Introduction to Pad Printing
Pad printing, also known as tampography, is a printing process that has become increasingly important to industrial applications over the years. In the early 1970s, the process began sagging market shares over hot stamping and screen printing, particularly in printing areas where other methods showed no transactions or could not. This includes printing on irregular shapes and surface wells and assembling complicated substrates at a reasonable speed.
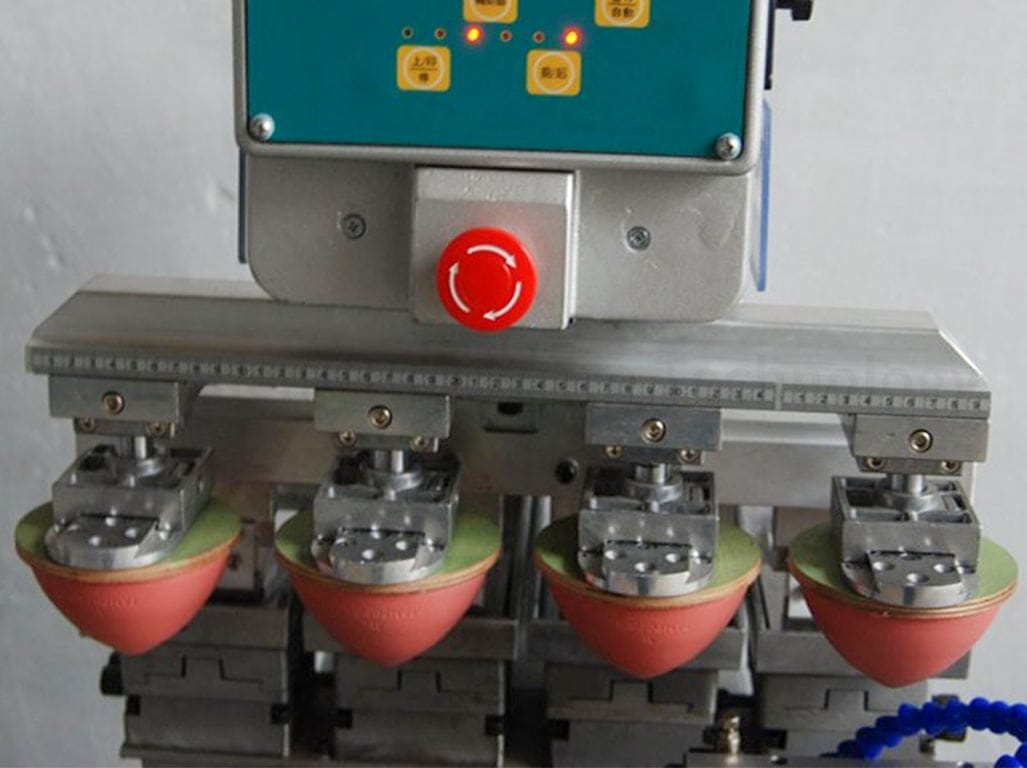

The unique aspect of pad printing lies in its ability to transfer a 2D image onto a 3D object. This is accomplished using an indirect offset (gravure) printing process that involves an image being transferred from the cliché via a silicone pad onto a substrate. The silquicklyad can quickly adapt to irregularly shaped surfaces, allowing pad printing on almost objectify. This versatility sets pad printing apart from conventional printing methods, such as silk screening, which is limited to flat or evenly rounded surfaces.
The Evolution of Pad Printing: From Origins to Modern Applications
The roots of pad printing can be traced back more than 200 years. Originally, pad printing was done by hand, with the first offset type of hand printing using a bag of soft gelatin material to transfer the image. Over time, the process has evolved significantly. For instance, printing plates were made from wood in the early days, and the photos were hand-printed. Nowadays, printing plates are made from various materials such as hardened steel and plastic, engraved photochemically or laser-engraved.
Decoding Pad Printing: A Basic Overview
Understanding how pad printing works involves understanding the components of the pad printer. Pad printers come in different designs, setups, and printing styles, but they all contain nearly the same components. The process involves an image being transferred from the printing plate (cliché) via a silicone pad onto a substrate (surface to be printed). The unique properties of the silicone pad enable it to pick the image up from a flat plane and transfer it to a variety of surfaces.
Comparing Pad Printing to Other Printing Techniques
Compared to other printing techniques, pad printing offers several unique advantages. For instance, it can efficiently transfer images on complex geometries, from printing on three-dimensional plastic parts to embossed or useless, or even golf balls. The process uses height compensators for ink cups to print at different levels in one printing run, offering versatility not commonly found in other printing methods.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Pad Printing Process
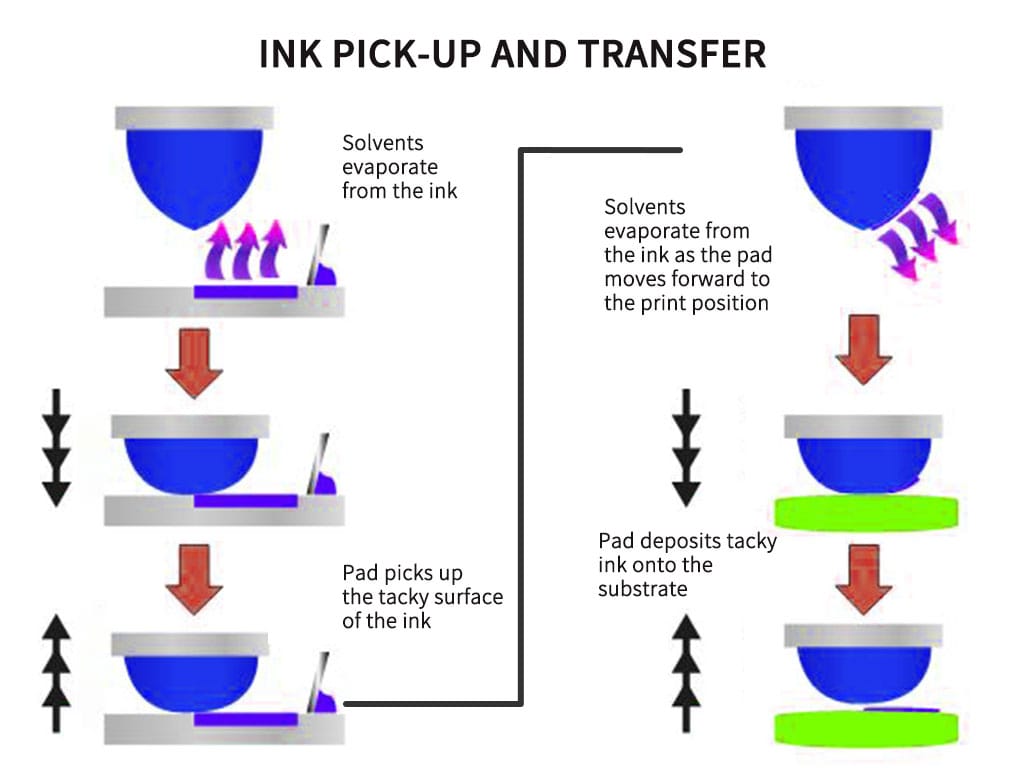
Ink Filling: The process begins with the ink cup sitting over the engraved artwork printing plate, covering the image, and filling it with ink. This is known as the home doctor’s.
Ink Drcter’s A “doctor’s” floods the etched image with only ink, and only then does the doctor’s blade remove the flat printing plate, leaving a deposit of ink in the etched area only.
Image Transfer: The silicone pad then lifts the ink from the etched image and transfers the image directly onto the surface to be printed. The shape of the silicone pad allows the ink to release onto the product to be decorated, and the silicone pad moves back to its ” Criticalome” position, ready for another print cycle.
Critical Components of Pad Printing Detoxines
Padto successfully delivers a print to a substrate: the plate, the ink cup, and the pad.
The Plate: The plate, or cliché, is etched with an image. The print quality can be influenced by the plate used. Leave. The cup houses the ink as it brushes over the etched plate, leaving a minuscule amount of ink in the etch.

The Pad: The printing pad is the delivery system where a somewhat soft silicone material is pressed onto the ink-filled etch to pick up the image and moved over the substrate, where it is pressed again to transfer the image. The hardness of the image complexity and the object’s dimensions depend on these factors.
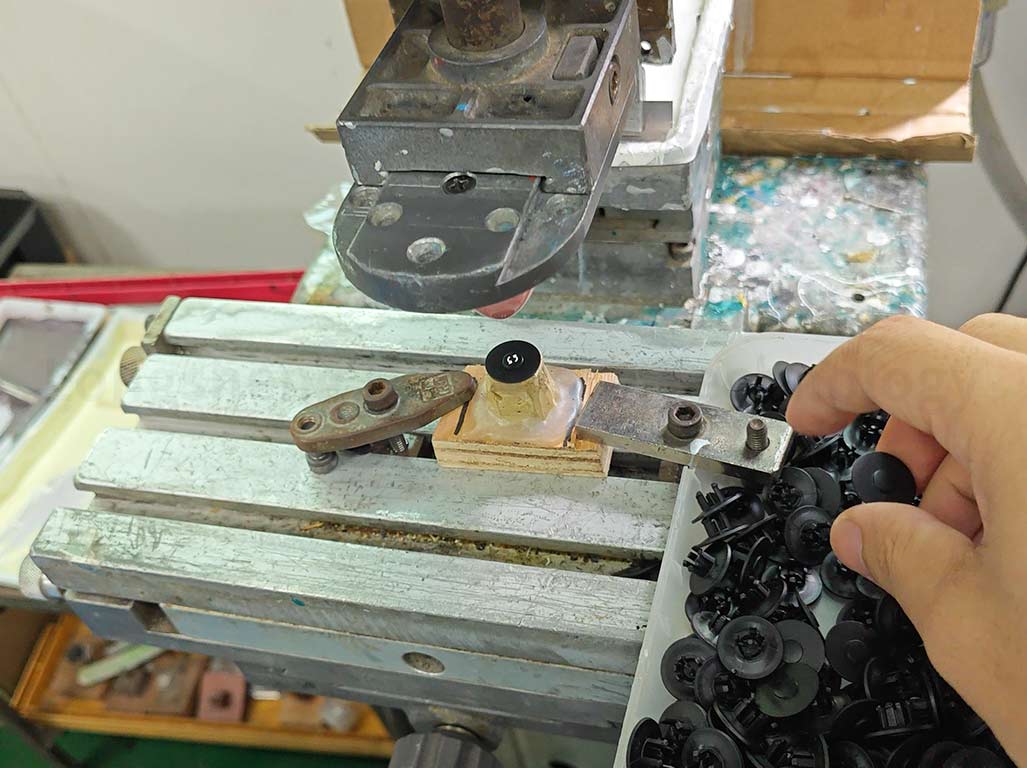

Understanding the Role of the Silicone Pad in Pad Printing
The silicone pad plays a crucial role in the pad printing process. It picks up the image from the flat plane of the cliché and transfers it to various surfaces, including those with irregular shapes. The unique properties of the silicone pad enable it to wrap around or adapt to the shape of the part without distorting the image, given some image size restrictions. The hardness of the pad can influence its performance, with more complex pads typically performing better. However, a hard pad may be impractical in some applications, such as when using a low-power machine or printing on a delicate item.
Advantages of Pad Printing
Teility of Pad Printing on Various rials
The silicone pad used in the pad printing app can be used on different surfaces to print on almost any object. This includes three-dimensional plastic parts, embossed or etched surfaces, and golf balls. The process can also use height compensators for ink cups to print at different levels in one printing run, further enhancing its versatility.
High-Quality and Durable Prints: The Strength of Pad Printing
Pad printing is known for delivering high-quality and durable prints. It provides exceptional image clarity and resolution, even on unusually shaped and irregular objects. The process is very accurate and offers tight color-to-color and artwork repeatability. Various ink compositions can be used in pad printing, including one-component ink for thermoplastics and two-component ink (ink mixed with a hardening chemical) for objects that will experience chemical or high-stress exposure.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency in Pad Printing
Pad printing is not only versatile and capable of producing high-quality prints, but it is also cost-effective and efficient. It is a fast, quick-drying process that adjusts ink coverage, density, and evaporation at each step. The setup costs for pad printing are relatively low, and the process is easy to learn. The equipment used in pad printing is also space-efficient, making it a practical choice for many businesses.
Applications of Pad Printing
Pad Printing in the Medical Industry: Precision and Safety
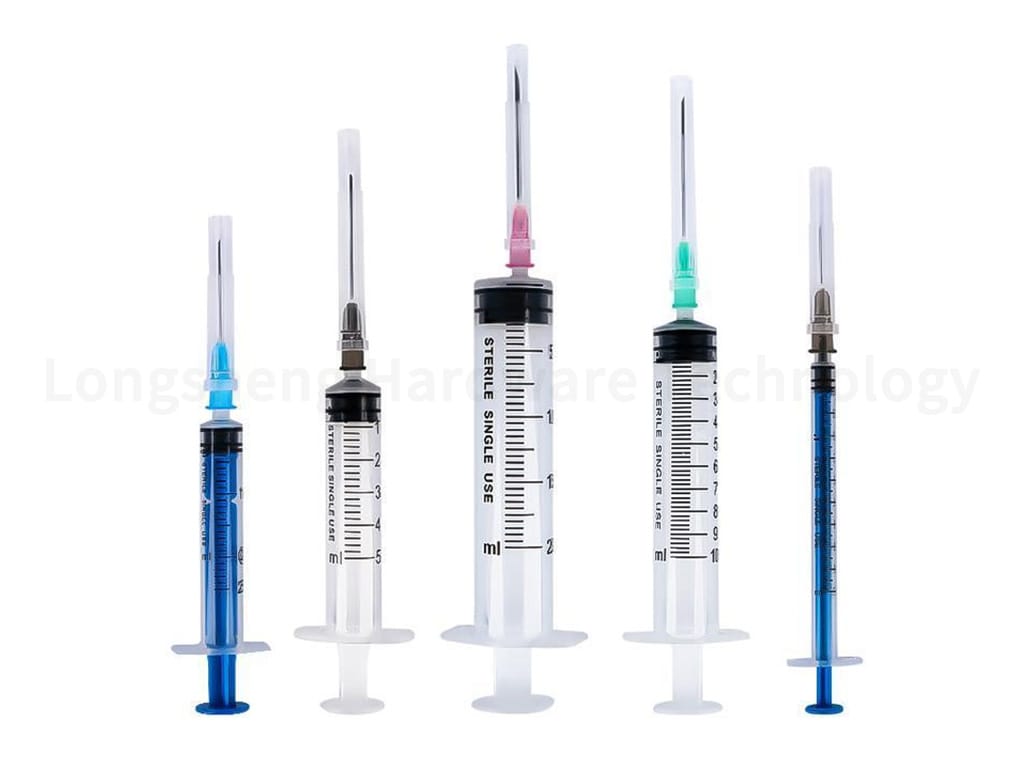
In the medical industry, pad printing is used for marking medical devices. These markings must be precise, legible, and durable, often containing essential safety instructions or identification information. The markings must not rub off, wash off, or fade, ensuring the information remains intact for the device’s lifespan. This is where the precision and durability of pad printing come into play. The process can handle the high degree of precision required, and the special inks used in pad printing can withstand the rigorous cleaning and sterilization processes that medical devices often undergo.
Automotive and Electronics: Enhancing Product Branding with Pad Printing

Pad printing is also widely used in the automotive and electronics industries. It prints logos, control labels, and other information on various parts and components. In the automotive sector, pad printing prints on parts such as switches, buttons, and additional interior and exterior components. The ability of pad printing to print on irregular and curved surfaces makes it ideal for these applications. In the electronics industry, pad printing prints on remote controls, casings, and circuit boards.
The Role of Pad Printing in Consumer Goods and Promotional Items
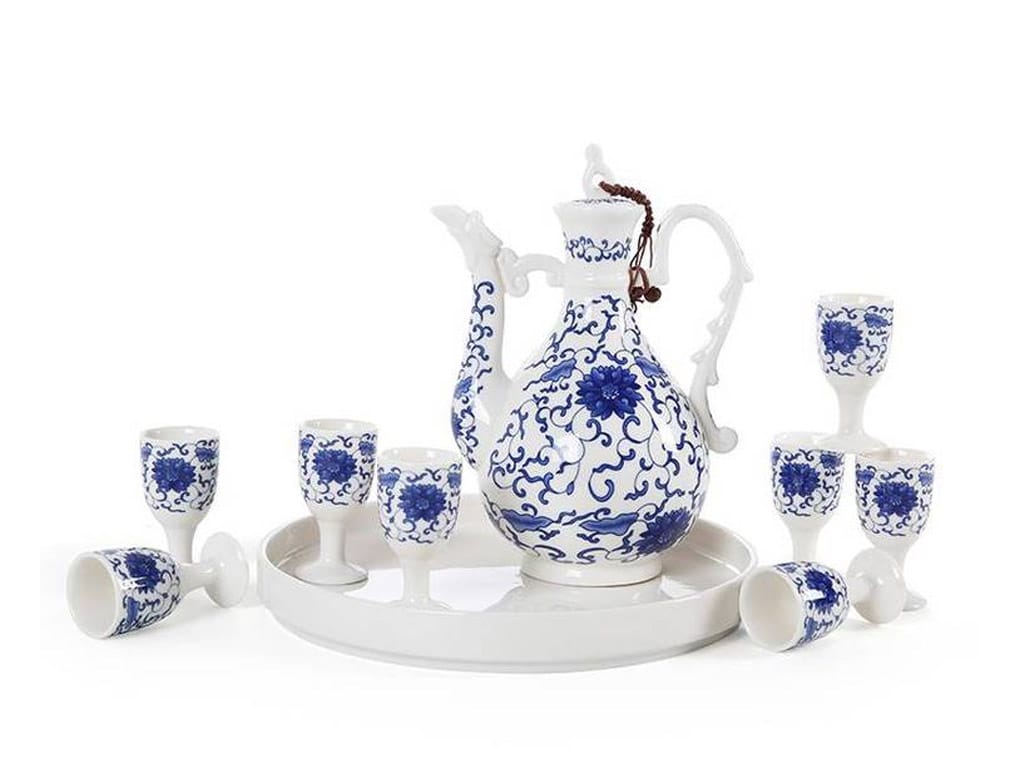

In the consumer goods industry, pad printing prints logos, instructions, and decorative designs on various products, including toys, appliances, and sports equipment. The process is also used extensively in producing promotional items, where it is used to print company logos and other branding elements on items such as pens, keychains, and mugs. Pad printing’s versatility, ability to print on a wide range of materials, and ability to deliver high-quality, durable prints make it an ideal choice for these applications.
Technical Considerations in Pad Printing
Choosing the Right Equipment and Materials for Pad Printing
The quality of the equipment used in pad printing can significantly influence the quality of the final print. High-quality equipment can facilitate high-quality printing, and it’s also essential to consider automation, which can enhance productivity and reduce the risk of errors. The type of pad used also plays a crucial role in the success of the printing process. Pads come in various sizes, shapes, and mechanical properties, and choosing the right one for your project can influence the success of the printing. Larger pads, for example, have a lower probability of distortion, minimizing deformation during printing1.
The Importance of Ink Quality and Mixing in Pad Printing
The quality of the ink used in pad printing is another critical factor. Compared to screen printing, the theoretical ink lay down in pad printing is much less, and inks formulated for screen printing applications are not suited for pad printing due to their lack of opacity. Actual pad printing is nearly four times tunavaiunavailable; mixing inks may be necessary, and inks may be required to mix inks. This should be done carefully, using the right technology, tools, and experience to achieve the target color.
Addressing Common Printing Errors and Solutions
Despite the best efforts, errors can occur in pad printing. One common issue is excessive pad pressure during printing, which can lead to over-compression and cause split pads. This can be avoided by adjusting the downstroke and usually allowing the ink to work. Regular machine checks can also help identify and rectify mechanical faults that may lead to excessive pad pressure.
Innovations and Trends in Pad Printing
Eco-Friendly Advances in Pad Printing Technology
One of the significant trends in the printing industry is the shift towards more eco-friendly practices. This includes the use of environmentally friendly inks and materials, as well as energy-efficient printing machines. The goal is to reduce the environmental impact of the printing process while still delivering high-quality results. This trend Includes consumer demand for products and practices and regulatory pressures.
The Future of Pad Printing: Emerging Applications and Technologies
The future of pad printing looks at points pplicatadvancements ions. For instanadvancements ce, advancements in automation and digital technology are making the pad printing process more efficient and precise. These technologies allow for faster printing speeds, higher print quality, and greater flexibility in the types of materials withersatechnologiesan be printing.
Moreover, integrating pad printing with and h other and r tech, log, which used to be used as 3D printing, opens new possibilities. For example, pad printing can add detailed color prints to 3D-printed objects, enhancing their aesthetic appeal and functionality.
Customization and Personalization: The New Frontier in Pad Printing
Another significant trend in pad printing is the increasing demand for customization and personalization. Consumers today want products that are unique and tailored to their preferences. This trend drives the need for printing technologies to accommodate small batch sizes and highly customized designs.
In response, pad printing offers greater fleadvancements xibiladvancements and adaptability. For instance, digital pad printing technology advancements allow for easy design changes and quick setup times, making it ideal for customized and personalized printing applications.
Challenges and Limitations of Pad Printing
Overcoming Color and Registration Challenges in Pad Printing
One of the main challenges in pad printing is color and registration. Pad printing equipment is limited in the number of colors a machine can print, and machines with four to six colors can be challenging to register every color on the part. This is because each color needs to be applied separately, and aligning (or registering) these colors can be difficult, especially for complex designs. However, advancements in Four Color Pad Printing systems are helping to achieve superior print quality, accuracy, and color registration.
Addressing the Speed and Scale Limitations of Pad Printing
Another limitation of pad printing is related to speed and scale. While pad printing is efficient for small-scale production and complex designs, it can be time-consuming for large-scale production and large image sizes. For instance, image sizes larger than 150mm in diameter pose a challenge for printing equipment. However, devices such as pad sliding devices, rotary or shutter tables, etc., are used for heavy-duty purposes, helping to overcome these limitations.
Maintenance and Durability of Pad Printing Equipment
The maintenance and durability of pad printing equipment can also be a challenge. The printing pad is a crucial component of the printing process. Therefore, choosing hard essentials, pointed, and large transfer pads in color tampo pad price pad is essential. The pad may cause deformation. Thus, the pad may cause distortions caused by the pad during printing.
Case Studies and Industry Insights
Success Stories: Innovative Uses of Pad Printing Across Industries
Pad printing has been successfully applied across various industries due to its versatility and precision. For instance, in the medical sector, pad printing is used for equipment and products such as prosthetics, tubes, IV bags, syringes, and casings for identification and traceability purposes. The process is typical because of the need for strict precision and pad-printed mePad printing is used in cal Pad printing is used ints are always Pad printing is used for non-toxicity.
In the automotive industry, pad printing is used fitslabiitsg and, which allows it, sich allows I allow it, which enables it for interiors, exteriors, and underhood components due to the flexibility needed to tackle the different shapes and sizes of automotive parts. Examples of motor parts marked with the process include radiators and batteries.
Moreover, pad printing has found its place in the consumer appliances industry, where it is used for printing on various products, enhancing their aesthetic appeal and providing necessary information.
Expert Interviews: Tips and Tricks for Optimal Pad Printing Results
Experts in pad printing often emphasize the importance of choosing the right equipment and materials, maintaining the equipment properly, and using high-quality inks. They also highlight the need for proper training and understanding of the pad printing process to achieve optimal results. For instance, understanding how to adjust the downstroke and allow the ink to work can help avoid common issues like excessive pad pressure during printing.
Market Analysis: The Demand for Pad Printing Services Globally
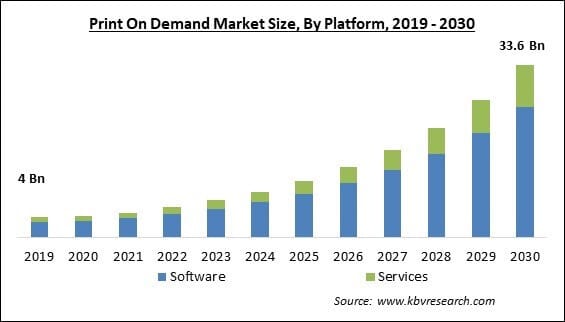
The demand for pad printing services is expected to grow, driven by print industries. The growth of medic industries, auto consumer goods, and electronics industries, where pad printing is widely used, will likely drive the demand for these services further. Moreover, trends such as the increasing demand for customization and personalization, the shift towards more eco-friendly practices, and the integration of pad printing with other technologies like 3D printing are expected to shape the future of the pad printing market.
Pad Printing vs. Screen Printing: Which is Right for You
When choosing between pad printing and screen printing, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your project. Here’s a synthesized comparison based on the provided key points:

Pad Printing
- Versatility and Detail: Pad printing is highly versatile and can transfer a 2-D image onto a 3-D object, making it suitable for printing on complex surfaces and materials such as polypropylene, Delrin, Acetal, or Urea.
- Acceptable Resolution: It offers superior resolution and can capture fine details, which is particularly beneficial for small images or intricate designs.
- Material Compatibility: Pad printing, including delicate and mechanically sensitive products, can be used on nearly any material.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It is often more cost-effective for small to medium print runs and requires minimal setup time, which is advantageous for short production runs or quick turnarounds.
- Color Limitations: However, pad printing is generally limited to fewer colors, and achieving precise registration can be challenging, especially for multi-color designs.
- Speed and Automation: While pad printing is relatively quick for small to medium production runs, it might be less efficient for high-volume production due to the individual transfer process for each print.
Screen Printing
- Large and Simple Designs: Screen printing is ideal for large images on flat surfaces, large two-sided images on cylindrical al Paris are s, and opaque images againsibstratesis.
- Ink Opacity: This method generally offers generalizable licensing on both flat and sscenting. Typically, screen printing is less expensive than pad printing, which can be a significant factor when budgeting for large print runs.
- Limitations on Surface Complexity: Screen printing is unsuitable for concave or highly irregular surfaces and generally cannot capture the sharp edges and finer details offered by pad printing.
- Color Complexity: If multiple colors are required, screen printing can become expensive as each color has to be applied separabetween pad printings
Choosing the Right Method
The decision between pad printing and screen printing should be based on the size and complexity of the design, the type of surface to be printed on, the number of colors involved, and the production volume. Pad priOn items screen prescreen printing noting with intricOnr objects wOn. Scscreen printing reen print screen printing thing, on the other hand, is more suitable for larger prints on flat surfaces or textiles, such as shirts, where a high-quality, sharp image is hesperidin summary, pad printing excels in precision and versatility for complex surfaces and detailed designs. In contrast, screen printing is more cost-effective for more extensive, simpler designs on flat or cylindrical surfaces.
Conclusion
Pad printing is a process that transfers 2D images engraved on printing plates to objects of different dimensions and sizes. It is highly accurate, precise, and efficient. However, choosing the best materials and thoroughly understanding the depth before, this article talked in-depth about the process, giving you a comprehensive understanding.
LongSheng offers a wide range of finishing services for your needs. If you need pad printing for prior high-volume production, you can contact us to request a quote today.
FAQs
1. What is the best pad to use for pad printing?
You’ll want to print with the giant pad possible that fits your image, part, and machine-parameterized image. It resembles the printed image, and many pads are designed for specific applications.
2. How does pad printing work?
Pad pPadhy or tampo printing, is an indirect,ct ofPadPa, d process where a silicon pad takes a 2-D image from a laser engraved (etched) printing plate (also called cliché) and transfers it to a 3-D obproducersocess making it efficient for all kinds of complex-shaped products such as curved (convex), hollow (concave), cylindrical, spherical, compound angles, textures, etc.
3. How fast is a pad printing machine?
A typical semiautomatic 1-color pad printing machine gives 1000 impressions per hour, tempered by the fixture and the speed of the operator who loads and unloads parts. A typical 2-color pad printer gives about 600 impressions per hour. Screen printing is generally capable of screen printing is usually photographic image producing photographic images, both black-and-white and full-color. Photo-quality pad printing is among the most challenging of pad printing applications, particularly when attempting a high-resolution reproduction, but the results can be pretty impressive.
5. How long does a printing plate last in pad printing?
The printing plate should last between 50,000 and 100,000 doctoring. Doctoring is when the ink cup passes on the printing plates. The longevity of the printing plate depends on factors such as printing plate materials, with steel being more durable than plastic, and the engraving method, with laser plate-making being more lasting.
6. How long does a pad printing pad last?
The lifespan of pad printing pads depends on how “rugged” a surface you’re printing on. A pad printing pad should last between 50,000 and 100,000 impressions.
7. What affects the longevity of the printing pad in pad printing?
Several variables, such as stray grits, improper pad use, and careless machine operation, affect the printing pad’s longevity.
8. What is the accuracy level of the pad printer?
The pad printer transfers images onto objects with the highest photographic accuracy. It adds accurate prints to critical things with line definition down to .0001 inches (25µm).
9. How thick is the pad printing’s ink?
The print job’s specific requirements determine the ink’s thickness in pad printing. The ink needs to be thick enough to provide good coverage and adhere well to the substrate but not so dense that it causes problems with the printing process. The exact thickness will depend on factors such as the type of ink used, the substrate material, and the printing conditions.


