Introduction to CNC Machining and Workshop Setup
Overview of CNC Machining
CNC, or Computer Numerical Control, is a computerized manufacturing process where pre-programmed software dictates the movement of machinery. This process is used in various complex machinery, including grinders, lathes, and turning mills, which are all utilized to cut, shape, and create parts and prototypes. CNC machines can handle a wide range of materials, making them a versatile tool in the manufacturing industry.
CNC machining involves various operations, including routing, milling, drilling, and cutting. These operations are controlled by a set of commands, usually in the form of a list of coordinates known as G-code. The precision of CNC machines allows for high accuracy in producing parts, with tolerances down to tiny measurements.
Importance of a Well-Equipped Workshop
A well-equipped CNC workshop is crucial for efficient and accurate production. The workshop should include a variety of CNC machines to handle different operations, such as milling, drilling, and cutting. Additionally, the workshop should be equipped with the necessary safety equipment and storage solutions for tools and materials.
Having a well-equipped workshop not only ensures the production of high-quality parts but also improves the efficiency of the manufacturing process. With the right tools and equipment, manufacturers can reduce errors, save time, and increase productivity.
Planning Your CNC Workshop Layout
Planning the layout of your CNC workshop is an essential step in setting up an efficient manufacturing process. The layout should consider the flow of work, the placement of machines, and the storage of materials and tools.
Workflow should be smooth, with minimal movement of materials between different machines. This can be achieved by placing machines in sequence close to each other.
The placement of machines should also consider safety. Machines should be placed to reduce the risk of accidents, such as collisions or tripping hazards. There should also be enough space around each machine for operators to move safely and comfortably.
Storage areas for materials and tools should be organized and easily accessible. This improves efficiency and reduces the risk of accidents caused by misplaced tools or materials.
The CNC Machinist’s Basic Toolkit
CNC Machine Selection: Milling Machines, Lathes, and Routers
The first step in building a CNC machinist’s toolkit is selecting the suitable machines. The most common types of CNC machines are milling machines, lathes, and routers.
Milling machines are versatile tools that perform various operations, such as drilling, slot cutting, and threading. The workpiece is held stationary on the machine bed or in a vice, and the material is removed using cutting tools or drills that rotate at high speed.
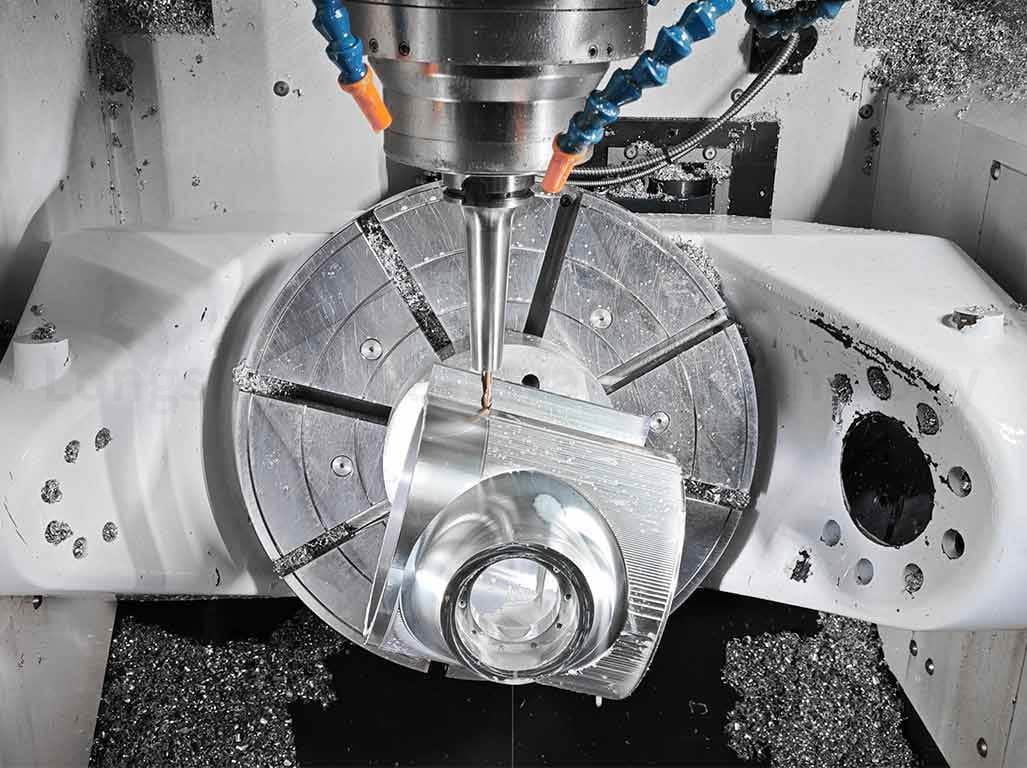

Lathes are used for operations like turning, facing, and threading. They rotate the workpiece against a cutting tool.
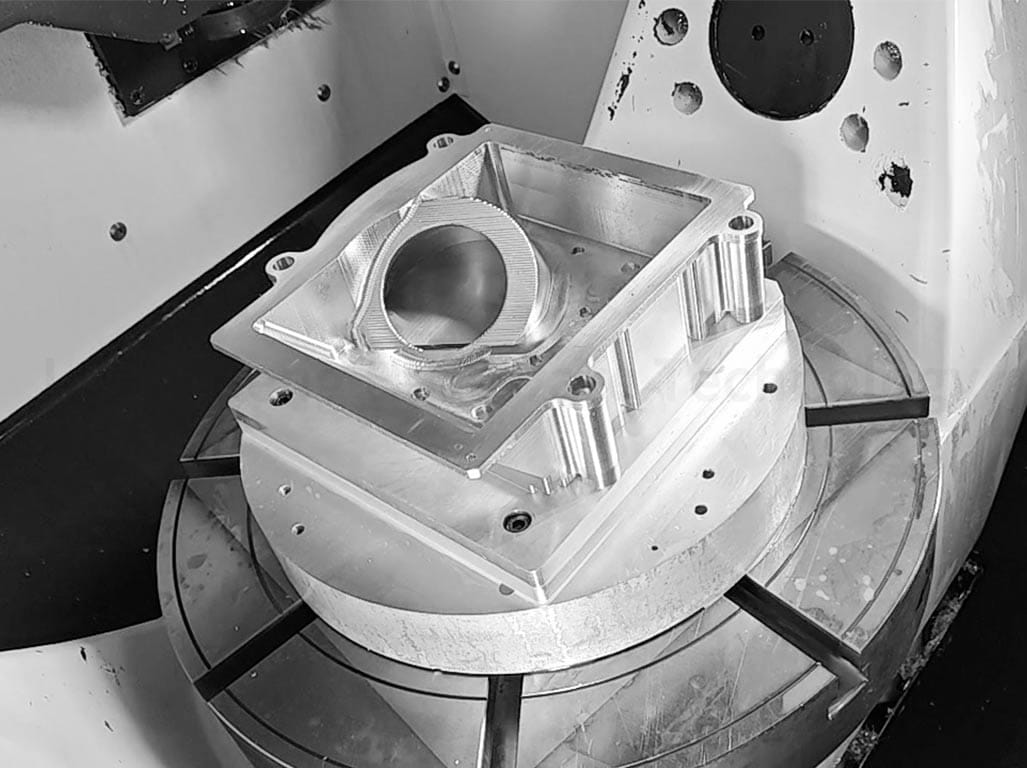
Routers are primarily used for cutting complex shapes and patterns in materials like wood and metal. They are handy for detailed and intricate designs.

Each machine has capabilities and uses, so the selection will depend on your workshop’s specific needs.
Measuring Instruments: Calipers, Micrometers, and Gauges
Accurate measurements are crucial in CNC machining. Therefore, a machinist’s toolkit should include a variety of measuring instruments.
Calipers are versatile tools that measure internal and external dimensions. They help check the materials’ thickness, the holes’ diameter, and the parts’ length.
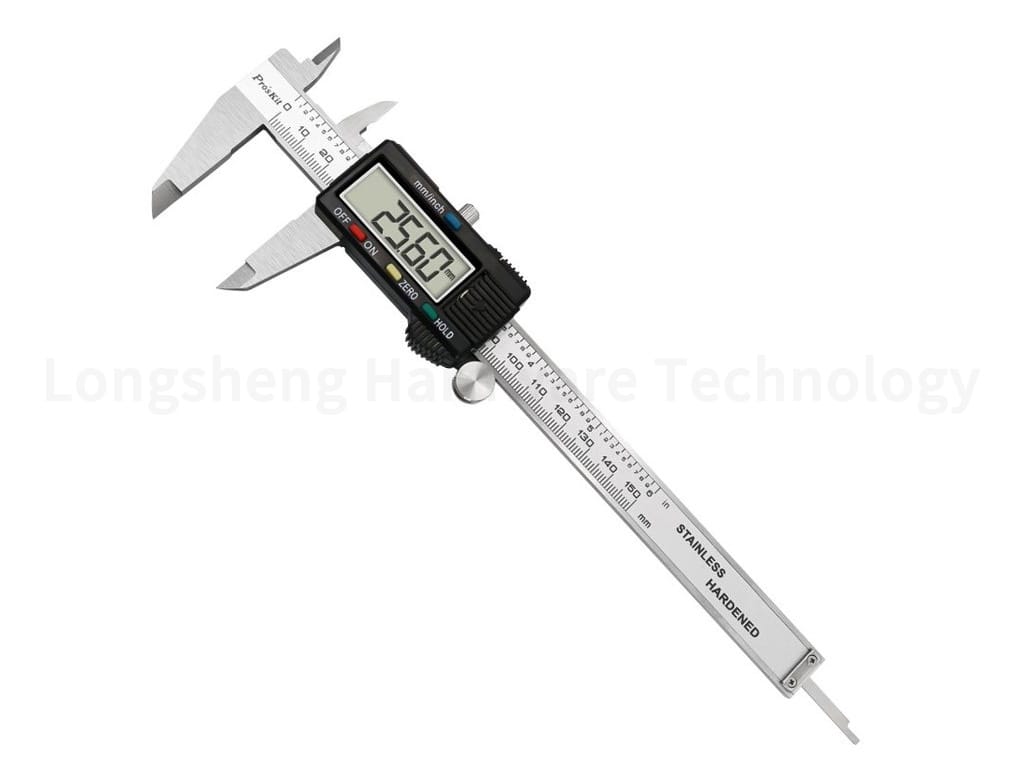

Micrometers provide even more precision than calipers, allowing measurements down to 0.001mm. They are typically used for measuring small dimensions and are essential for ensuring the accuracy of parts.
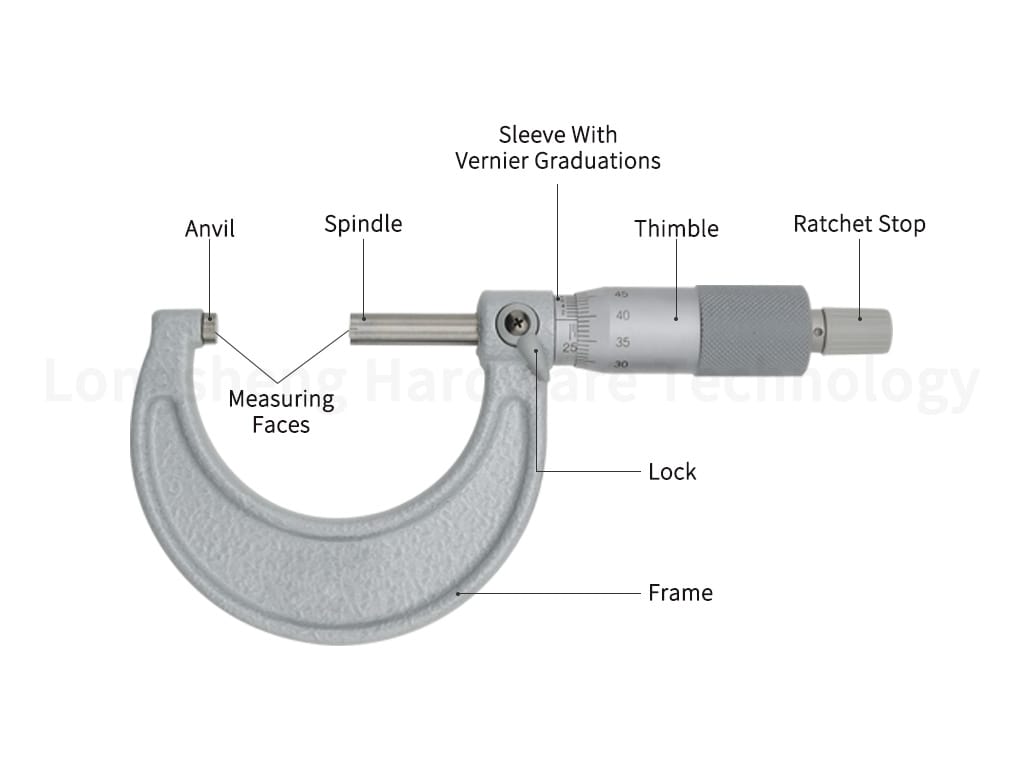
Gauges are used to check the size and alignment of parts. They come in various types, including thread gauges for checking screw threads and plug gauges for limiting the size of holes.

These measuring instruments are essential for ensuring the accuracy and quality of the parts produced by CNC machines.
Workholding Essentials: Vises, Clamps, and Fixtures
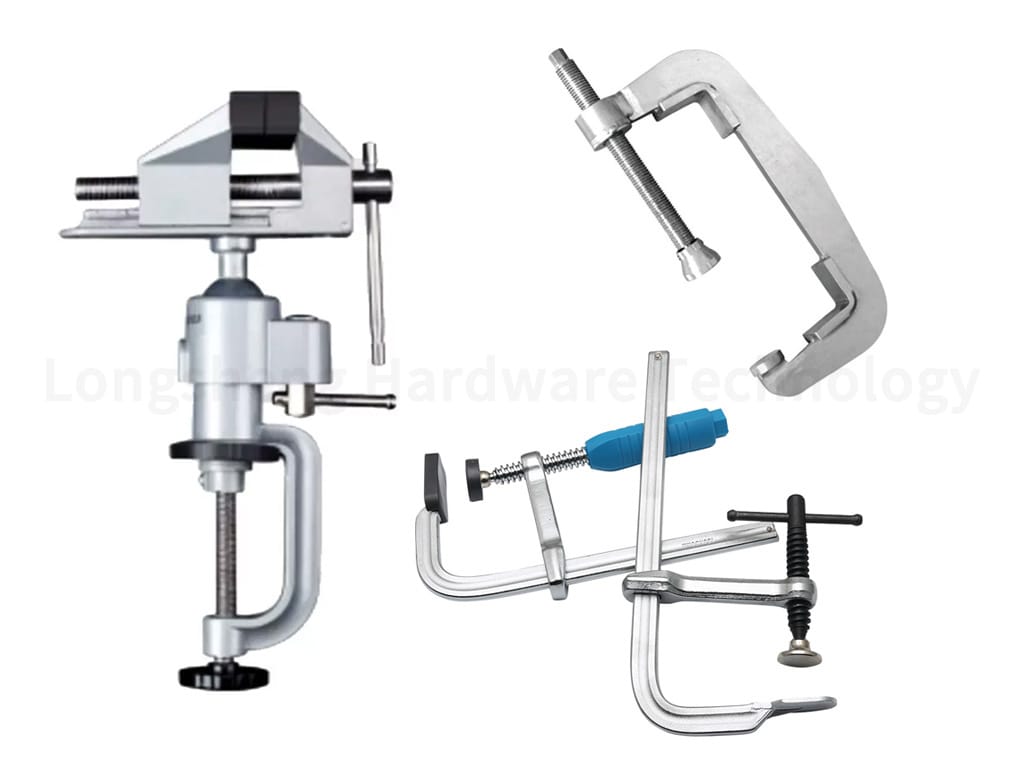

Workholding devices are another vital part of a CNC machinist’s toolkit. These devices secure the workpiece during Machining, ensuring accuracy and safety.
Vises are commonly used in milling operations. They hold the workpiece securely in place, allowing for precise Machining.
Clamps are versatile work-holding devices that can secure a variety of workpieces. They are easy to adjust, making them suitable for workpieces of different sizes and shapes.
Fixtures are custom-made devices designed to hold a specific workpiece. They are typically used for complex parts that cannot be kept securely by standard workholding devices.
These work-holding essentials are crucial for maintaining accuracy during Machining and ensuring the machinist’s safety.
Advanced CNC Machining Tools
Precision Tools for Complex Projects

The need for precision tools increases as CNC machining projects become more complex. These tools are designed to handle intricate designs and tight tolerances, ensuring the production of high-quality parts. Precision tools can include a variety of cutting tools, such as end mills, drills, and inserts, as well as precision measuring instruments like micrometers and gauges. These tools are essential for advanced CNC machining projects, where accuracy and precision are paramount.
Specialty Cutters and End Mills
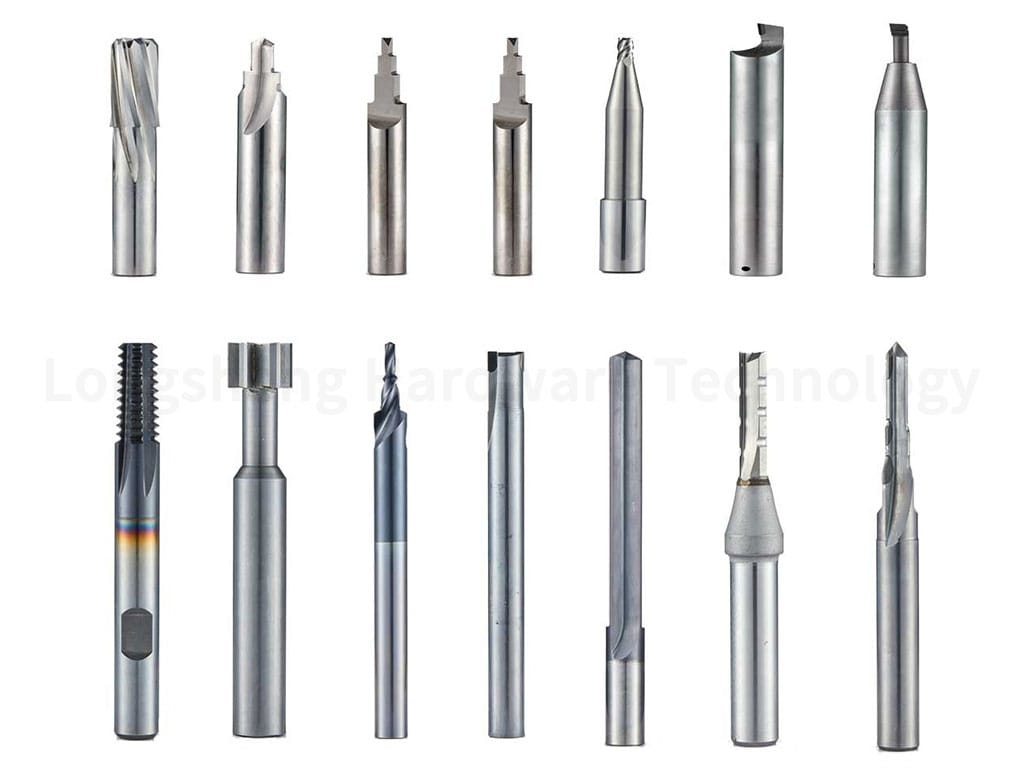

Specialty cutters and end mills are advanced tools used in CNC machining for specific applications. These can include ball end mills for 3D contouring, face mills for flat surfaces, and corner radius end mills for rounded edges. Specialty cutters can also have tools for specific materials, such as carbide cutters for hard materials or high-speed steel (HSS) cutters for softer materials. These tools allow machinists to perform a wide range of operations with high precision and efficiency.
Tool Holders and Collets: Maximizing Performance
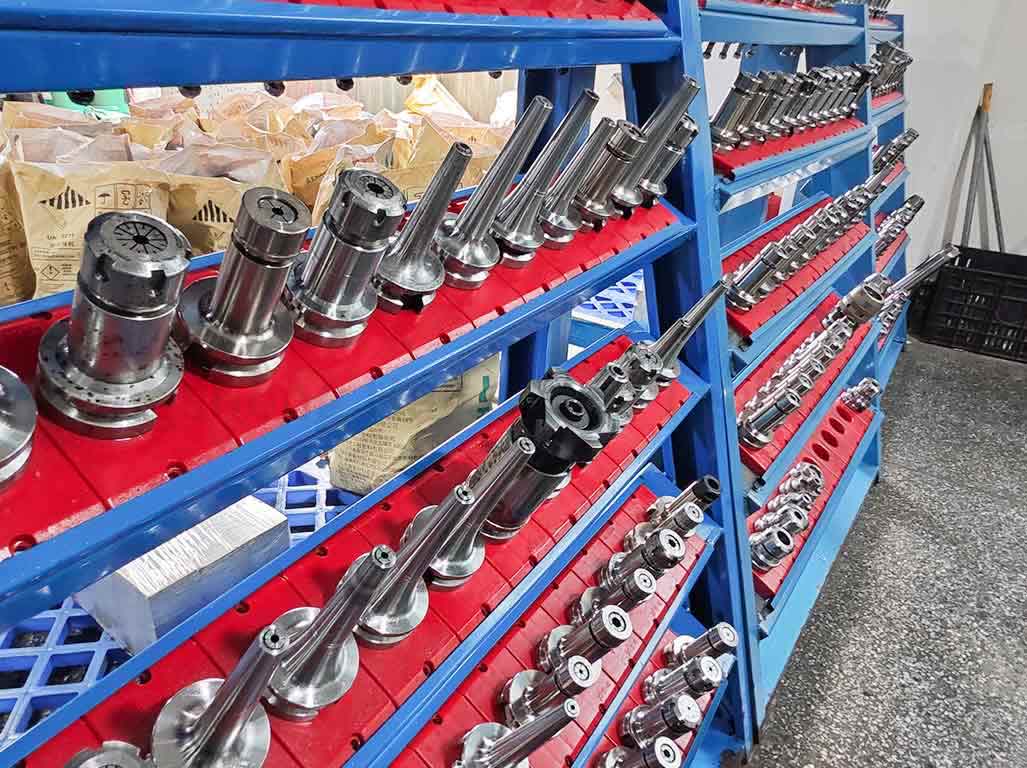

Tool holders and collets are essential components of a CNC machine that contribute to its performance and accuracy. Tool holders are devices that connect the machine’s spindle to the cutting tool, while collets are sleeves that hold the cutting tool in place in the tool holder.
Tool holders come in various types, including end mill holders, collet chucks, and drill chucks, each designed for a specific cutting tool. The right tool holder can improve the machine’s performance and extend the cutting tool’s life.
Collets, on the other hand, are designed to hold the cutting tool securely without damaging it. They come in various sizes to accommodate different tool diameters and can be easily changed to suit different tools.
CNC Machine Maintenance Tools
Cleaning and Lubrication Supplies
Maintaining a CNC machine involves regular cleaning and lubrication. Cleaning supplies such as brushes, compressed air, and industrial-grade cleaners are essential to keep the machine from dust and debris. Frequent cleaning can enhance the machine’s efficiency and prolong its lifespan.
Lubrication is equally essential in maintaining the smooth operation of the machine. Lubricants reduce friction between moving parts, preventing wear and tear. Essential lubrication supplies include oils and greases suitable for various machine parts, such as the spindle and the axes. Regular checks on coolant levels and concentration are also necessary to prevent overheating and damage to machined parts.
Alignment and Calibration Instruments
Alignment and calibration are crucial for maintaining the accuracy and precision of a CNC machine. Tools for alignment and calibration include dial indicators, laser alignment tools, and calibration blocks. Regular alignment checks and calibrations can help ensure the machine continues functioning well despite frequent and prolonged use. For example, semi-annual axis inspections and yearly spindle alignments can help maintain precision and productivity.
Replacement Parts and Tooling Maintenance Kits
Having a stock of replacement parts is essential for minimizing downtime when a component of the CNC machine fails or wears out. Common replacement parts include bearings, belts, and filters.
Tooling maintenance kits are also crucial for maintaining the performance of the cutting tools used in CNC machining. These kits typically include supplies for cleaning, sharpening, and storing the tools. Regular tool maintenance can help extend the life of the tools and ensure consistent cutting performance.
Digital Tools for the Modern Machinist
CAD/CAM Software Essentials

Computer-aided design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software are essential tools for the modern machinist. CAD software creates a 3D model of a part, while CAM software plans the manufacturing process for that part. These software tools allow machinists to design, simulate, and manufacture parts highly and efficiently. They also facilitate the production of complex parts that would be difficult to fabricate using traditional methods.
Simulation and Toolpath Visualization Tools
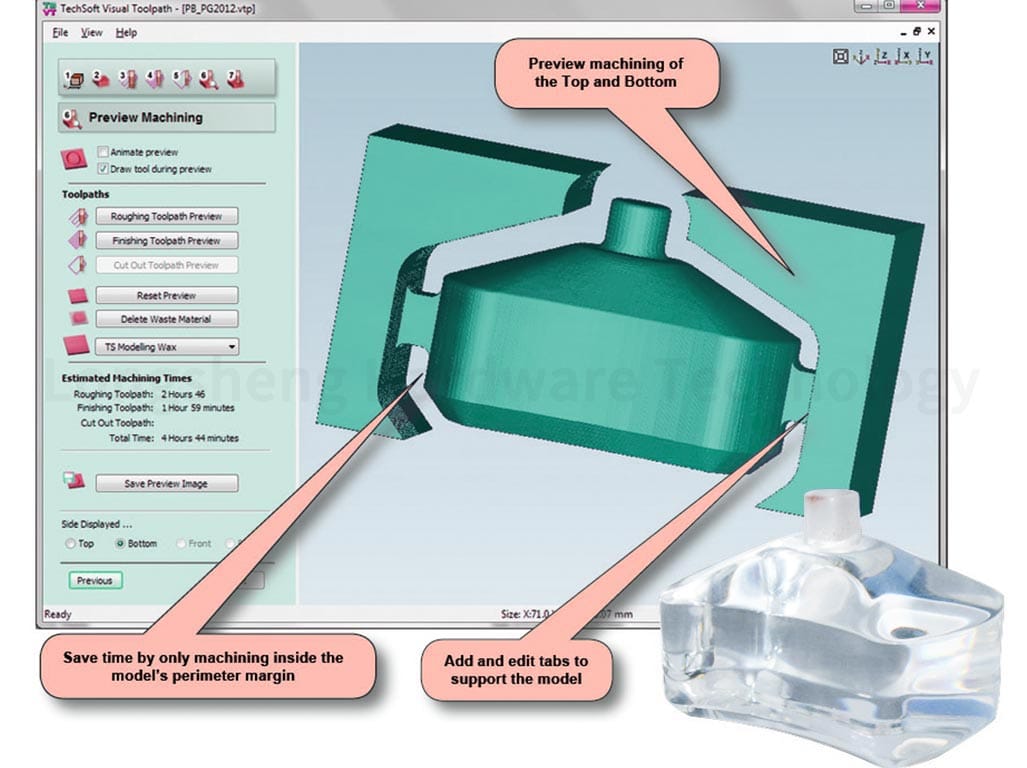
Simulation and toolpath visualization tools are digital tools that allow machinists to preview and optimize the machining process. These tools can simulate the movement of the machine and the cutting tool, allowing machinists to identify potential problems before the machining process begins. They can also visualize the toolpath, the path the cutting tool will follow during Machining. This can help machinists plan the most efficient and effective toolpath, reducing machining time and improving the quality of the finished part.
G-Code Editors and Machine Controllers

G-code editors and machine controllers are digital tools used to control CNC machines. G-code is a language that CNC machines understand and is utilized to dictate the machine’s movements. G-code editors allow machinists to write, edit, and optimize G-code, ensuring that the machine operates as intended.
Machine controllers, on the other hand, are used to send the G-code to the CNC machine and control its operation. They allow machinists to start, stop, and pause the machine and monitor its status during operation.
Safety Gear and Personal Protective Equipment
Essential Safety Gear for CNC Machinists
Safety should always be a priority in any CNC workshop. CNC machinists are exposed to various hazards, including flying debris, loud noise, and potential contact with moving machinery. Therefore, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is the last defense against these workplace hazards.
Critical items of PPE for CNC machinists include safety glasses to protect the eyes from flying debris, hearing protection to guard against loud noise from the machinery, and appropriate foot protection to safeguard against any objects that might be dropped. While most CNC machines have suitable enclosures, these pieces of PPE are always recommended to provide an extra layer of protection.
Understanding OSHA Guidelines for Workshop Safety
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides workplace safety guidelines, including CNC workshops. These guidelines cover a range of safety measures, including providing PPE, noise protection, and employee training. Employers must supply the necessary equipment and training to meet these standards, ensuring a safe working environment for all employees.
First Aid and Emergency Equipment for Workshops
In addition to PPE, a CNC workshop should also be equipped with first aid and emergency equipment. This can include a well-stocked first aid kit, fire extinguishers, and emergency stop buttons on all machinery. Employees should be trained in using this equipment and what to do in an emergency. Regular drills can also be beneficial in ensuring that everyone knows how to respond effectively and safely.
Organizational Tools for CNC Workshops
Storage Solutions for Tools and Accessories
Proper storage solutions are crucial for maintaining an organized and efficient CNC workshop. These solutions include tool cabinets, shelves, and specialized CNC tools and accessories storage systems. Proper storage not only keeps the workspace tidy but also protects tools from damage and makes them easily accessible, enhancing productivity in the workshop.
Labeling and Inventory Management Systems
Labeling and inventory management systems are essential for keeping track of tools and materials in a CNC workshop. These systems can help prevent misplaced inventory, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
Inventory management systems can track items at cost centers and analyze tool usage, differentiating consumables, durables, and service or regrind items. This can help workshop managers maintain an optimal inventory level, ensuring that the necessary tools and materials are always available when needed.
On trend, labeling can help machi labeling lists quickly identify the necessary tools and materials, reducing the time spent searching for items and increasing productivity.
Creating a Clean and Efficient Workspace
Creating a clean and efficient workspace is another crucial aspect of workshop organization. This involves keeping the workspace free of clutter, putting away items that are not in use, and arranging tools and materials in a way that facilitates workflow.
A clean and efficient workspace not only enhances productivity but also contributes to safety in the workshop. It reduces the risk of accidents caused by tripping over clutter or coming into contact with misplaced tools.
Specialty Tools for Specific CNC Applications
Tools for High-Precision Machining
High-precision machining requires specialized tools that can handle intricate designs and tight tolerances. These tools are designed to produce parts with high accuracy and surface finish. They are often used in industries where precision is critical, such as aerospace, medical devices, and automotive. High-precision machining tools can include a variety of cutting tools, such as end mills, drills, and inserts, as well as precision measuring instruments like micrometers and gauges.
Accessories for 4th and 5th Axis Machining
4th and 5th axis machining are advanced CNC machining techniques that allow for machining complex 3D shapes and tilted surfaces of a part without compromising precision. These techniques require specialized accessories, such as 4th and 5th-axis rotary tables and multi-axis workholding fixtures. These accessories enable the CNC machine to rotate the part along additional axes, allowing the cutting tool to access areas difficult to reach with 3-axis Machining.
Custom Tooling for Unique Manufacturing Challenges
Custom tooling is often required for unique manufacturing challenges that standard tools cannot address. This can include tools designed for specific materials, such as hard metals or composites, or for particular operations, such as deep hole drilling or micro-machining. Custom tooling can also include tools developed for specific applications, such as producing complex aerospace parts or medical devices.
Investing in Quality Tools: When and Why
The Long-Term Benefits of High-Quality Tools
Investing in high-quality tools can have significant long-term benefits. High-quality tools are typically more durable and reliable, leading to less frequent replacements and repairs. This can result in substantial cost savings over time. Moreover, high-quality tools often perform better, improving productivity and efficiency. They can help you complete your projects more quickly and achieve better results, which can contribute to the success of your business.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Premium vs. Budget Tools
While high-quality tools often come with a higher upfront cost than budget tools, considering the long-term cost implications is essential. Budget tools may seem like a cost-effective choice initially, but they may require more frequent replacements, leading to increased downtime due to tool failures, impacting productivity. On the other hand, while premium tools may need a more significant initial investment, they often offer better performance and longer lifespan, resulting in lower long-term costs.
Vendor Selection and Tool Lifespan Considerations
When investing in tools, it’s also crucial to consider the vendor and the expected lifespan of the tools. Reliable vendors often provide better customer service, including warranties and after-sales support, which can be valuable if issues arise with the tools. The expected lifespan of a tool is also an important consideration. High-quality tools often have a longer lifespan, meaning they can provide value for a more extended period, further enhancing their cost-effectiveness.
Building Your CNC Toolkit: A Step-by-Step Guide
Assessing Your Current and Future Project Needs
The first step in building your CNC toolkit is to assess your current and future project needs. This involves understanding the types of projects you’ll be working on, the materials you’ll be performing with, and the level of precision required. This assessment will help you identify the tools and equipment you need to complete your projects efficiently and effectively.
Prioritizing Purchases: A Phased Approach to Tool Acquisition
Once you’ve identified your needs, you can start prioritizing your purchases. A phased approach to tool acquisition can be beneficial, especially if you’re working with a limited budget. Start by investing in the essential tools you’ll need for most projects. As your needs and budget allow, you can gradually add more specialized tools to your toolkit.
It’s also important to consider the long-term benefits of investing in high-quality tools. While these tools may come with a higher upfront cost, they often offer better performance and longer lifespan, which can result in cost savings over time.
Keeping Up with Industry Trends and New Tool Technologies
Finally, keeping up with industry trends and new tool technologies is crucial. The world of CNC machining is constantly evolving, with technological advancements pushing the boundaries of what is possible. For example, the emergence of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and big data analytics, transforms the operations of CNC machines. These technologies allow CNC machines to communicate with each other and other systems in real time, improving the efficiency and speed of the manufacturing process.
The Future of CNC Machining Tools
Innovations in CNC Tooling
Exciting advancements and innovations are shaping the future of CNC machining. One of these is the increasing use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in CNC machining. With its ability to learn from data, make decisions, and improve over time, AI is poised to bring about a new wave of innovation in CNC machining. AI can help manufacturers predict when parts are approaching the end of their life cycles, reduce downtime, and enhance precision and productivity.
Another significant innovation is the growing use of Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR) in CNC machining. VR/AR technologies allow users to experience and interact with digital environments and objects similarly to the real world. This can be particularly useful in CNC machining, where it can help machinists visualize and plan their work more effectively.
The Impact of Automation and AI on CNC Machining
Automation and AI are having a profound impact on CNC machining. Automation drives the trend towards more ‘done-in-one’ CNC machining, particularly in high-mix, low-volume production. This is being facilitated by the increasing use of robotics in CNC machining. However, this also presents challenges, such as the need for specialized tooling and potentially higher maintenance and operating costs.
Outsource to Us at LongSheng CNC Machining
Knowing the necessary machine shop tools and equipment you need is the right step if you have a workshop and want to get things done efficiently. However, if you like something different, what you must give your trust must be worth it. If you sincerely desire the best, you should outsource to us at LongSheng CNC Machining.
By selecting us, you have placed your choosing us an assignment in reliable, capable, and experienced minds. In Machining, we have a heightened understanding of machining operations, and it is easy for you to request our services. Therefore, it does not matter your schedule. You can easily use our online quotation and deliver your quotes as your internet deems. At Rapid Direct, you are assured of quality, reasonable price, and faster lead time.
Conclusion and Checklist Summary
Recap of Must-Have Tools for Your CNC Workshop
Building a CNC toolkit is a process that requires careful consideration of your current and future project needs—essential tools for your CNC workshop range from basic hand tools to specialized CNC machining tools. The most important ones include calipers, a center punch, an edge finder, a dial, a micrometer, and a 6-scale ruler. These tools are crucial for achieving the precision required in CNC machining and can significantly enhance productivity and efficiency.
Final Checklist of Essential CNC Machinist Tools
Here’s a final checklist of essential CNC machinist tools:
- Calipers: For precise measurement of the distance between two opposite sides of an object.
- Center Punch: This tool marks the center of a point and draws the center of a hole before drilling.
- Edge Finder: To locate the edges of a workpiece.
- Dial Indicator: To measure small distances or angles with high accuracy.
- Micrometer: For exact measurements of small objects.
- 6 Scale Ruler: For taking accurate measurements in the workshop.
RemeInvesting high-quality tools can offer significant benefits, including improved performance, increased durability, and cost savings.
Next Steps: Continuing Education and Community Resources
As CNC machining continues evolving, machinists and manufacturers must stay abreast of the latest trends and technologies. This includes understanding the potential benefits and challenges of new technologies like AI, automation, and VR/AR and adapting to these changes.
Continuing education is a great way to stay updated on these trends. Many resources include online training courses, webinars, and industry publications. Participating in community forums and networking events can also provide valuable insights and opportunities to learn from other professionals in the field.
Each article in this directory can be designed to provide in-depth information, practical advice, and actionable tips for both novice and experienced CNC machinists looking to equip their workshops with the necessary tools for success.
FAQs
What are the must-have tools for a CNC workshop?
The essential tools for a CNC workshop include calipers, a center punch, an edge finder, a dial, a micrometer, and a six6-scale ruler. These tools are vital for every machining operation and can significantly enhance productivity and efficiency.
What is the difference between must-have and essential machinist tools?
While the terms may sometimes be used interchangeably, “must-have” tools typically refer to those essential for most machining operations, such as calipers and micrometers. On the other hand, “basic” tools may refer to those necessary for a beginner machinist or for more straightforward tasks.
How can I choose the right tools for my machining projects?
Choosing the right tools for your machining projects involves understanding the project’s requirements and the tools’ capabilities. The right tool can provide the best in terms of efficiency and productivity. It’s also important to consider the quality of the tools, as using high-quality tools is the first step to producing quality work.
How can I buy good machinist tools on a budget?
While good machinist tools can be expensive, there are ways to buy them on a budget. One approach is to start with a small collection of essential tools and gradually add more as your needs and budget allow. It’s also worth investing in high-quality tools, as they often offer better performance and longer lifespan, which can result in cost savings over time.
What are some recommended tools for a beginner machinist?
For a beginner machinist, some recommended tools include calipers for making accurate measurements of thickness and dimensions, edge finders for locating the edges of a workpiece, and center finders for locating the machining center on a workpiece. A dial or digital indicator is also helpful in making precise measurements.
How can I keep my machinist tools in good condition?
Keeping your machinist tools in good condition involves regular maintenance and proper storage. This includes cleaning your tools after each use, storing them in a dry and clean environment, and regularly checking them for signs of wear and tear. It’s also important to use your tools correctly to prevent damage.
What are some resources for learning more about machinist tools?
Many resources are available for learning more about machinist tools. These include online training courses, webinars, and industry publications. Participating in community forums and networking events can also provide valuable insights and opportunities to learn from other professionals in the field.


