Computer Numerical Control (CNC) milling is a manufacturing process that involves the use of computer-controlled machines to remove material from a workpiece to create a desired shape. This process is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and many others, due to its versatility and accuracy. The CNC milling process involves several dimensions that are critical to the success of the operation. In this article, we will explore these dimensions in detail.
Dimension 1: Machine Setup
Machine setup is the first dimension of CNC milling operations. It involves the installation of the workpiece, selection of cutting tools, and programming of the machine. The workpiece is installed on the machine bed using clamps or vises to hold it in place during the milling process. The selection of cutting tools is based on the material and shape of the workpiece. The programming of the machine involves the use of Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) software to create a tool path for the cutting tools. The tool path is a sequence of instructions that guides the cutting tools to remove material from the workpiece.
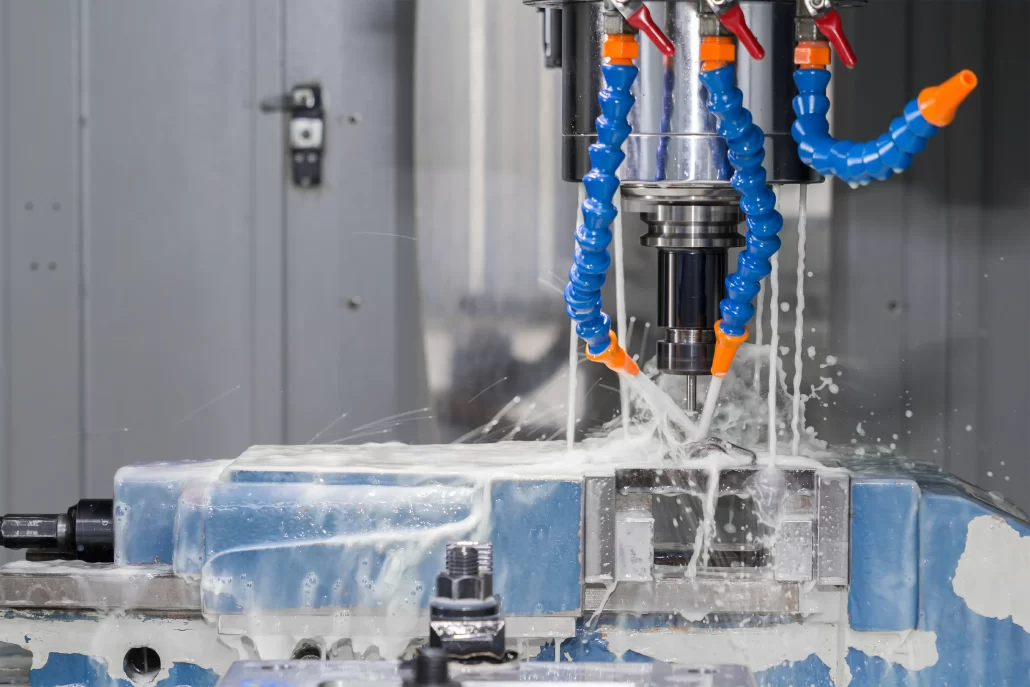

Dimension 2: Material Removal
Material removal is the second dimension of CNC milling operations. This dimension involves the actual cutting of the workpiece. The cutting tools move along the programmed tool path to remove material from the workpiece. The material removal can be done in various ways, such as roughing, finishing, and drilling. Roughing is the process of removing the bulk of the material from the workpiece, while finishing is the process of removing the remaining material to create a smooth surface. Drilling is the process of creating holes in the workpiece.
Dimension 3: Quality Control
Quality control is the third dimension of CNC milling operations. It involves the inspection of the finished workpiece to ensure that it meets the required specifications. The inspection is done using various measuring tools, such as micrometers, vernier calipers, and height gauges. The quality control also involves the use of statistical process control techniques to monitor the process and detect any variations. Quality control is important to ensure that the final product meets the required standards and specifications.
Dimension 4: Maintenance
Maintenance is the fourth dimension of CNC milling operations. It involves the regular maintenance of the machine to ensure optimal performance. The maintenance includes cleaning, lubrication, and replacement of worn-out parts. Regular maintenance can prevent breakdowns and prolong the lifespan of the machine. Proper maintenance also ensures that the machine operates at peak performance, which is essential for achieving the desired results.
Dimension 5: Safety
Safety is the fifth dimension of CNC milling operations. It involves the use of personal protective equipment, such as safety glasses and gloves, and following safety procedures to prevent accidents. The operator should be trained on how to operate the machine safely and be aware of the potential hazards. Following safety procedures is crucial to prevent injuries and accidents during the milling process.
In conclusion, CNC milling operations involve several dimensions, including machine setup, material removal, quality control, maintenance, and safety. Each dimension is critical to the success of the milling process, and understanding them can help optimize the process and achieve the desired results. By paying attention to each of these dimensions, manufacturers can produce high-quality products efficiently and safely.


