Metal plates are a versatile material commonly used in the manufacturing of various products, from simple household items to complex automotive parts. However, designing sheet metal products is not a simple task. To ensure that the final product is both practical and aesthetically pleasing, it is important to follow some key design guidelines.
As a sheet metal designer, you need to master various skills and knowledge. This guide will introduce you to the basics of sheet metal design and provide some sheet metal design techniques and practical suggestions.Let’s get started!
Understanding Sheet Metal
Firstly, what is sheet metal material?
Sheet metal material is a type of metal material that can be molded into various shapes through pressure and bending. Sheet metal is commonly used for various applications, such as automotive manufacturing, electronic equipment manufacturing, and construction engineering. In sheet metal design, it is necessary to consider the strength, hardness, and reliability characteristics of the material.
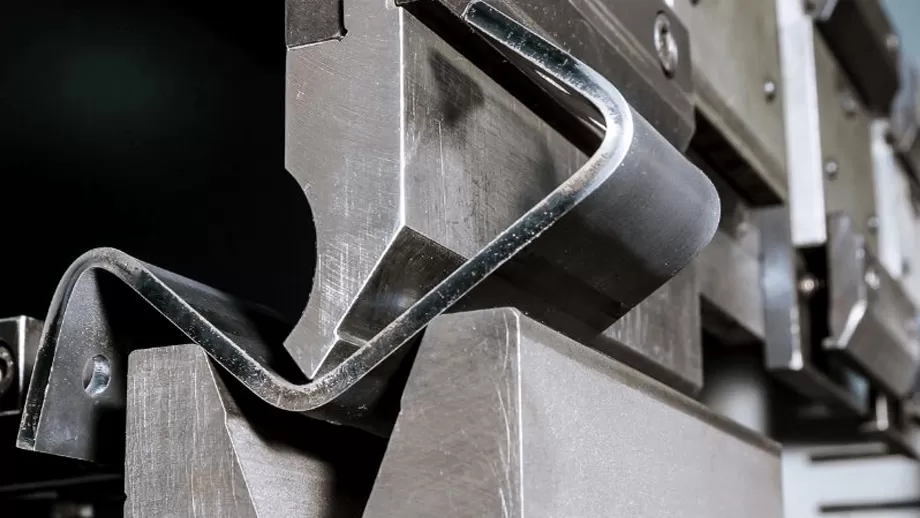

Secondly, what is sheet metal fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication is a common metalworking technique, usually starting with a flat sheet of metal. This metal plate goes through a series of operations, such as bending, shearing, stamping and welding, and finally becomes a finished product
Sheet metal fabrication requires the use of professional machines and equipment, such as laser cutting machines, bending machines, stamping machines and welding equipment. These devices can help machining personnel complete a variety of machining tasks, including cutting, forming, bending, punching, stamping and welding.
In addition, Longsheng sheet metal fabrication Plant provides sheet metal design and engineering services to help customers design and develop their parts and products.
How sheet metal fabrication works
The definition of sheet metal fabrication is to use metal sheets for fabrication to transform them into components of the required size and shape. The main principle is to change the shape of the metal sheet by applying force to it. Specifically, it includes the following three steps:
1.Pressing: Place a metal sheet into the equipment and use pressure to deform the sheet.
2.Bending: To bend a thin plate into the desired shape through a specific operating method.
3.Assembly: Assemble different components together to form the final product.
Sheet metal fabrication usually requires the use of computer controlled (CNC) equipment to make the fabrication process more precise. These machines have functions such as high-speed cutting, forming, and stamping. And parts made of sheet metal usually do not require post-processing, but may require surface finishing and welding, depending on the application field of the sheet metal parts
6 main sheet metal fabrication technologies
The following describes six major sheet metal fabrication technologies:
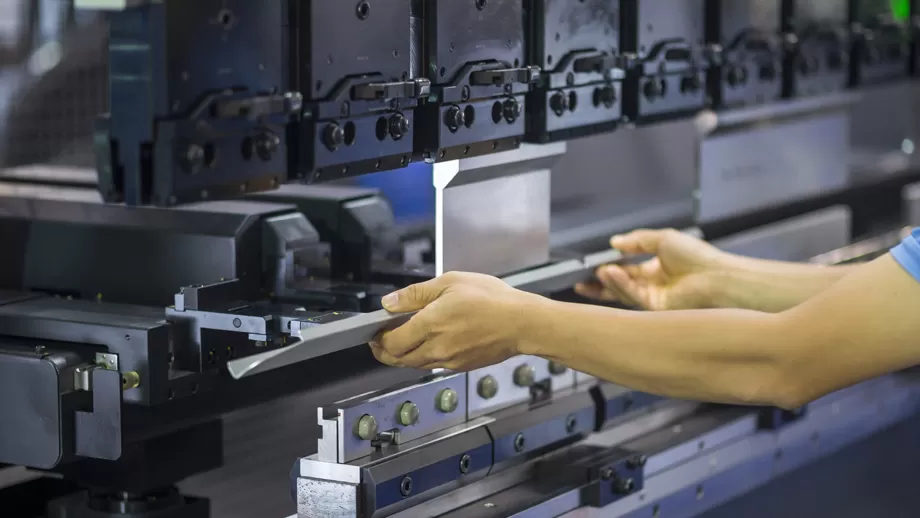
Bending
Bending mainly involves bending specific parts of the steel plate to produce the required curvature or angle. This method is generally completed by using a mechanical Press brake or a manual bending tool. Usually, multiple bends are required to obtain the desired shape.

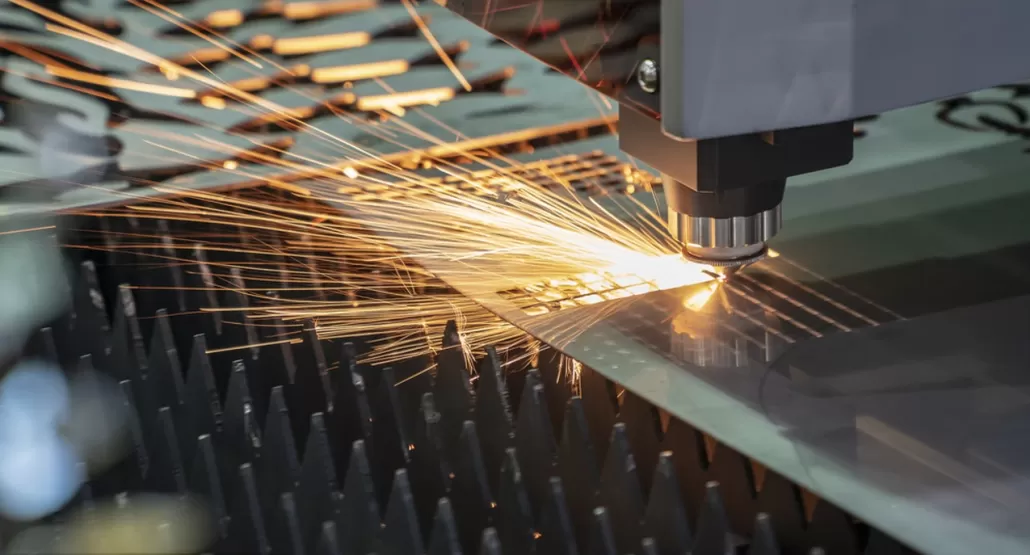
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a processing technology that uses high-energy laser beams to accurately cut metal sheets. Laser beams can be controlled and focused to cut complex shapes and contours.

stretching
Stretching is a method of elongating a steel plate. This method is usually used to make thin sheet parts or equipment. In this process, the material needs to be stretched to make it thinner in the length direction and also longer. Stretching is usually accomplished using a press and specialized stretching equipment.
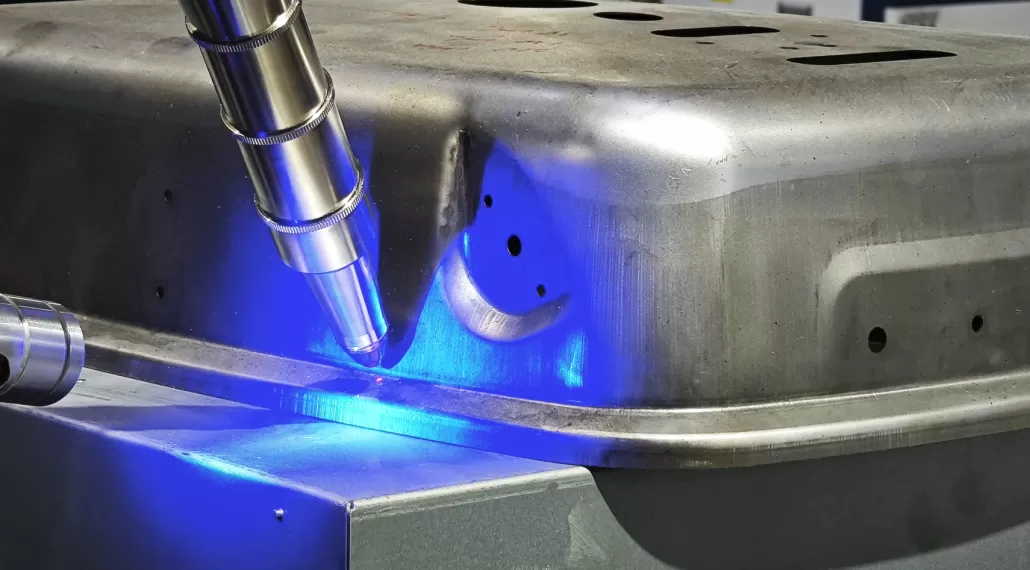
Welding
Welding is a processing method that connects metal sheets together through a heat source. Common welding methods include Arc welding, Laser beam welding, gas shielded welding, etc., which are used to connect different parts or plates.

Rolling
Rolling is the process of applying force to a metal sheet through a roller, causing it to pass through the gap between the rollers, thereby changing the shape and size of the sheet. Rolling is often used for thinning, leveling, and shape correction of sheet metal.
stamping
Stamping is a method of making steel plates into the desired shape, usually used to produce high-precision parts. This method uses a special stamping tool to place the steel plate on a fixed base plate, and then uses high-pressure gas or mechanical force to press the steel plate to form the desired shape.
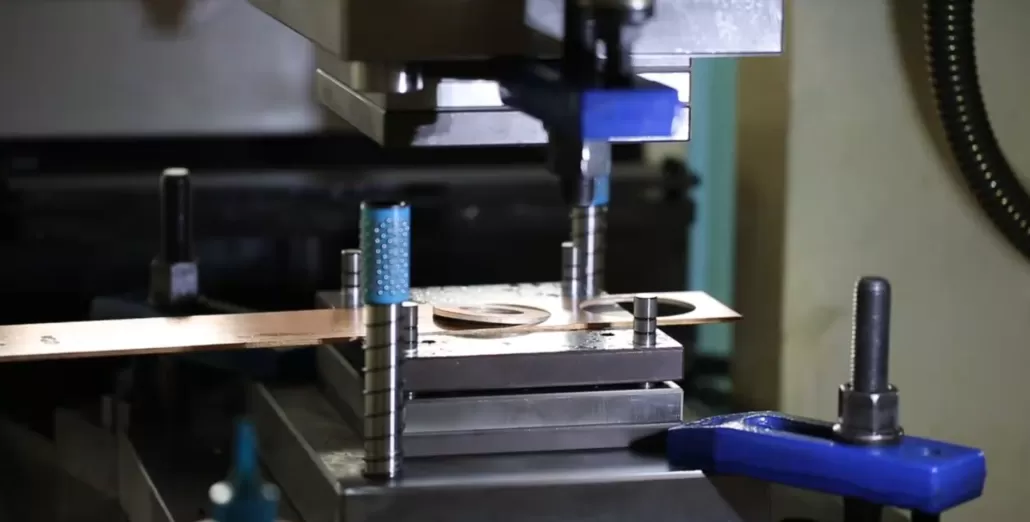
Sheet Metal Design Guidelines
Sheet metal fabrication mostly depends on the overall design of the product. For example, producing a simple sheet metal part naturally does not have too many requirements, but for complex geometric sheet metal parts, more processes are required to produce parts that meet the requirements. The design criteria for sheet metal include the following 6 categories.
Material Selection
The first step in sheet metal design is selecting the appropriate material for the product. Factors to consider include the type of metal, thickness, and finish. Common types of sheet metal include stainless steel, aluminum, and brass. Each type of metal has its own unique properties, such as strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance, so it is important to choose the right material for your product. Thicker metals are more durable but also more difficult to form, so the thickness should be chosen based on the product’s intended use. The finish should be chosen based on the product’s intended use and aesthetic preferences.
The following are some common materials in sheet metal fabrication :
| Material | Density (g/cm ³) | Thermal Expansion Coefficient (10 ^ -6/℃) | Modulus (GPa) | Processing Difficulty | Physical Property | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminium | 2.7 | 23-24 | 70 | Easy to process | Lightweight, good thermal conductivity and conductivity | Aircraft parts, automotive components, electronic equipment casings |
| Stainless Steel | 7.9 | 16-18 | 193 | Moderate | Corrosion resistance, high strength | Kitchenware, ship components, chemical equipment |
| Cold-rolled Steel | 7.8 | 11-13 | 200 | Easy to process | High strength and wear resistance | Automotive body parts, home appliance casings |
| Carbon Steel | 7.8 | 11-13 | 210 | Moderate | High strength, moderate price | Building structure, pipeline |
| Copper | 8.9 | 16-18 | 120 | Moderate | Good conductivity and corrosion resistance | Electrical parts, pipelines, decorations |
| Titanium Alloy | 4.5-5.6 | 8-10 | 110-130 | Difficult to process | Lightweight, high-strength | Aerospace components, medical devices |
| Magnesium Alloy | 1.7-2.0 | 26-28 | 45-60 | Easy to process | Lightweight, good strength | Automotive parts, electronic equipment casing |
| Steel | 7.8 | 12-14 | 200 | Moderate | High strength, wear-resistant | Frame member, Machine element |
| Zinc Plate | 7.1 | 30-34 | 70 | Easy to process | Corrosion resistance, good plasticity | Roofs, pipes, sinks |
| Brass | 8.4-8.7 | 19-20 | 100-125 | Moderate | Good conductivity and corrosion resistance | Music instruments, decorations, pipes |
Bend Radius
Bend radius refers to the minimum radius that can be achieved when bending a sheet metal product. A smaller bend radius makes the product more prone to cracking, so it’s important to choose a radius that will not compromise the product’s integrity. As a general rule, the bend radius should be at least twice the thickness of the sheet metal.
Hole Placement and Size
When designing sheet metal products, it’s important to consider the placement and size of any holes. Holes that are too close to the edge of the product can compromise its strength. The size of the hole should also be appropriate for the intended use of the product. For example, larger holes may be required for ventilation, while smaller holes may be used for mounting or fastening.
Forming and Fabrication
Sheet metal products are formed using a variety of techniques, including bending, stamping, and cutting. The fabrication process should be carefully planned to ensure that the product’s design is maintained throughout the process. It’s also important to consider the manufacturing equipment that will be used to create the product. For example, some equipment may be better suited for certain types of sheet metal, while others may be better suited for more complex shapes.
Tolerances
Tolerances refer to the allowable variation in dimensions or other characteristics of the product. When designing sheet metal products, it is important to consider the tolerances that are acceptable for the intended use of the product. Tighter tolerances may be required for certain applications, such as those that require precise fit or alignment.
General tolerance table for sheet metal fabrication
| Metal Part Type | Tolerance Range |
|---|---|
| bending parts | Bending angle tolerance: ± 1 ° to ± 3 °, bending dimension tolerance: ± 0.15mm to ± 0.5mm |
| Stamped parts | Dimensional tolerance: ± 0.1mm to ± 0.5mm, positioning tolerance: ± 0.1mm to ± 0.3mm |
| Shear parts | Dimensional tolerance: ± 0.1mm to ± 0.3mm, edge flatness tolerance: ± 0.2mm to ± 0.5mm |
| Drawing parts | Dimensional tolerance: ± 0.2mm to ± 0.5mm, tensile length tolerance: ± 0.5mm to ± 1mm |
| Bending parts | Dimensional tolerance: ± 0.1mm to ± 0.5mm, angular tolerance: ± 1 ° to ± 3 ° |
| Weld parts | Dimensional tolerance: ± 0.1mm to ± 0.5mm, weld width tolerance: ± 0.1mm to ± 0.3mm |
| Threaded parts | Dimensional tolerance: ± 0.1mm to ± 0.3mm, thread tolerance: according to standard requirements |
| Perforated parts | Dimensional tolerance: ± 0.1mm to ± 0.3mm, hole spacing tolerance: ± 0.2mm to ± 0.5mm |
| Surface coating parts | Dimensional tolerance: ± 0.1mm to ± 0.3mm, coating thickness tolerance: ± 0.02mm to ± 0.05mm |
| Assembly parts | Dimensional tolerance: ± 0.1mm to ± 0.5mm, assembly tolerance: according to assembly requirements |
Surface Finishing
Surface finishing is an important consideration when designing sheet metal products. The finish can affect the product’s appearance, corrosion resistance, and durability. Common surface finishes for sheet metal products include painting, powder coating, anodizing, and plating. The finish should be chosen based on the product’s intended use and aesthetic preferences.
| Surface finishing method | Appearance effect | Applicable materials | design requirement | Usage environment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| galvanization | Bright Silver | steel | Corrosion resistance requirements to prevent rust and corrosion of steel | Outdoor environment, high humidity environment, contact with water or damp media |
| nickeling | Silver or gold | Steel, copper, alloy | Wear resistance, corrosion resistance, appearance requirements | High humidity environment, decorative parts |
| chrome-plating | Silver or mirror effect | Steel, copper, alloy | Corrosion resistance, high glossiness, and decorative requirements | Indoor environment, decorative parts, automobile appearance parts |
| flame platin | Multiple colors available | any material | Appearance requirements, color selection, and corrosion resistance requirements | Indoor environment, outdoor environment, various application scenarios |
| electrophoretic coating | Smooth and uniform coating | Aluminum, steel, alloy | Smooth coating, corrosion resistance, appearance requirements | Indoor environment, automobile appearance parts, electronic equipment shell |
| Hot Dip Galvanizing | silvery | steel | Extremely high corrosion resistance and anti-corrosion requirements | Outdoor environment, high humidity environment, parts exposed to harsh conditions |
| Anodization | Silver or color coating | aluminum alloy | Improve hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and decorative requirements | Indoor environment, high humidity environment, electronic equipment parts |
| burnishing | Smooth and shiny surface | Stainless steel, copper, etc | Improve appearance and provide a smooth surface | Indoor environment, decorative parts, highly demanding appearance surface |
| sand blast | Rough Surface | any material | Increase roughness, prepare surfaces for painting or bonding | Preparation before painting, bonding, and surface treatment |
| Shot peening | Rough Surface | Steel, cast iron, etc | Improve coating adhesion, anti slip performance, remove oxide layer and dirt | Surface treatment for coating and anti slip requirements |
Solutions to common sheet metal design errors
Sheet metal fabrication involves designing, cutting, bending, and assembling sheet metal into the final product. During the design process, even the most skilled designers inevitably make mistakes, leading to rework or scrapping of sheet metal parts. To avoid these errors, it is important to understand sheet metal manufacturing design errors and take measures to avoid them.
We will list several common sheet metal design errors and provide solutions to avoid corresponding problems:
Error 1: Lack of consideration for material bending radius
In sheet metal production, it is common to bend the material into the desired shape, but if the radius is too small, it can lead to material cracking and stretching. Therefore, the design must take into account the bending radius of the material to ensure correct bending without damaging the material.
Solution
Conduct bending radius testing on the material and record it in the design file. This helps to ensure that designers and manufacturers understand the correct bending radius and are able to bend the material correctly.
Error 2: design does not comply with the sheet metal mold
If a design cannot be carried by standard sheet metal molds, then the design cannot be produced. This mistake seems to waste a lot of time and money because you have to redesign and make a new mold.
Solution
Before designing sheet metal, evaluate the capability of the selected mold and confirm that your design is compatible with the mold.
Error 3: Welding error
Welding errors are a dangerous mistake in sheet metal design. Incorrect welding can lead to strength issues, defects left in the welding position, and other issues. As a result, your design cannot meet the requirements, which has an impact on productivity.
Solution
Correct welding techniques must be maintained during the welding process. You can also refer to the advice of welding experts to ensure the accuracy of welding.
Error 4: Plate selection error
When selecting sheet materials, it is easy to make mistakes in selection. It may be due to the selection of thicker materials than actually needed, or the use of non corrosion-resistant materials, etc. This will lead to increased costs and also affect product quality and lifespan.
Solution
When selecting sheets, it is necessary to select materials based on actual needs, determine the thickness and performance of the sheets. It should be noted that selecting different materials can also affect processing costs, so necessary comparisons and analysis are needed.
Error 5: Design error of irregular parts
During sheet metal processing, there will be many bends or bends. If the design of irregular parts is not reasonable, it will lead to problems during processing and production.
For example, the design is asymmetrical, resulting in an imbalance in the overall shape; Inappropriate design angle increases the difficulty of production process; The designed die casting material is too weak, resulting in shape deformation, etc.
Solution
We need to make better planning for the design of irregular parts. Firstly, we need to have a deeper understanding of customer needs and engage in excellent communication; Secondly, we need to make reasonable use of corresponding sheet metal processing techniques in order to meet the design requirements of irregular parts; It is also necessary to pay attention to the selection of materials and reasonable design to ensure the perfect presentation of accuracy and shape.
Error 6: Vertical bending distance too short
If the vertical bending distance is too short during bending, it can cause stretching and deformation of the sheet during bending. Moreover, as sheet metal may require multiple bends, this error may be further exacerbated during the next bending process.
Solution
In order to avoid such errors, we need to avoid excessive bending as much as possible during the design phase. This problem can be solved by increasing the width, thickness, etc. of the sheet metal material. In addition, we can reduce the deformation caused by the stretching of the bent material by bending one side first.
Longsheng Technology: providing sheet metal fabrication services
At Longsheng Technology, our team of experts is equipped with the latest tools and technologies to provide comprehensive manufacturing design (DFM) analysis. We will work closely with you to optimize your manufacturability design and identify potential issues early to minimize the risk of production delays or quality issues.
Whether you want to customize electronic equipment shell, chassis, billboard, booth and other sheet metal products, or need to customize commercial equipment, machine tools, special tools, etc., Longsheng technology can provide you with a satisfactory overall solution.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you bring your design to life and speed your time to market. Look forward to cooperating with you!
Conclusion
Designing metal sheet products requires careful consideration of various factors. By following these design guidelines, you can ensure that your sheet metal products are both practical and aesthetically pleasing.
Please remember that these guidelines are only a starting point, and it is important to work closely with manufacturers to ensure the best results. By using the correct design and manufacturing techniques, you can create sheet metal products that meet your specific needs and exceed your expectations.
I hope this article will be helpful to you in discussing the content of “Sheet Metal Design Guidelines”!
Author: Longsheng Technology
FAQ
In sheet metal design, there are many factors that need to be considered, such as strength, stiffness, sealing, protection, aesthetics, etc. In addition, factors such as craftsmanship and cost-effectiveness need to be considered. Before designing, it is important to fully consider and plan comprehensively.
Yes. Sheet metal can come in various complex shapes, including bending, curling, cutting, and forming. When designing, it is necessary to consider the possibility of craftsmanship, but the final product can be highly customized.
The cost of sheet metal fabrication is determined by various factors, such as the selection of materials, the quantity and degree of components, and the specific process. To obtain accurate cost estimates, it is necessary to communicate with sheet metal manufacturers or processing service providers.


