The importance of welding in modern manufacturing is self-evident. It is a bridge connecting the manufacturing world and one of the key technologies to achieve complex structural design and product manufacturing. With the continuous advancement of technology and the continuous expansion of application fields, welding technology will play a more important role in the future manufacturing industry. Choosing the right welding metal is the prerequisite for completing welding. Today, I will take you to learn how to choose the right welding metal. of welding metal?
what is welding?
Welding is an operation whereby two or extra parts are united via warmth or strain or each. It’s used on metals, thermoplastics, and typically wooden. Welding includes the applying of warmth, strain, or each to fuse two parts, and it’s a fabrication course of that requires a excessive talent degree and sensible data of topics like physics, chemistry, and metallurgy. The method of welding can be utilized to completely be a part of two related metals collectively, and it’s a vital construction-related exercise that’s usually used for binding supplies collectively by means of the applying of warmth. The welding course of includes varied varieties and strategies, similar to arc welding, MIG welding, TIG welding, and stick (guide steel arc) welding, every with its personal distinctive traits and purposes. Total, welding is a elementary course of for becoming a member of supplies and performs an important position in varied industries and purposes.
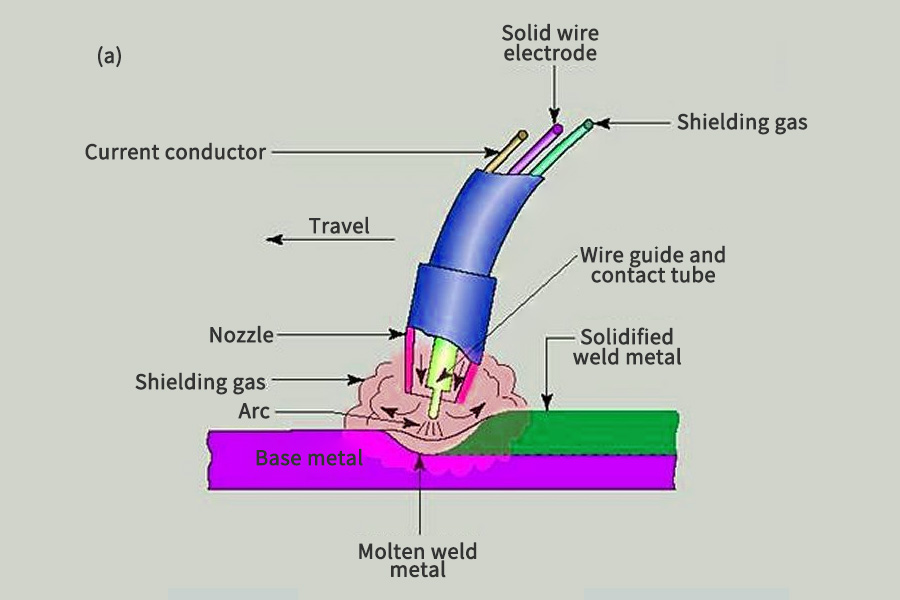
How does welding work?
Joining Metals
Welding is a high-temperature process that melts the base metal. Filling material is often added. Heating at high temperatures creates a pool of molten material that cools to form a weld, which may be stronger than the base material. Pressure can also be used for welding, either simultaneously with heat or alone. It can also use shielding gas to protect molten metal and filler metal from contamination or oxidation.
Joining Plastics
Plastic welding also uses heat to join materials and is done in three stages. First, the surface is prepared before applying heat and pressure, and finally the material is allowed to cool to create fusion. Joining methods for plastics can be classified as external or internal heating methods, depending on the specific process used.
Joining Wood
Wood welding uses heat generated by friction to join materials. The materials to be joined are subjected to a lot of pressure, and then linear frictional motion generates heat that bonds the workpieces together. It’s a quick process that joins wood together in just seconds, without the use of adhesives or nails.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Welding
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Welding establishes strong, durable, and permanent joint links. | It is hazardous when performed under the safety and security guidelines. |
| It is a simple process that results in a great finish. | It is a difficult task to dismantle the joined material through welding. |
| The technique, when used with filler material, produces a stronger weld than the base material. | Requires skilled labor and electric supply. |
| It can be performed at any place. | |
| It is an economical and affordable process. | |
| It is used in various sectors like construction, automobile, and many more industries. |
Welding Tools And Expertise
Welding tools and know-how embody a big selection of equipment, processes, and developments that play an important position in varied industries. Listed here are some key insights from the search outcomes:
- Tools and Expertise: Welding tools and know-how from firms like Lincoln Electrical and R-Tech supply a variety of welding machines with easy-to-use options, distinctive worth, and strong development. These machines make the most of the most recent ultra-reliable inverter energy parts sourced from American and German firms, offering excessive responsibility cycles and nice reliability. The tools consists of parts originating from a number of international locations, and the primary a part of the inverter vary makes use of IGBT and energy modules produced by American and German firms. Welding Expertise Corp, based mostly within the USA, presents welding controls, electrical panels, and full load take a look at stations for validation and high quality acceptance, assembly ISO 9001:2000 requirements and AS9100 Aerospace High quality System Customary.
- Industrial Purposes: Welding know-how has purposes in varied industries, together with aerospace, medical, vitality, electronics, automotive, manufacturing, development, and extra. Developments in welding know-how have led to the event of processes like laser welding, which is outstanding within the automotive trade for enhancing productiveness at a low value when welding automotive parts similar to roof, door, or filler assemblies.
- Prices and Developments: The price of welding performs an important position in manufacturing selections, with variables similar to tools value, labor value, materials value, and vitality value impacting the entire value. Totally different welding processes have various tools prices, from cheap strategies like shielded steel arc welding and oxyfuel welding to costly strategies like laser beam welding and electron beam welding, that are utilized in excessive manufacturing operations.
What industries use welding?
Welding is a flexible course of with purposes throughout a variety of industries. Listed here are a few of the key purposes and industries using welding:
- Aerospace and Transportation Industries: Welding performs an important position within the development of airplanes, spacecraft, and different transportation sectors. Gasoline Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) is employed within the development of airplanes and different transportation sectors, the place the precision of GTAW works effectively with aluminum and unique alloys used to scale back weight and gasoline consumption. Practically 95% of NASCAR racecars are welded by hand utilizing the GTAW course of, highlighting its significance within the automotive trade.
- Development Trade: Welding applied sciences are broadly used within the development trade for the fabrication of structurally sound steel frameworks by fusing varied steel parts. Additionally it is used to create and preserve non-structural parts. Welding is essential in constructing development, industrial development, and infrastructure initiatives, overlaying a broad and numerous vary of buildings and purposes.
- Manufacturing and Fabrication: Welding is important within the manufacturing trade for assembling advanced equipment and fabricating intricate parts that may be unattainable to provide by means of different means. It’s broadly used for the fabrication of strain vessels, bridges, constructing buildings, plane and spacecraft, railway coaches, and common purposes moreover shipbuilding, car, electrical, digital, and protection industries.
- Automotive Trade: Welding is extensively used within the automotive trade for varied purposes, together with automotive repairs, manufacturing of tanks, strain vessels, and pipes. Laser beam welding, which gives concentrated warmth perfect for slim, deep welds and excessive becoming a member of charges, is definitely automated and ideal for high-volume purposes throughout the automotive trade.
- Different Industries: Welding finds purposes in quite a lot of different industries, together with shipbuilding, meals processing, prescribed drugs, telecommunications, oil and fuel, and extra. It’s used for becoming a member of items of steel collectively and is a really expert commerce, with various kinds of welding catering to particular wants in varied industrial purposes.
What are the best metals for welding?
Mild steel
Mild steel, also known as mild steel, contains very low carbon (less than 0.3%) and can contain up to 0.4% manganese (AISI 1018 steel). This commonly used steel has excellent ductility due to its low carbon content. High ductility means high weldability because it reduces the potential for heat-affected zone (HAZ) brittleness, which can lead to hydrogen cracking. Mild steel can be welded using almost any type of equipment and is one of the most weldable metals.
Stainless steel
The weldability of stainless steel is quite high, depending on the grade of stainless steel. Ferritic and austenitic stainless steels are fairly easy to weld, but martensitic stainless steels are inconvenient to weld because martensitic stainless steels tend to crack. Stainless steel tends to bend at high temperatures, which affects the shape and strength of the final workpiece. Another problem is that the chromium in stainless steel combines with carbon during the welding process, making the workpiece more susceptible to rust without a protective layer of chromium oxide. To prevent this problem, do not heat the workpiece above the recommended temperature, or choose a low-carbon stainless steel grade.
aluminum
Forming a defect-free weld in aluminum is not the same as welding steel, but can be done within prescribed guidelines. Choosing the right grade is important because some types of welding are much easier to do than others. Due to the high thermal conductivity of aluminum, heat is quickly transferred away from the weld. Equipment with higher welding currents may be required to provide the necessary heat. Aluminum shrinks much more than steel as it cools, so special care must be taken to prevent pitting and cracking. Finally, the natural aluminum oxide coating on the base metal can add contaminants and should be removed before welding to avoid porosity in the weld.
How to Choosing the Right Metal for Welding?
Strength and durability
The resiliency of the weld depends on the strength and durability of the metal chosen. It’s not just about getting two pieces of material to stick together, it’s also about making sure they stand the test of time and the stress they’re put under. Metals with high tensile strength often produce welds that can withstand significant loads. For applications such as construction or heavy machinery, this consideration is critical. Not all materials can be easily matched. The properties of the parent metal play a vital role in determining compatibility with the filler metal. Different metals have different chemical compositions, and using filler metals with widely different compositions can result in poor weld quality. Ideally, the filler metal should have a similar chemical composition to the base metal to ensure they fuse together effectively during the welding process. When considering tensile strength, if the filler metal used has a lower tensile strength than the base metal, the joint may be weaker and prone to failure. If the filler metal has a higher tensile strength, the welded joint may crack or deform due to a mismatch in strength properties.
Ductility and weldability
Ductility—the ability of a metal to reshape without breaking—plays a key role in weldability. Highly ductile metals can be welded easily, ensuring ductility at high temperatures and forming strong joints. Metals that resist ductility often result in poor welds that are prone to cracks and failures.
Corrosion resistance
Over time, metals are susceptible to environmental wear and especially corrosion. Metals with high corrosion resistance are particularly popular, especially for welds affected by moisture, chemicals or temperature fluctuations. Even non-corrosion-resistant metals that are skillfully welded can deteriorate, affecting the strength of the weld. This is especially true in industries such as marine or chemical processing.
cost
Cost considerations are always important when choosing the best welding metal. While it may be tempting to choose premium metal, budget constraints are a reality to consider. Choosing affordable metal doesn’t mean sacrificing quality. It’s possible to find a balance between a metal that meets your welding requirements while being cost-effective.
What are the common welding processes?
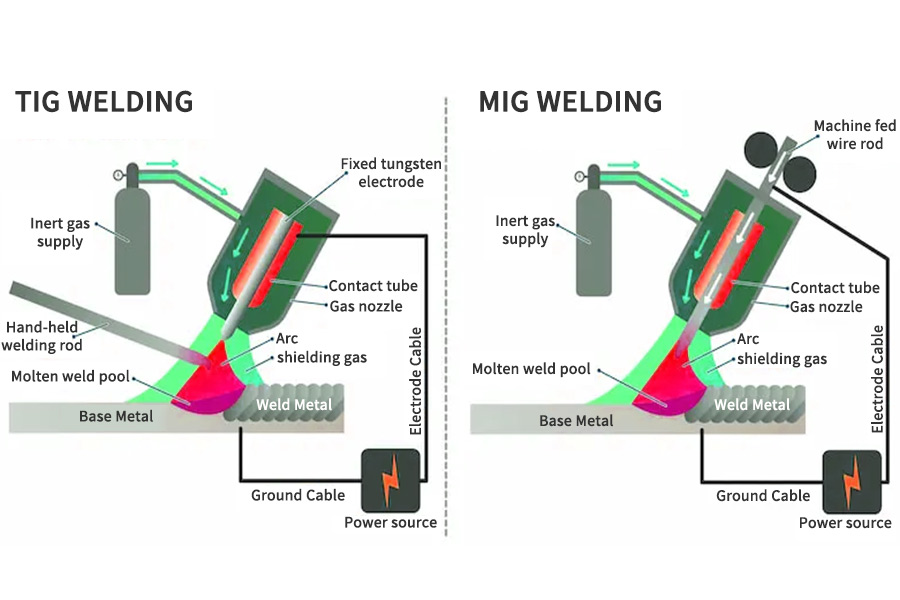
1. MIG Welding (Gas Metal Arc Welding – GMAW)
It uses a shielding gas along a wire electrode to heat the two metals being joined. This method requires a constant voltage and DC power source and is the most common industrial welding process, including sheet metal and large diameter pipe.
2. TIG Welding (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding – GTAW)
It uses tungsten electrodes and shielding gas to protect the weld from contamination. Suitable for welding a variety of metals and alloys, including thin sheets and rare metals such as titanium. It provides excellent welding quality and precise control of the welding process. Requires a high level of skill and experience to perform.
3. Stick Welding (Shielded Metal Arc Welding – SMAW)
It uses consumable electrodes coated with flux to protect the weld from contamination. Suitable for welding a variety of metals and alloys, including thick sections and dirty or rusty surfaces. Offers good portability and versatility, but produces lower quality welds than other methods. Relatively easy to learn and commonly used in field applications.
4. Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
Flux-cored welding is similar to MIG welding but utilizes a tubular wire filled with flux instead of a solid wire. It generates its shielding gas, making it suitable for outdoor and windy conditions, similar to stick welding. FCAW is fast and highly productive, making it ideal for thick materials, structural steel, and shipbuilding.
5. Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
Submerged Arc Welding involves feeding a continuous solid or tubular electrode and a layer of granular flux over the weld area. The weld is shielded from atmospheric contamination by the flux, allowing for deep penetration and high welding speeds. It’s primarily used for welding thick materials in industries like shipbuilding, heavy equipment manufacturing, and pressure vessel fabrication.
How does welding processes affect metal selection?
1. MIG Welding (Gas Metal Arc Welding – GMAW)
- Metal type: MIG welding is suitable for stainless steel, aluminum, magnesium, copper and other metals. Similar to TIG welding, MIG welding also uses inert gas (such as argon) or reactive gas (such as carbon dioxide or mixed gas) for protection. For welds that require higher welding speed and larger penetration depth, MIG welding is a more suitable choice.
- Limitations: MIG welding has high requirements on the welding environment, and the gas protection effect needs to be ensured to avoid weld oxidation.
2. TIG Welding (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding – GTAW)
- Metal type:The biggest advantage of TIG welding is that it can weld a variety of metals and alloys, including stainless steel, nickel alloys, titanium, aluminum, magnesium, copper, etc. Its arc is concentrated and the heat input is controllable, making it ideal for welding thin plates and high melting point metals.For active metals (such as aluminum, magnesium) and their alloys, TIG welding can effectively prevent oxidation due to its inert gas protection (such as argon) and ensure the quality of the weld.
- Limitations:Although TIG welding is widely applicable, it may be less efficient for high-volume production and thick plate welding.
3. Stick Welding (Shielded Metal Arc Welding – SMAW)
- Metal type: Arc welding can weld carbon steel, low alloy steel, stainless steel and other metals. It protects the weld seam through the gas and slag generated by the welding rod coating and avoids contamination of the weld seam by oxygen and nitrogen in the atmosphere. For welds with complex structures that are difficult to mechanize or automatically weld, arc welding has good adaptability.
- Limitations: The welding efficiency of arc welding is relatively low and requires high skills of the welder.
4. Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
- Metal type: Flux-cored wire arc welding combines the advantages of electrode arc welding and gas shielded welding, and is suitable for welding a variety of metal materials. The welding wire is filled with powder, which melts during the welding process and produces protective gas and slag to protect the weld.It is especially suitable for occasions where high-quality welds are required, such as the welding of pressure-bearing equipment.
- Limitations: Flux-cored arc welding has high requirements on wire quality and welding process. It is necessary to ensure that the powder powder is evenly distributed and the welding parameters are reasonable.
5. Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
- Metal type: Submerged arc welding is widely used in the welding of heavy workpieces such as steel structures, boilers and pressure vessels due to its high efficiency, high quality and ease of automation.It is suitable for welding carbon steel, low alloy steel and other ferrous metals, but there are applicability problems when welding non-ferrous metals (such as copper, aluminum, magnesium) because its high thermal conductivity and easy oxidation may lead to poor welding quality.
- Limitations: Submerged arc welding has high requirements on the welding environment, and it is necessary to ensure uniform flux coverage and stable combustion.
What are the factors that influence the selection of welding processes?
1. Material Type
Different welding processes are better suited for specific materials. For instance, while MIG welding is versatile and suitable for various materials, TIG welding excels in welding thinner materials and non-ferrous metals. Understanding the material being welded is crucial in selecting the appropriate welding process.
2. Material Thickness
The thickness of the material plays a significant role in the selection of the welding process. Some processes, like TIG and MIG, work well with thinner materials, while stick welding or flux-cored welding might be more suitable for thicker sections due to their ability to provide deeper penetration.
3. Welding Position
Consideration of the welding position, whether it’s flat, vertical, horizontal, or overhead, is crucial. Some processes might be more suitable for specific positions due to their ability to control the weld puddle and prevent slag or spatter from falling into the weld.
4. Joint Design And Project Specifications
The type of joint and the project specifications also influence the welding process choice. Some processes might be more suitable for certain joint designs, such as fillet welds or groove welds. Understanding the project requirements and the desired weld characteristics is essential in making the right selection.
5. Welding Speed And Productivity
Different welding processes vary in their speed and productivity. For high-volume production, a process like MIG or flux-cored welding might be preferred due to their high deposition rates and efficiency. However, for high precision and clean welds, TIG welding might be the preferred choice despite being slower.
6. Environmental Conditions
Consideration of the welding environment is crucial. For outdoor or windy conditions, processes like flux-cored arc welding or stick welding, which are less susceptible to atmospheric interference, might be the better choice.
Case Research
| Case | Describe |
| Automotive Trade (Case Research) | Welding, significantly Friction Stir Welding (FSW), is used within the automotive trade to hitch parts collectively. FSW is a solid-state course of that joins two going through surfaces, utilizing much less warmth than different welding strategies, which might be useful in automotive manufacturing the place weight and vitality effectivity are vital concerns. |
| Development Trade (Case Research) | Welding is a elementary course of within the development trade, used within the development of buildings, bridges, pipelines, and different engineering gadgets needed for infrastructure in city environments. Varied welding processes are used, together with arc welding, laser reducing and welding, laser-arc hybrid welding, friction applied sciences, and electron beam welding. |
| Comparative Evaluation in Related Industries | Welding is used throughout a variety of industries, together with development, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, the place the becoming a member of of particular perso n parts is important for structural integrity and performance. |
Conclusion
Choosing the right metal is critical to the quality of your weld. When selecting a metal, several factors such as its physical and chemical properties as well as the choice of welding process and the selection criteria of the welding metal need to be considered. Only by comprehensively considering these factors can we ensure that the quality and performance of welded joints meet the usage requirements and ensure the safety and reliability of the entire welded structure.The future development trend of the welding industry will feature technological innovation and intelligent development, environmental protection and sustainable development, market demand and application field expansion, talent training and skills improvement, and international competition and cooperation. These trends will jointly promote the development of the welding industry to a higher level and higher quality.Visit our Instant Quote Engine to get a free, no-obligation quote in minutes.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. LongSheng makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through LongSheng’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please contact to our for more information.

Team LongSheng
This article was written by various LongSheng contributors. LongSheng is a leading resource on manufacturing with CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, injection molding,metal stamping and more.
FAQs
How to choose appropriate welding materials according to the working environment?
It is crucial to select the appropriate welding consumables according to the working environment of the weldment. For example, when the weldment works in a corrosive medium, the medium type, concentration, operating temperature, and corrosion type (general corrosion, intergranular corrosion, stress corrosion, etc.) must be distinguished to select appropriate stainless steel welding consumables. Similarly, when the weldment is working under wear conditions, it is also necessary to select appropriate surfacing welding materials according to the wear type and working environment.
How to consider welding efficiency during welding process?
In the welding process, improving welding efficiency is an important way to reduce costs and improve production efficiency. For structures with a heavy welding workload, high-efficiency welding materials should be used as much as possible, such as welding wire, iron powder welding rods, etc. These welding materials have the advantages of fast welding speed and high welding efficiency, which can significantly shorten the entire welding time and improve production efficiency.
How to prevent porosity problems when welding?
Preventing welding porosity problems requires comprehensive consideration and implementation from multiple aspects such as pre-welding preparation, welding process control, environmental control and other measures. By strictly implementing these preventive measures, the incidence of welding porosity can be significantly reduced and the welding quality improved.


