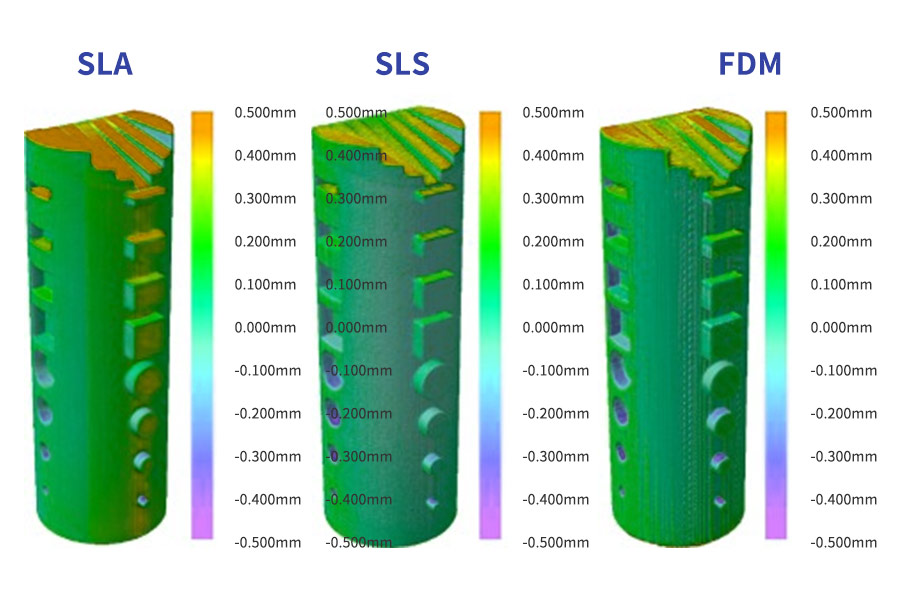
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling): FDM parts usually present seen layer traces and will have inaccuracies round advanced options, which may have an effect on the general aesthetic and purposeful high quality of the print .
- SLA (Stereolithography): SLA is famend for its excessive decision and accuracy, producing parts with the clearest particulars and smoothest floor finishes amongst plastic 3D printing applied sciences . The know-how achieves sharp edges and minimal seen layer traces, making it ultimate for purposes requiring advantageous particulars .
- SLS (Selective Laser Sintering): Whereas SLS parts have a barely tough floor end, they exhibit virtually no seen layer traces, providing a stability between smoothness and structural integrity .
Printing Velocity And Manufacturing Time
- SLA: SLA printers can produce parts with advanced designs and complex options extra effectively than FDM printers . Nevertheless, the manufacturing velocity of 3D printing basically could also be slower in comparison with conventional manufacturing strategies .
- FDM: FDM struggles with advanced designs and complex options, which may decelerate the printing process . Nonetheless, it’s well-suited for fundamental proof-of-concept fashions and fast, low-cost prototyping of easy parts .
- SLS: SLS is good for advanced geometries, together with inside options and skinny partitions, and might produce purposeful parts effectively . Additive manufacturing can scale back lead occasions in situations like product growth and low quantity manufacturing .
Vary Of Purposes
- SLA: SLA is used throughout varied industries, together with engineering, product design, manufacturing, dentistry, drugs, jewellery, and schooling, on account of its excessive decision and floor end high quality .
- SLS: SLS is trusted for its means to provide sturdy, purposeful parts and is utilized by engineers and producers throughout completely different industries .
- FDM: FDM is suitable with a variety of normal thermoplastics and is appropriate for prototyping easy parts and fundamental fashions .
Put Up-Processing And Ease Of Use
- SLA: SLA requires post-processing, together with cleansing and curing, to realize the specified power and stability of parts . This may be time-consuming however is important for high-detail prototypes and purposeful parts.
- SLS: SLS parts have an economical benefit in limited-run or bridge manufacturing and require much less intensive post-processing in comparison with SLA .
- FDM: FDM is usually thought-about user-friendly and requires minimal post-processing, making it accessible for rookies and appropriate for instructional functions.
Why Choose Us For Online 3D multi color Printing Services?
1.FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) multi-nozzle technology
- LongSheng’s FDM service can print multi-material and multi-color models, which is ideal for prototypes and visible models.
- They offer a variety of fabric options to ensure the printed model has a smooth surface and precise details.
2.SLA (stereolithographic printing) resin coloring technology
- Longsheng offers high-precision SLA printing services for models that require front-facing surfaces and intricate details.
- Longsheng will help you choose the appropriate photosensitive resin material and provide post-processing services such as cleaning, curing, and coloring.
3.SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) powder dye technology
- Longsheng’s SLS printing service is suitable for the production of functional parts, especially those that require robustness and power.
- Longsheng will help you choose the best thermoplastic powder material and provide necessary post-processing, such as grinding and dyeing.
Longsheng can provide professional advice and high-quality 3D printing services according to your specific needs. Whether you need prototypes, functional parts, or creative pieces, they’ve got you covered!
Conclusion
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) multi-nozzle technology is rich in variety, colorful, and cheap, but it cannot produce thin walls, sharp corners, and sharp edges on vertical planes. The precision and stretch are not as high as other technologies. SLA (stereolithographic printing) resin coloring technology is known for its high precision and smooth surface, and is suitable for printing models with rich details, but it is slower and more expensive. SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) powder dye technology is good at producing functional parts and is cost-effective, but surface quality and part resolution are not as high as other technologies. Which technology you choose depends on your needs, including printing purpose, material properties, accuracy, budget, post-processing time, and more. With the development of technology, future 3D printing will be more automated and intelligent, material innovation will expand applications, and environmental protection and functional integration will become the focus.
FAQs
How to choose a 3D printing service provider?
Choosing a suitable 3D printing service provider requires consideration of multiple factors, including qualifications and reputation, technical strength, service response speed, after-sales service, quotation and delivery time, and intellectual property protection. Only by comprehensively understanding and comparing different service providers can you choose the most suitable 3D printing service provider and obtain a high-quality service experience.
Which 3D printers support multi-color printing?
Stratasys, Tuozhu and Chuangxiang 3D all provide 3D printers that support multi-color printing. These printers not only provide multiple colours printing functions, but also have optimization and improvements in structure, performance, user experience and other aspects. However, the specific technical parameters such as the number of colors, printing speed, and resolution may vary between different models, and you need to choose a suitable printer based on your specific needs.
What is the file format for 3D printing multi-color models?
Common file formats for 3D printing multi-color models include .STL, .0BJ, .gcode, .3MF, .VRML, .AMF, .FBX.
What additional software is needed to 3D print multi-color models?
① Modeling software (3DS Max, Maya, ZBrush, TinkerCAD, FreeCAD) ② Slicing software (PrusaSlicer, Simplify3D,) ③ Print monitoring and management software (BambuLab, DeepCube, Chuangxiang Cloud)


