Injection molding is a Injection molding used to produce plastic parts in large numbers with superior precision and accuracy,which requires careful planning, precise execution, and accurate monitoring. One of the most challenging issues in this manufacturing technique is the generation of scrap, which can significantly affect both the quality and the profitability of the final product.
To help injection molding companies tackle this problem, we have put together a highly informative and persuasive article that includes practical tips, expert advice, and real-life examples of successful scrap reduction initiatives.

What is Scrap in Injection Molding
Before we dive into the tips and techniques for reducing scrap in injection molding, let’s first define what scrap is. In manufacturing, scrap refers to any material that is discarded during the production process due to defects, imperfections, or quality standards that do not meet the desired specifications. Scrap is a costly and wasteful outcome of the manufacturing process, as it requires resources to produce and dispose of.
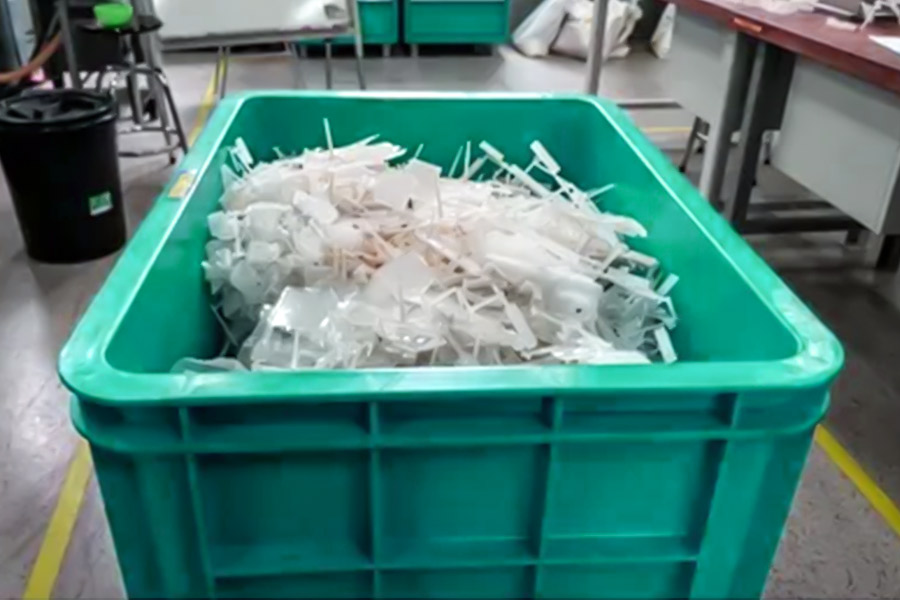

What Scrap Comes From Injection Molding?
The injection molding process does not produce large amounts of scrap per unit. Still, because large volumes of parts are produced per manufacturing cycle, the waste can accumulate rapidly if not properly addressed. The scrap usually comes from the following sections of the mold:
- The Sprue
- Runner
- Ejector pins
- Gate locations
- Runner system channels
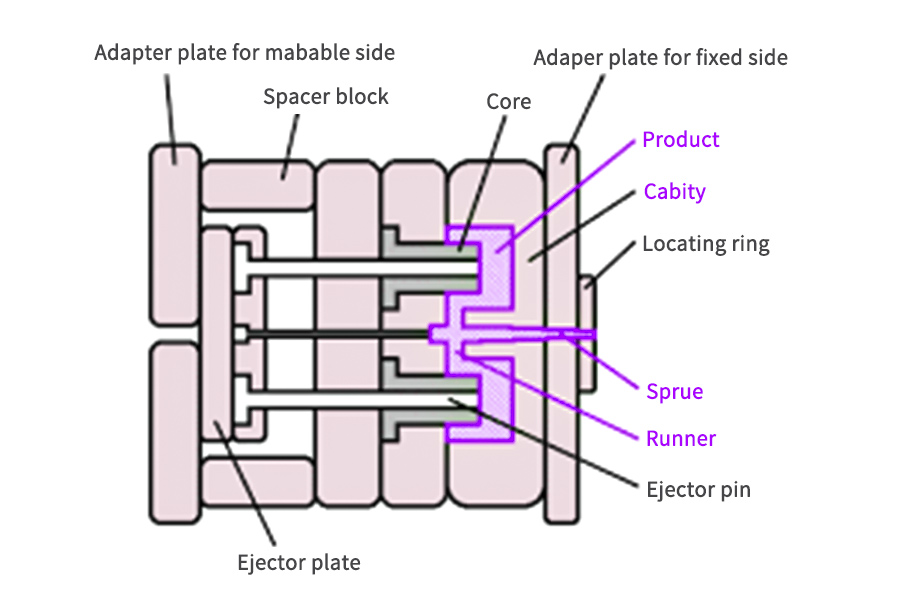
what are the causes of scrap in injection molding
Identification of scrap and defects is the first step in eliminating scrap in production. Common sources of scrap and defects during injection molding processes include:
- Poor design or construction of the mold
- Variations in material quality
- Inconsistent process parameters like temperature, pressure, and fill rate
- Lack of or inadequate maintenance of the injection molding machine
- Human error or lack of training
To identify the sources of scrap and defects in an injection molding process, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive analysis. This includes collecting data on process parameters, performing visual inspections of parts produced, as well as inspecting mold and tooling for signs of wear and tear.
Additionally, it’s essential to involve process technicians and other personnel in the analysis process as they can offer valuable insights into what causes scrap and defects. By recognizing the root causes of scrap and defects, you can implement targeted solutions to address them and reduce production scrap.
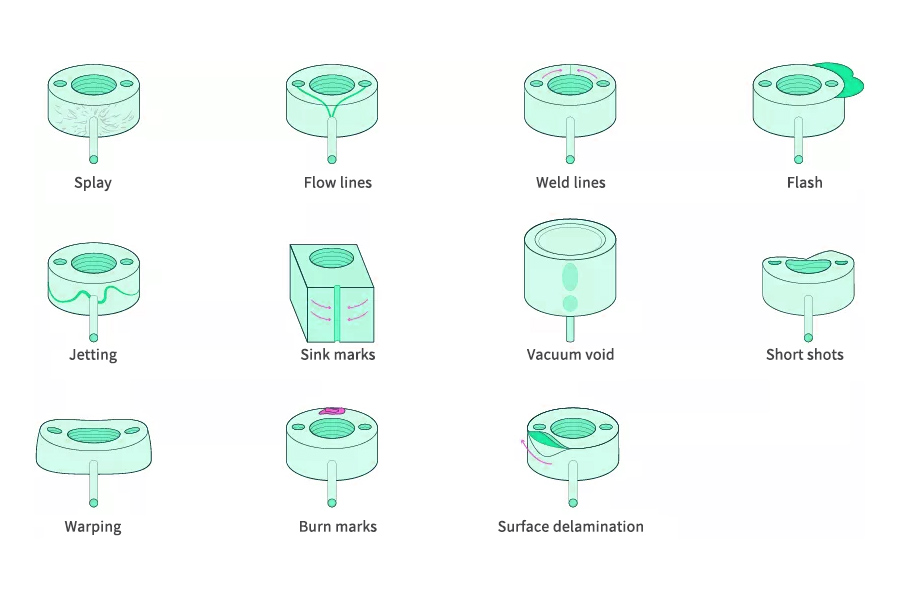
Overall, pinpointing the causes of scrap and defects is essential to reduce production waste and enhancing part quality. By conducting an in-depth analysis of the injection molding process with input from process technicians and other personnel involved, you can implement effective solutions that increase efficiency and consistency throughout this step-by-step endeavor.
Why Reducing Scrap is Critical for Injection Molding
Scraps are a common byproduct of injection molding, where excess material is generated during the molding process. This waste can take different forms, such as flash, short shots, voids, sink marks, warpage, or defects, and can result from various factors, such as machine settings, material properties, mold design, or operator errors. Regardless of the specific cause, the presence of scrap can have several negative effects on an injection molding company, including:
| Reduced productivity | Scrap requires additional handling, sorting, and disposal, which can slow down production lines and increase downtime. |
| Higher costs | Scrap generates additional material, energy, and labor costs, which can increase the overall cost of production and reduce profit margins. |
| Lower quality | Scrap can affect the quality of the final product, as defects or imperfections can compromise its functionality, reliability, or aesthetics. |
| Environmental impact | Scrap can contribute to pollution, waste, and carbon emissions, affecting the sustainability and eco-friendliness of the manufacturing process. |
Given these consequences, reducing scrap should be a top priority for injection molding companies. To achieve this goal, they need to adopt a comprehensive approach that involves addressing the root causes of scrap, implementing corrective actions, and monitoring their effectiveness over time.
meanings of scrap reduction
| Cost Savings | Improving quality helps in achieving a higher yield of usable parts, reducing rework or scrap-related interruptions during the production process, and maximizing overall production efficiency |
| Customer Satisfaction | High-quality injection-molded parts are crucial for meeting customer expectations. By minimizing defects and maintaining consistent quality, manufacturers can ensure customer satisfaction, build trust, and enhance their reputation in the market |
| Production Efficiency | Improving quality helps in achieving a higher yield of usable parts, reducing rework or scrap-related interruptions during the production process, and maximizing overall production efficiency |
| Operational Competitiveness | Efficient scrap reduction and quality improvement practices enable manufacturers to remain competitive in the industry. It allows them to offer cost-effective production, reliable parts, and timely delivery, giving them an edge over competitors |
| Sustainability | Minimizing scrap aligns with sustainability goals by reducing material waste and environmental impact. It contributes to a more sustainable manufacturing process and supports the overall environmental responsibility of the company |
tips to Reduce Scrap in Injection Molding
- The use of purging compounds should be preventive, avoiding the degradation of the resin and its additives or pigments. Use purging compounds that can be left loaded in the barrels, molds, dies, and generally in the system. In this way, we will avoid the entry of oxygen that promotes degradation, we will leave a thermally stable material that will be able to withstand the residual heat while the machine cools or heats.
- It is common to leave the heats on or on standby. As a general rule, no machine should be left on. The degradation may be so great that it forces the spindle to be dismantled or worse still, reach the point of ignition of the plastic and cause flames. Sometimes it is left at very low temperatures. Consider that this will eventually cause layers to adhere which will eventually come off in the form of black specks. Ideally, the system should be left off, the “time savings” normally thought to be achieved by reaching operating temperature are regularly lost when hours have to be spent manually cleaning the machines or sorting out contaminated parts. Turn off the heaters, because in some cases the purging compound will have a contracting effect that can help in the removal of some contaminants that were just forming.
- After producing the last product, the first thing you must do before switching to another color/material or stopping the machine is to clean the material barrel and mold. If the machine is still running well on parts and needs to be cleaned immediately, there is no reason for contamination to occur. This puts you in a better starting position. This has great benefits for both you and your customers.
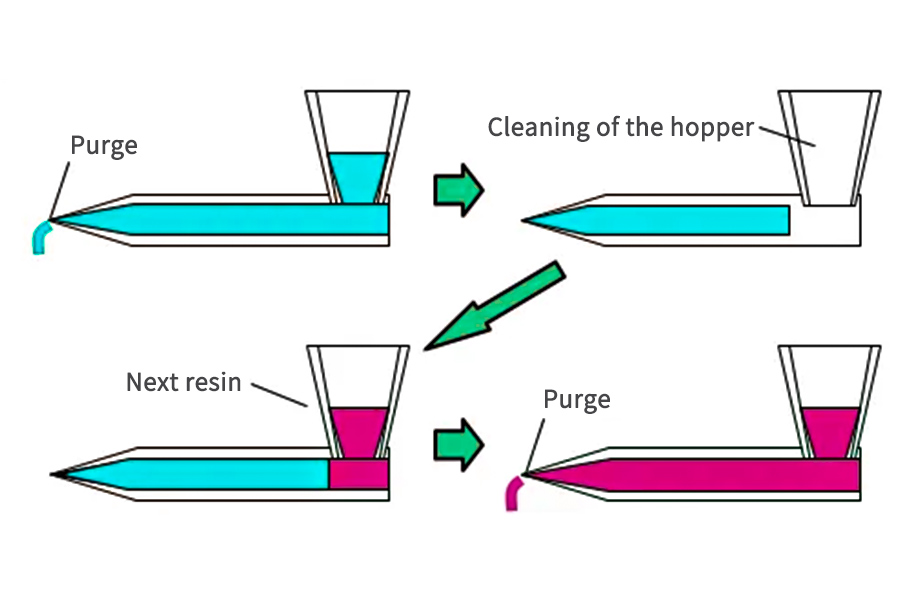
- On the day of start-up, turn on the machines in an orderly manner, starting with those that are most urgently needed to produce and secondly those that will work at a lower temperature. Those machines that have very high process temperatures will have to get up to their temperature. Keeping a machine running for hours above 230°C without producing will promote the formation of crusts and black specks.
Different resins, colors, quality criteria, etc… require the correct material to be used for purging. There are a wide variety of purgatives on the market. Select one that allows you to make the product change efficiently, this implies that it is in the shortest possible time. Keep in mind that while adjusters, process technicians, or operators are doing a long and inefficient purge on one machine, another machine may be idle waiting to be serviced. Do not allow downtime to multiply because the staff does not have the tools and knowledge to do their job and therefore lead you to success.

Strategies for Scrap Reduction in Injection Molding
Plastic manufacturing produces waste in the form of scraps.various strategies can be used by manufacturers to reduce scrap waste. Below are some strategies used.
1.Optimize Manufacturing Processes
This can be achieved through analyzing and streamlining production processes to reduce energy and material consumption, improve productivity and minimize waste. Manufacturers can reduce scrap, cost of production and resources through ensuring effective practices are incorporated in the production process.
To make this strategy effective, incorporating lean principles in the production process is important. To improve production efficiency and reduce waste automation and other other advanced technologies can be used.
2.Optimize Mold Design
Optimizing your mold design minimizes the scrap rate by ensuring that the final product meets the required quality standards. Mold design optimization ensures that the mold is robust enough to withstand the injection pressure, and the product is uniform in shape, size, and weight.
Reducing scrap in injection molding is a critical task that requires a comprehensive approach combining technical expertise, quality control, employee engagement, and continuous improvement. By adopting the tips and best practices outlined in this article, injection molding companies can reduce their scrap rates, improve their productivity and profitability, and enhance their environmental sustainability and reputation.
3.Invest in Sustainable Technologies
To reduce the environmental impact of production, manufacturers can invest in sustainable technologies by using materials, processes and products that are environment friendly. These materials should be renewable, recyclable and biodegradable. In addition the use of energy conserving and efficient technology such as solar energy should be utilized.
Investing in sustainable technologies is significant in reducing carbon emission and water pollution caused during production. Additionally sustainable technology can help streamline production processes that need less energy and other resources. Through using sustainable technologies,you can reduce your waste output and provide an efficient production process that is suitable for the environment.
4.Enhancing Injection Molding Quality
To ensure that the final product is of high quality, it is crucial to maintain the proper melt temperature and pressure in your plastic injection molding process. Melt temperature is the temperature at which plastic material turns into a molten state. Pressure variation in injection molding is the pressure difference between the injection unit and mold cavity.
Constant monitoring of these process parameters is important. This is achieved through the use of sensors and softwares that monitor the temperature and pressure data in real time. This enables detection of deviation and the necessary adjustments are made.
Another factor that is essential in improving injection molding efficiency is controlling process and viscosity variation. Process variation is the changes in process parameters such as temperature and pressure. Viscosity variation on the other hand refers to changes in plastic resin flow behavior which could impact mold filling and part production quality.
To control process variation and viscosity variations, you need to implement process monitoring and control systems. This could include sensors and software that continuously adjust parameters based on collected data.
5.Controlling Tooling and Molding Cycle
Tooling and molding cycle management is essential for improving injection molding quality. The mold plays an integral role in this process, its design and construction directly affecting parts produced. Furthermore, other stages such as filling, packing, and cooling can have an effect on finished parts produced during injection molding.
To effectively manage the injection mold cycle and molding cycle, it is essential to work with experienced tooling engineers and mold makers. This includes selecting appropriate mold materials, designing the cavity and gating systems, as well as optimizing cooling systems. Furthermore, regular inspection and upkeep of the mold is necessary in order to prevent wear-and-tear that could affect product quality.
Management the molding cycle involves optimizing the fill, pack and cooling stages to guarantee uniform plastic resin distribution throughout the mold and that parts produced meet desired specifications. This may involve adjusting process variables such as temperature, pressure and fill rate to achieve ideal outcomes.
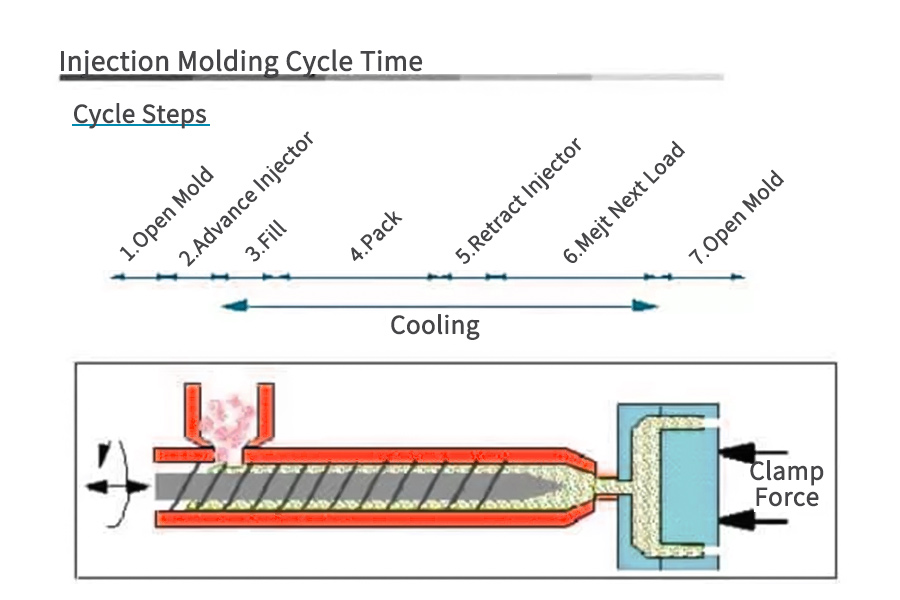
recycling injection molding scrap
Injection molding is a naturally low-waste process, but we still strive to limit waste and repurpose it when possible.
Because injection molding most commonly uses thermoplastic materials (such as PET, PETE, HDPE, LDPE, and ABS), nearly all scrap plastic from injection molding projects can be recycled for later reuse. Occasionally, thermoset plastics (such as PVC, silicone, epoxy, and polyurethane) are used, though the injection molding process for thermosets is somewhat different. Because these plastic formulations cannot be melted down to their original state, they cannot be as easily recycled.
conclusion
Injection molding is a commonly used technology in industry, and reducing scrap it geneates is crucial. For companies, reducing the scrap generated by injection molding can not only save costs, improve production efficiency, and bring customer satisfaction. For the entire environment, it can reduce environmental pollution and waste of resources, achieve sustainable development and fulfill the company’s environmental responsibility. This article also provides tips on reducing injection molding scrap in production and provides some strategies to reduce waste. If you have any questions, you can leave us a message or send us an email, and we will try our best to solve your doubts.
resources
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Injection_moulding


