In the vast world of manufacturing, casting technology occupies a pivotal position. It shapes parts and products of various complex shapes by heating metal or alloy to a molten state and then pouring it into a mold to cool and solidify. Among them, CI casting has become an indispensable part of the casting process with its unique material properties and wide range of applications.
In this article, we will take you through the entire CI casting process and we will also discuss the benefits of CI casting, its applications in different areas and the factors to consider when choosing a foundry to meet your casting needs.
What is CI Casting?
CI casting, the full name is Cast Iron casting, is an alloy composed of elements such as iron, carbon, silicon, etc., which is melted and poured into a pre-prepared mold. After cooling and solidifying, a predetermined shape is obtained. Dimensions and properties of the casting process. CI casting is an important type of casting process and is widely used in various industrial fields.
What are the hard conditions for CI Casting?
To produce cast iron, iron must be extracted from iron ore. The ore is smelted in a blast furnace where it is separated into pig iron and slag. The blast furnace is heated to around 1800 degrees Celsius in an oxygen atmosphere and the slag that forms rises to the top where it can be removed.
The molten pig iron below contains approximately 3 wt.% – 5 wt.% carbon. This is then mixed with iron, steel, coke and limestone.Once the impurities are selectively removed from the iron, the carbon content is reduced. At this point, silicon can be added to convert the carbon content into graphite or cementite. The iron is then cast into various shapes.
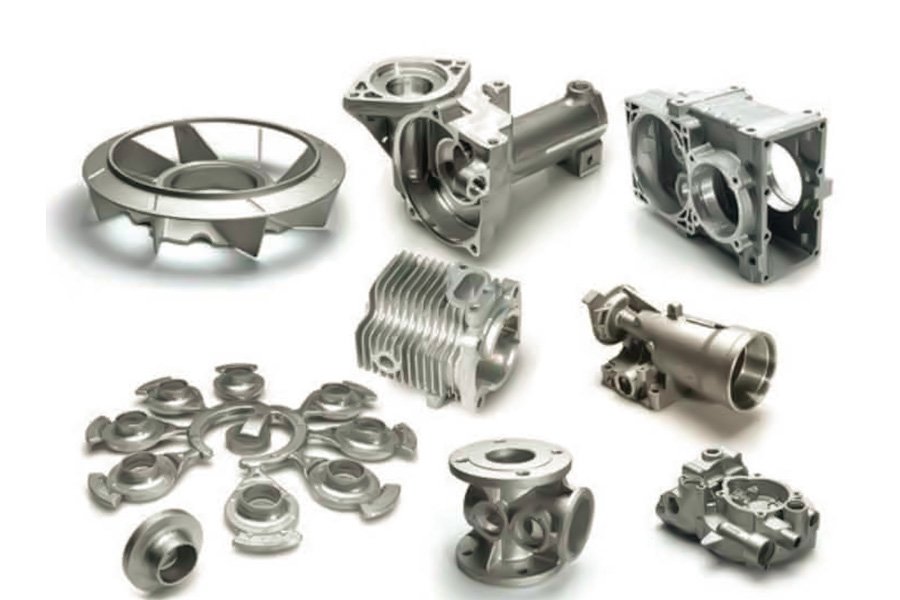

What Are The Advantages Of CI Casting?
- Design Flexibility: CI Casting can produce complex shapes with high precision and repeatability. Molds can be designed with intricate details and fine features, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Excellent Castability: Cast iron is extremely castable, which means the cast iron can easily flow into the mold and fill complex cavities without any defects. This makes it an ideal material for manufacturing products with complex shapes and thin sections.
- High strength and wear resistance: Cast iron has high strength and wear resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and wear resistance. It can withstand heavy loads and is not easily deformed under high pressure.
- Good workability: Cast iron is known for its good workability, which means it can be easily cut, drilled and shaped using conventional machining techniques. This makes cast iron products easy to post-process and customize.
- Thermal Conductivity: Cast iron has excellent thermal conductivity, which means it can transfer heat efficiently. This makes it suitable for applications requiring heat dissipation, such as engine blocks and brake discs.
- Cost-effective: CI casting is a cost-effective process, especially suitable for large-scale production. Initial tooling costs may be higher compared to other casting methods, but as production volumes increase, unit costs decrease.
What are the applications of CI casting?
Machine made
CI casting is a crucial link in the development of equipment manufacturing industry and can produce complex-shaped and large-scale castings.
It occupies a large proportion in machinery manufacturing, and is widely used in fields such as machine tools, automobile manufacturing, instrumentation, shipbuilding, oil and gas resources, and aerospace.
auto industry
A large number of key components such as automobile engines, gearboxes, and axle assemblies use castings, such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, flywheels, crankshafts, etc. With the rapid growth of the new energy vehicle market, the application of castings in the field of new energy vehicles is also expanding.
Aerospace
The aerospace field has extremely high requirements on the quality, precision and performance of castings. The casting process can meet these requirements and produce complex aerospace castings.
buildings and infrastructure
CI castings are used in the construction and infrastructure sectors to manufacture pipes, manhole covers and drainage systems. Cast iron’s durability and corrosion resistance make it suitable to withstand the harsh conditions of underground and outdoor environments.
Cookware and kitchen utensils
Cast iron cookware, such as skillets and Dutch ovens, are popular for their excellent heat retention and even heat distribution. Cast iron’s thermal conductivity allows for efficient cooking and helps preserve the flavor of your food.
energy production
CI castings are used in the energy production sector to manufacture turbine casings, wind turbine components and steam engine components. Cast iron’s high strength and thermal conductivity make it suitable to withstand the extreme conditions of power generation.
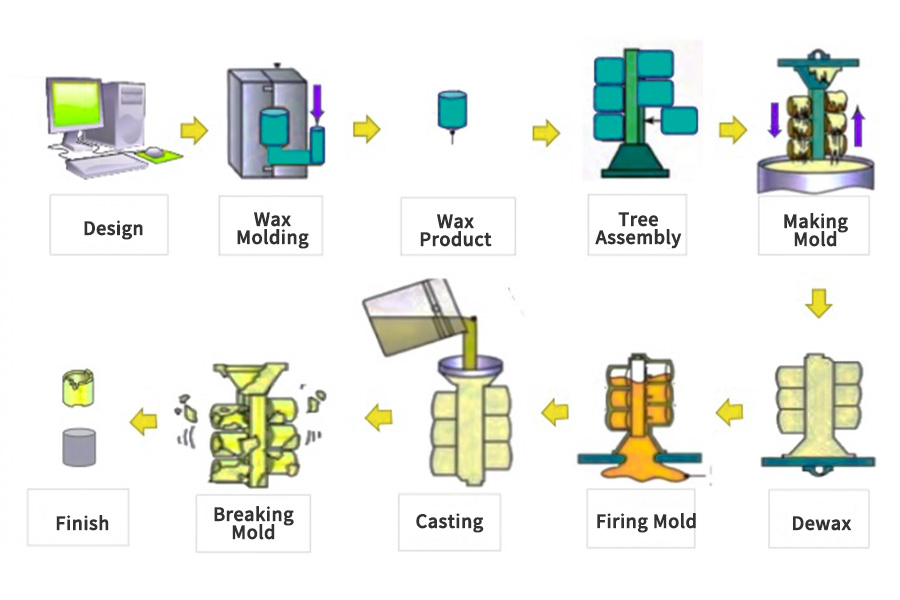
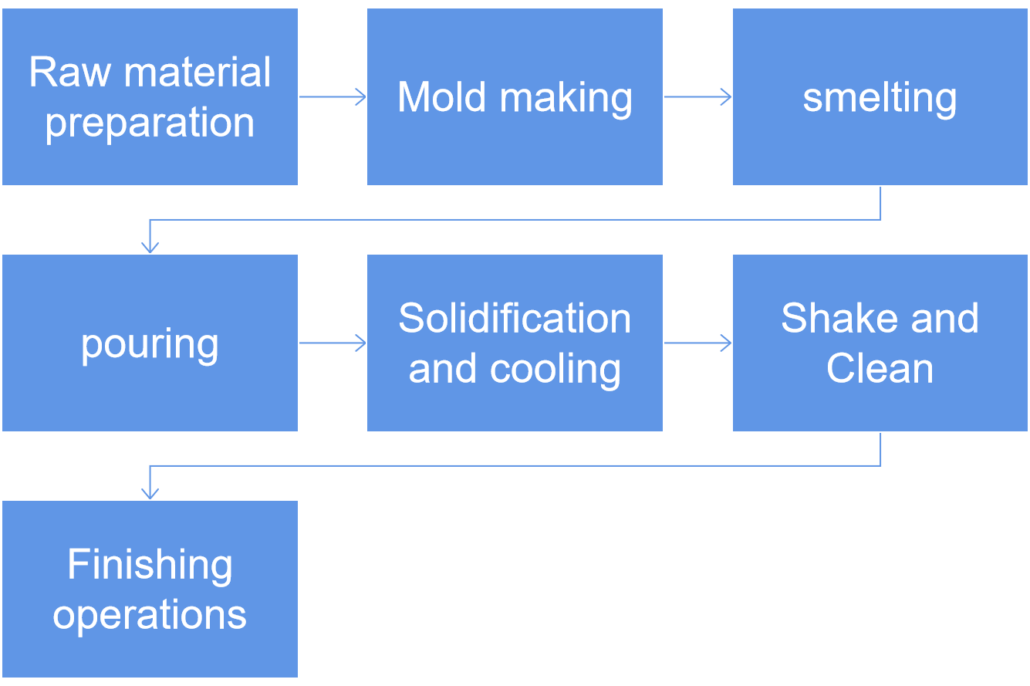
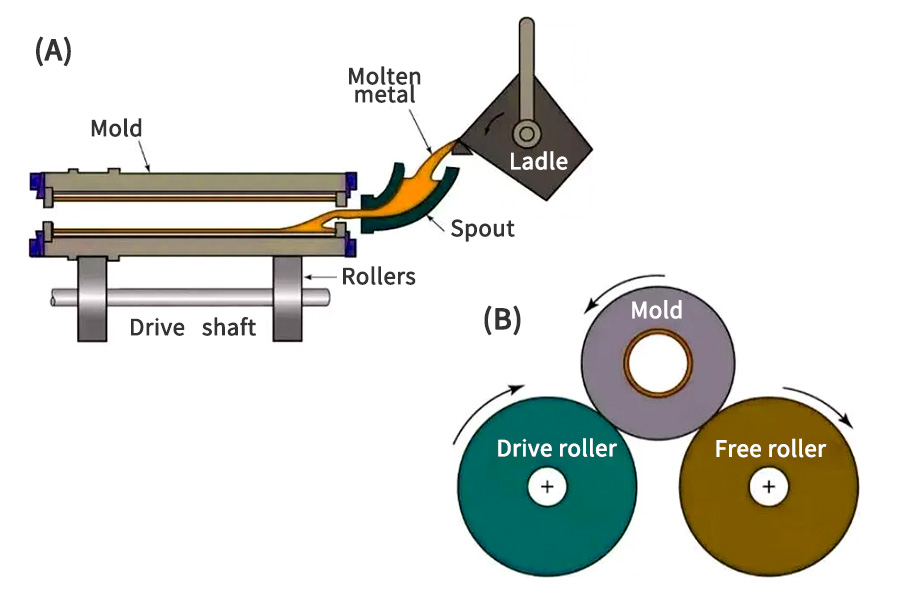
What is the CI Casting process?
- Raw material preparation:The main raw materials for cast iron casting include pig iron, scrap steel, recycled materials, etc. Select appropriate raw materials according to production needs and prepare them in strict accordance with the proportions. Raw materials are screened, cleaned and pre-treated to remove impurities and undesirable substances to ensure the quality of raw materials.
- Mold making:Mold design is carried out according to the requirements of castings, including shape, size and structure. Molds are manufactured through processes such as drawing, mold opening, mold making and debugging. The accuracy and quality of the mold have a direct impact on the quality of the casting.
- smelting:The raw materials are melted using smelting equipment such as electric furnaces and cupola furnaces. During the smelting process, the furnace temperature and smelting time need to be controlled to ensure that the metal is fully melted and pure. At the same time, depending on the performance requirements of the casting, it may be necessary to add an appropriate amount of alloying elements to adjust the chemical composition of the metal.
- pouring:Before pouring, the mold needs to be preheated and cleaned to ensure the smooth progress of the pouring process. Pour the molten iron into the mold smoothly and quickly, while controlling the pouring speed and temperature to avoid defects such as pores and inclusions.
- Solidification and cooling: After pouring, the molten iron begins to solidify and cool. The solidification process is crucial as it determines the final properties of the cast iron product. Cooling rate and the presence of alloying elements affect the microstructure and mechanical properties of cast iron.
- Shake and Clean: After the cast iron has solidified and cooled, the mold is removed through a shaking process. The shaking process involves breaking the mold to expose the cast iron product. After shaking, clean cast iron products to remove any remaining sand or other impurities.
- Finishing operations: Depending on the requirements of the final product, additional finishing operations may be performed. These operations can include machining, grinding, polishing or heat treatment. Finishing operations help achieve the required surface finish, dimensions and mechanical properties of cast iron products.
What are the types and characteristics of cast iron?
Gray Cast Iron
The most common type, gray cast iron features a graphite microstructure consisting of many small fractures. It’s called “gray cast iron” because the presence of these small fractures creates the appearance of a gray color. When gray cast iron is produced, the fractures open up to reveal the gray-colored graphite underneath the surface. Gray cast iron isn’t as strong as steel, nor is it able to absorb the same shock as steel. With that said, gray cast iron offers similar compressive strength as steel. As a result, it’s become a popular choice of metal for applications involving compressive strength.
White Cast Iron
While not as common as gray cast iron, white cast iron is another type worth mentioning. It receives its namesake from its off-white color, which is the result of iron compounds known as cementite. Like gray cast iron, white cast iron features many small fractures. The difference is that white cast iron features cementite below its surface, whereas gray cast iron features graphite below its surface. The graphite creates the appearance of a gray color, while the cementite creates the appearance of a white color. White cast iron is hard and offers excellent resistance against abrasions.
Ductile Cast Iron
Also known as nodular cast iron, ductile cast iron is a type of soft, ductile iron alloy with a high carbon content. It’s typically made with trace amounts of other compounds, including magnesium and cerium. When added, these trace compounds inhibit the speed at which graphite grows, thereby keeping the metal soft and ductile. Ductile cast iron was invented in the early to mid-1940s.
Malleable Cast Iron
Finally, malleable cast iron that easily “workable.” It’s typically created using heat treatment processes on white cast iron. The white cast iron is heated treated for up to two days, after which it’s cooled. When finished, malleable cast iron can be bent and manipulated to achieve unique shapes and sizes.
| Cast iron type | Carbon (C) | Silicon (Si) | Manganese (Mn) | Sulfur (S) | Phosphorus (P) |
| Grey Cast Iron | 2.5-4.0 | 1.0-3.0 | 0.2-1.0 | 0.02-0.25 | 0.02- 1.0 |
| Ductile Cast Iron | 3.0 -4.0 | 1.8-2.8 | 0.1-1.0 | 0.01- 0.03 | 0.01-0.1 |
| White cast iron | 1.8-3.6 | 0.5-1.9 | 0.25-0.8 | 0.06-0.2 | 0.06-0.2 |
| Malleable cast iron | 2.0-2.9 | 0.9-1.9 | 0.15-1.2 | 0.02-0.2 | 0.02-0.2 |
What are the characteristics of cast iron?
| Cast iron type | Cast iron Properties |
| Grey Iron | Good machinability; Good thermal conductivity; High compressive strength; Low tensile strength; Good resistance to galling and wear; Brittle |
| Ductile Iron | High ductility; High strength |
| White iron | High compressive strength; Difficult to machine; Good hardness; Resistance to wear |
| Malleable iron | High ductility; Tougher than gray cast iron; Be twisted or bent without fracture; Excellent machining capabilities |
What are the factors that affect the performance of cast iron?
Design craftsmanship
During design, the geometry and size of the cast iron parts need to be determined based on the working conditions and metal material properties. In addition, the rationality of the design must be considered from the perspective of casting alloy and casting process characteristics to avoid or reduce defects such as component segregation, deformation, and cracking of cast iron parts.
Casting process
Reasonable casting process is the key to ensuring the quality of cast iron parts. This includes selecting appropriate parting surfaces, shapes and core-making methods based on the structure, weight and size of the cast iron parts, as well as the characteristics and production conditions of the casting alloy, and rationally setting up the chilled iron, risers and gating systems. In addition, cast iron manufacturers need to formulate reasonable process operation specifications to improve the technical level of workers so that the process regulations can be correctly implemented.
Raw material quality
The quality of the metal charge directly affects the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the cast iron parts. If the charge contains too many impurities or harmful elements, defects such as pores, pinholes, and slag inclusions will occur in cast iron parts.
chemical composition
※Carbon: Carbon is the most basic component of iron castings and directly affects the mechanical properties of castings. Too high or too low carbon content may lead to quality problems in castings, such as graphite floating, shrinkage and porosity, etc. Therefore, it is necessary to reasonably select the carbon content according to castings with different quality requirements.
※Silicon: Silicon is a beneficial element in castings, which can promote graphitization and improve the plasticity, heat resistance and corrosion resistance of castings. However, too high silicon content will also reduce the anti-wear performance of castings.
※Manganese: An appropriate amount of manganese helps to increase the solidity, strength and wear resistance of castings, but too high a manganese content will deteriorate the mechanical properties.
※Sulfur and phosphorus: Sulfur and phosphorus are often considered impurity elements, which can reduce the mechanical properties and stability of castings. Therefore, it is necessary to minimize the sulfur and phosphorus content during the casting process.
cooling rate
Factors affecting the crystal structure of cast iron are the solidification and cooling conditions of the casting. If you cool it quickly, you get white iron, if you cool it slowly, you get gray iron. The cooling rate of cast iron depends on the type of casting pattern and the thickness of the casting.
Difference Between Cast Iron and Cast Steel
| Difference | Elaborate |
| castability | Cast iron is a fairly simple material because it pours smoothly and shrinks far less than steel. Because it flows so well, cast iron is an excellent metal for construction or ornate wrought iron structures such as fences and street furniture. |
| preservative | Iron is superior to steel when it comes to corrosion resistance. But this does not mean that both metals have the potential to corrode. Both metals will oxidize in moist environments if not protected. They will eventually rot completely. It is recommended that both steel and iron castings be coated to prevent this. |
| cost | Cast iron is generally less expensive than cast steel due to the lower price of materials, energy, and labor required to create the final product. Although raw steel is more expensive, prefabricated steel is also available. These include plates, rods, rods, tubes and beams. |
CI Casting vs. Other Casting Methods
- Sand Casting: Sand molds are made using foundry sand and a sand binder and are used to produce large and complex-shaped castings. Sand casting is one of the most commonly used methods in the production of cast iron castings, and is suitable for manufacturing gray cast iron, ductile iron and other castings.
- Investment casting: Use fusible material to make a pattern, cover the surface with refractory material and then melt the pattern to form a mold without parting surfaces. It is suitable for producing high-precision, complex-shaped castings. Although investment casting is mainly used to produce precision castings, it can also be used to produce cast iron castings, especially those that require high precision and complex shapes.
- Die casting: Using high pressure to quickly press molten metal into the mold cavity to form castings, it is suitable for mass production of high-precision, high-quality castings. The die-casting process is usually used to produce non-ferrous metal castings, such as aluminum alloys, zinc alloys, etc., but it can also be used to produce cast iron castings under certain conditions, but it is relatively rare.
- Metal mold casting:Casting is performed using a metal mold that can be used repeatedly and is suitable for mass production of castings with complex shapes and high precision requirements. Metal mold casting is also used in the production of cast iron castings, especially when high precision and high quality castings are required.
Why are cast iron castings so popular?
Among materials, cast iron castings are the most common in metal foundries due to their excellent casting properties. Cast iron castings show great advantages in many applications due to their series of excellent properties.
①cast iron is extremely castable due to its high carbon content and high silicon content. This material can be cast under different heat treatments and processing techniques. Therefore, it can cast different products in various styles and designs.
② cast iron generally has good fluidity, small shrinkage, low melting point, and is easy to fill molds. It is a good pressure-resistant material with large static load and wear resistance.
③cast iron is extremely durable. Therefore, it is ideal for outdoor street furniture applications.
④cast iron is divided into different types with typical properties so that foundries can use it flexibly in a variety of applications.
What are the common challenges in CI casting?
★Shrinkage and Porosity: Shrinkage and porosity are common defects in CI casting. Shrinkage occurs during the solidification of molten iron, causing voids or shrinkage cavities in the cast iron. Porosity is the presence of small voids or voids in cast iron, which affects its mechanical properties.
★Inclusions and impurities: Inclusions and impurities (such as sand, slag, or oxides) can become trapped in cast iron during the casting process. These inclusions weaken the cast iron and reduce its mechanical properties.
★Warping and deformation: Cast iron has a high coefficient of thermal expansion, which can cause warping and deformation during cooling and solidification. Warping and deformation can cause dimensional inaccuracies and affect the functionality of cast iron products.
★Mold and pattern mismatch: Mold and pattern mismatch can lead to casting defects such as insufficient castings or incomplete castings. It is important to ensure that the mold and model are properly aligned and matched to prevent such defects.
★Heat Treatment and Machining: Cast iron requires careful heat treatment and machining to achieve the desired mechanical properties and surface finish. Improper heat treatment or machining can result in brittleness, excessive hardness, or poor dimensional accuracy.
How to improve the quality of CI castings?
Improving the quality of CI castings requires starting from many aspects:
- Optimize casting process parameters, such as temperature, pressure, time, etc., to ensure that the casting process is stable and controllable.
- Strengthen the quality control of raw materials to ensure that the alloy elements such as iron, carbon, and silicon used meet standard requirements.
- Improve the level of mold design and production to ensure accurate mold size and shape.
- Strengthen the management of casting post-processing processes, such as cleaning, heat treatment, etc., to eliminate casting defects and improve its performance.
- Strengthen employee training and skill improvement to improve the professionalism and operational skills of casting operators.
Reasons to choose Longsheng as CI casting manufacturer
No matter what type of casting process service you need, we will help you. With our expertise and industry-leading technology, we can provide you with the highest quality castings.
- Multi-material processing: We have the ability to handle a variety of materials, no matter which material you need to process, we can provide professional solutions.
- Custom Services: Provide custom solutions according to customer design requirements and specifications to ensure that the castings meet their unique needs.
- Competitive price: We provide competitive price and cost-effective solutions to ensure that customers get the greatest advantage in cost control.
- Rapid delivery: We have an efficient production process and flexible production planning that enables us to timely deliver customer orders and meet urgent project needs.
Longsheng ensures the quality of your casting parts through ISO 9001:2015, ISO 9001:14001 and IATF16949.At Longsheng, we can manufacture castings according to your business needs, whether cast iron, steel or nickel alloy. Click here to contact us today.

Summary
CI casting (cast iron casting) is a widely used metal casting process that offers several advantages in terms of design flexibility, strength, durability and cost-effectiveness. It is a versatile and reliable choice for a variety of applications in industries such as automotive, machinery, construction and cookware.Understanding the CI casting process, its benefits and challenges is critical to making informed decisions regarding cast iron products. Quality control measures and careful process monitoring play a vital role in ensuring the production of high-quality cast iron products.
While CI casting has its unique advantages, it is important to consider other casting methods and their suitability for specific applications. Sand casting, investment casting, die and permanent mold casting, metal mold casting are some of the alternatives worth exploring.We hope this guide provides you with valuable insights into CI casting and provides you with the knowledge to understand and appreciate this fascinating casting process. Whether you are a manufacturer, designer, or just curious about the world of casting, CI Casting offers endless possibilities for creating durable and reliable cast iron products.Visit our Instant Quote Engine to get a free, no-obligation quote in minutes.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. LongSheng makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through LongSheng’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please contact to our for more information.
Team LongSheng
This article was written by various LongSheng contributors. LongSheng is a leading resource on manufacturing with CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, injection molding,metal stamping and more.
FAQs
What are the basic principles of CI casting?
The basic principle of CI casting is to melt an alloy of iron, carbon, silicon and other elements (i.e. cast iron) into a liquid state, and then pour it into a pre-prepared mold. After it cools and solidifies, it is taken out and cleaned to obtain a predetermined shape and size. and performance castings.
What are the common quality problems in the CI casting process and their causes?
① Flash or burrs on castings: This may be caused by improper storage of gypsum powder, excessive stirring and vacuuming time, improper control of steel cup heating time, etc. ② Incomplete casting: It may be caused by the wax tree trunk being too small, the wax mold not being completely burned, the temperature during casting being too low or the metal weight being insufficient. ③Rough surface of castings: Reasons may include unclean burning of the wax mold, excessive furnace temperature, uneven mixing of powder and water, etc. ④ Castings have micropores: This is usually related to the metal temperature being too high, the steel cup temperature being too high, the proportion of old metal in the metal being too high, or too much flux added. ⑤ There are particles on the surface of the casting: It may be caused by the steel pot entering the furnace too quickly, the oven heating up too quickly, abnormal particles in the metal, or the rust in the steel pot not being cleaned.
Is cast iron heavy?
Cast iron is quite heavy. It is a dense and strong material. However, the weight of cast iron will vary depending on the shape and size of the object. For example, cast iron pans are quite heavy compared to aluminum or stainless steel pans. On the other hand, weight can also be an advantage. This is because it ensures even heat distribution during cooking.
What types of casting production is suitable for the CI casting process?
CI casting process is widely used in the production of various types of castings due to its low cost and excellent performance. Especially for those castings with complex shapes and low dimensional accuracy requirements, such as engine blocks, crankcases, machine tool beds and other heavy components, the CI casting process has obvious advantages.


