Metal springs, as indispensable and important components in mechanical engineering, are widely used in various types of equipment and systems. They take advantage of the elastic properties of metal materials to deform when exposed to external forces and quickly return to their original shape after the external forces disappear. There are many types of metal springs, each with its own characteristics. According to its different force properties, shape and use, it can be divided into many types.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the three main types of metal springs: compression springs, extension springs, torsional springs. These spring types play a vital role in their respective fields, providing strong guarantee for the normal operation of various equipment and systems. Next, I will lead you to explore the mysteries of these three metal springs.
What is a metal spring?
A spring is a flexible mechanical element that stores mechanical energy when subjected to tension, compression, bending or torsion forces. When a spring deflects, it stores energy while exerting a reaction force. The relationship between deflection and applied force depends on the characteristics of the spring.
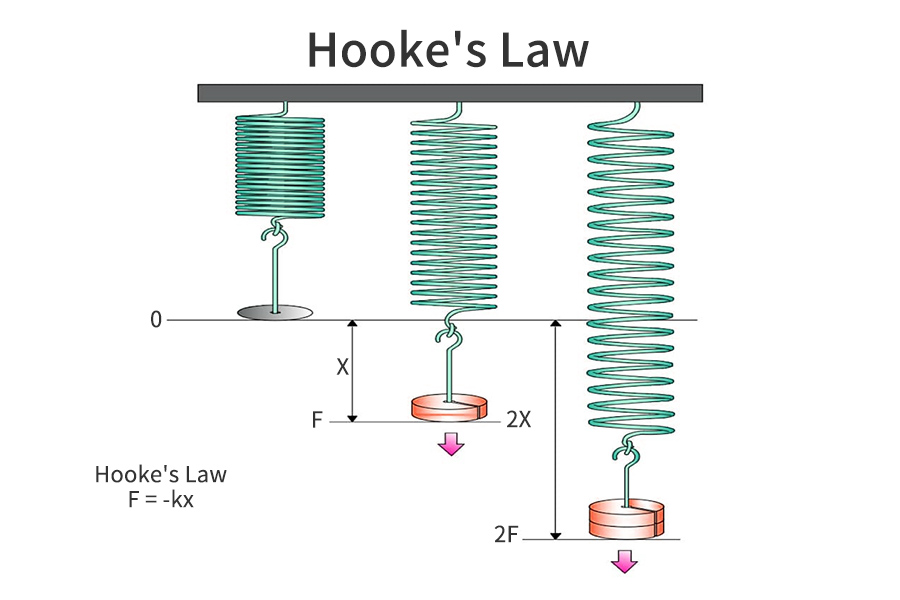
Hooke’s Law: Understanding The Principle Of Spring
Spring is a mechanical component that, when compressed by a load, stores the energy, and releases it when the load is removed. This is the normal way all springs function irrespective of their types, as expressed by Hooke’s law.
Hooke’s law relates the force exerted by a load on a spring and its elasticity. According to the law, the force exerted by a load needed to compress or extend a spring is directly proportional to the displacement, as expressed by the mathematical expression below: F= -kX
among:
F = force exerted by the load on the spring
X = spring displacement (it is a negative value indicating the force to restore the spring is opposite the direction)
k = spring constant, which shows the spring stiffness and depends on the spring type
What are the three types of metal springs?
we’ll take a closer look at the three main types of metal springs:
compression springs
Compression springs are the most common type of springs in the industry. These mechanical devices in the shape of a helix made from spring wire are used to store or release energy. Compression springs can be used to absorb shock or maintain a force between two surfaces.
Compression springs are named that way because the name defines the action the spring carries out when a load or force is placed on it, it compresses.
Compression springs have pitch in between the coils in order to store energy when a load or force is placed on it. Once the load or force is removed it then releases such energy and returns to its original form. In other words, it ¨springs back.¨
Compression springs usually range in wire sizes from 0.006 inches to 1.250 inches. More standard stock spring sizes are around 0.06-0.6.
extension springs
Extension springs, also known as a tension spring, are helical wound coils, wrapped tightly together to create tension. As their name states, the action that it carries out when a load or force is placed on the ends is to extend or expand. That is why they can also be called expansion springs sometimes.
Extension springs usually have hooks, loops, or end coils that are pulled out and formed from each end of the body. The function of an extension metal spring is to provide extended force when the spring is pulled apart from its original length.
The hooks tend to be the weakest point of the extension metal spring. If there is a risk of the hook breaking or bending due to the level of force it needs to withstand, then it is recommended that t instead of hooks, bolts be placed on the ends to attach it to the necessary place.
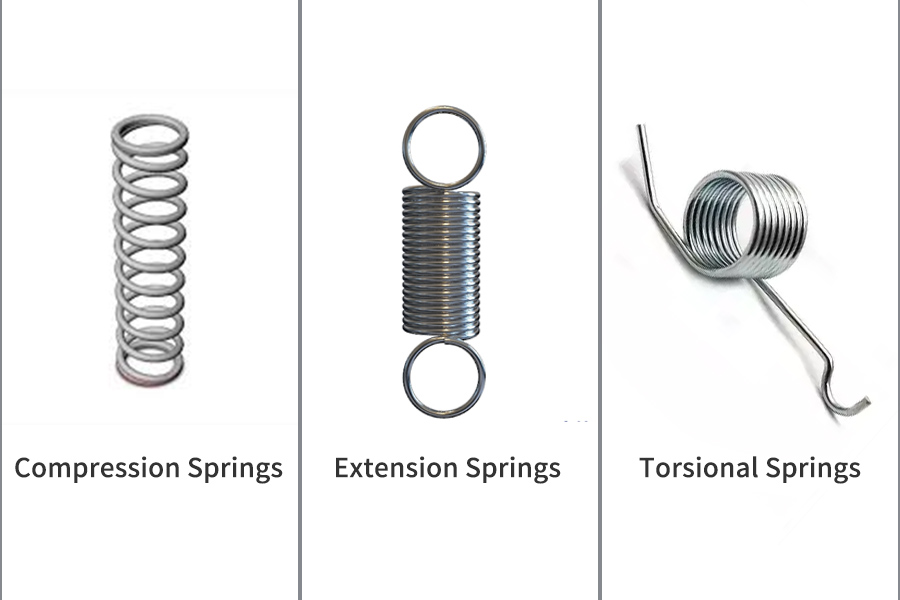
Torsion springs
Torsion metal springs are the least common of the three main types of springs. They can also be called torque springs, torsional springs, or rotational springs. All of these names describe the action or motion that the spring carries out when a load or force is placed upon it.
Torsion springs are wire springs whose coils twist to perform a rotational motion when torqued. They then release this stored energy and eject it when the force or load is removed.
What makes torque springs special is that their shape and function as a close wound coil spring is to eject a radial force thus producing torque instead of a linear load.
Functions of Springs
A spring’s main function is to store energy and to release that energy when the force upon it is removed.
Compression Springs
A compression spring’s unique design means that their compressed helix shape allows them to resist compressive forces.
Extension Springs
The extension spring, also known as a tension spring, has coils that are wound together, designed to give a pull force through an end fitting or loop when extended.
Torsion Springs
The torsion spring is a coiled spring designed to have a rotational or twisting motion that exerts a force.
Characteristics of metal springs
Characteristics of compression springs
- Various shapes: The shape can be cylindrical, conical, etc. to adapt to different usage environments.
- High elasticity: able to effectively absorb and release energy, and withstand large deformation and compression forces.
- Strong load capacity: able to maintain stable elastic characteristics within a certain range.
- Long life: Made of high-strength materials, with good wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
- Easy installation: just compress to required length and secure.
Characteristics of extension springs
- Elongation and elasticity: Tension springs can elastically deform when subjected to tensile force and have the ability to store and release potential energy.
- Elongation and elastic coefficient: The elongation of a tension spring is related to the applied tension and the elastic coefficient of the spring material.
- Strength and durability: Tension springs need to have sufficient material strength to resist breaking or twisting and to maintain their elasticity with repeated use.
- Cross-sectional shape: The cross-sectional shape of the tension spring can be round or square to suit different application needs.
- End shape and fixation method: There are various end shapes, including hook shape, ring shape, etc., which can be selected according to application requirements.
Characteristics of Torsion springs
- Mitigating impact and absorbing vibration: It has large elastic deformation ability and can absorb vibration and impact.
- Control the movement of the mechanism: the force changes little within a certain deformation range.
- Storage of energy: requires greater elasticity and more stable force.
- Measuring the magnitude of force: There is a linear relationship between force and deformation.
How do metal springs work?
Springs store mechanical energy and release it when the opposing force is removed. A spring helps create movement or hold a certain object in place without using engines or other powered means.
compression springs
Compression springs store and release energy when they are compressed. When a spring compresses, it stores energy within its structure. When the force is removed, the energy is released and the spring stretches to its original length. They are used in a variety of products and applications, from smaller household items to larger industrial machinery, including pens, garage doors and vehicle suspension systems.
extension springs
A tension spring works by resisting tension, absorbing and storing energy as it stretches. When stretched to a certain length, it generates a restoring force that returns the two parts to their original positions. In the unloaded state, the coils of the tension spring are in contact.
Torsion springs
Torsion springs are usually wound tightly so that each coil touches the next coil. Their terminal configurations are different. Like tension springs, torsion springs must be connected to other components at both ends in order to function. When forces act on the ends of the spring, they tighten the coils of the torsion spring. When the spring returns to its resting coil diameter, it brings the connected parts back with it.
To hold a torsion spring in place, it is usually placed on a mandrel (a small rod or spike) that is inserted into the coil. The fixture must be tight enough to avoid excessive play, but loose enough to allow full movement. Alternatively, the entire spring can be placed in a blind hole to hold it in place. In other cases, like the clothespin example, the ends of the spring are configured in such a way that they securely connect the spring to its adjacent parts.
Common applications of metal springs
Applications of compression springs
- Medical Equipment: Compression springs are widely used in the medical industry for medical equipment. These springs can be used in small devices such as syringes, pill dispensers, and inhalers.
- Electronics: In the electronics industry, compression springs play a vital role in ensuring the functionality of electronic components and connectors. They are used in devices such as switches, battery compartments, and circuit board connections to ensure correct electrical contact.
- Precision instruments and tools: Precision instruments and tools require extremely high precision, and compression springs can meet this requirement. They are used in equipment such as micrometers, dynamometers and laboratory equipment for tasks such as load testing, calibration and shock absorption.
- Industrial Equipment: Compression springs are used in machinery, conveyors and assembly equipment where they absorb shock, maintain tension and provide resilience. Industries such as manufacturing, packaging and construction rely on these springs for smooth operation. These springs are used in: valves, conveying systems, actuators, mold and mold ejection applications.
- Mining and Drilling Equipment: In the mining industry, compression springs withstand harsh conditions, dampen vibrations, maintain tension in drilling components, and ensure the safety and reliability of mining and drilling equipment.
- Pen or Notebook: Everyday items such as pens and notebooks are equipped with compression springs to enhance their functionality. These springs allow the nib to extend and retract smoothly.
- Toys: When it comes to toys, compression springs can be used to provide the necessary kinetic energy for movement, action and sound effects in a variety of toys, from push-button toys and wind-up toys to spring-loaded surprise toys.
- Mattress: Compression springs are an integral part of the mattress support system that adapt to weight and body shape, enhancing comfort and durability.
Applications of extension springs
- Garage Doors: Garage doors are probably one of the most well-known extension spring applications. These springs are installed on both sides of the garage door and come into play when you try to lift or lower the garage door, helping to reduce the force required to lift or close the garage door, which can weigh hundreds of pounds.
- Automobiles: You may rarely see tension springs in modern cars as they are a key component of the car’s carburetor. However, automotive tension springs still have plenty of uses inside and outside cars.
- Trampolines: Trampolines are another very popular use of tension springs. Each trampoline may have hundreds of tension springs. The more tension springs a trampoline has, the more flexible, or “bouncy,” it is.
- Toys: Many toys have previously used tension springs for the shooting action, but both the tiny springs themselves and the pellets they fired were considered unsafe for children. You’ll still find tension springs in many toys, especially those with fast or throwing motions, especially those for older children. Some very safe and popular toys that use tension springs include wind-up toys and pinball machines.Pliers: Vise-style pliers not only clamp, they also lock into place to maintain the clamping, using a tension spring that is used to hold the clamped object in place.
- Washing Machine: When it comes to the application of mechanical tension springs, washing machines may be one of the last things that come to your mind, but in fact, they are an important part of the machine. When you start your washing machine, the drum spins at high speed, agitating the clothes and starting the washing process. Without a tension spring holding the drum in place, the spinning drum would bang against the sides of the machine, causing it to bounce around the room and make a loud noise while you wash your clothes.
- Medical Devices: For centuries, the medical community has relied on springs to function. To be sure, this includes tension springs as well. You can find tension springs in stretchers, surgical lights, and more.
- Farm Equipment: Just like many automobiles use tension springs, agricultural vehicles also use tension springs. However, they are particularly useful for agricultural vehicles because these machines are very heavy and require a lot of pulling power. You’ll see them in combines, tractors, and more, with applications ranging from hauling freight to plowing fields, and everything in between.
- Fence Gate: You don’t have to do anything, the fence gate will automatically bounce back and close after passing through it, that’s what the tension spring does.
Applications Of Torsion springs
- Clothespins and Clipboards: Clothespins are the simplest application for torsion springs. Once finger pressure is released, the torsion spring causes the prongs of the clothespin to open and grip the fabric.
- Spring hinge: A spring hinge inserts a torsion spring at the joint, and the legs of the torsion spring are fixed on a rectangular plate.
- Clock Spring: A clock spring or mainspring is a helically wound torsion spring. This type of spring is known for providing a constant force output that can produce multiple turns of large angle deflection with very little change in torque. Clock springs are available in square, rectangular and D-shaped inside diameters.
- Clock Springs in Vehicles: Clock springs are typically located within a car’s steering mechanism, specifically between the steering wheel and steering column. It maintains all electrical connections to the airbag, horn, radio and steering electrical systems connected to the steering wheel.
- Torsion Bar Suspension: A torsion bar suspension is a torsion bar used in automobiles that supports the trailing arm when a lateral or vertical force is applied to the wheel. In this case, the torsion bar twists around its axis to avoid deflection of the trailing arm.
Common materials for custom metal springs
| Aluminum Alloy Material | Stainless Steel | Alloy Steel | Copper Alloy | Other Alloy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum alloy 6061 | Stainless steel 303 | Q235 (A3 steel) | Bronze-H59 | Electrician pure iron-DT4C |
| Aluminum alloy 5052 | Stainless steel 304 | 45 steel | Bronze-H62 | Electrician pure iron-DT4E |
| Aluminum alloy 2A12 | Stainless steel 316 | Cr12 | Copper-T2 | Titanium alloy-TC4 |
| Aluminum alloy 7075 | Stainless Steel 316L | 3Cr13 | Oxygen Tu2 | Magnesium alloy -AZ91D |
| – | Stainless steel 420 | Spring Steel-65MN | Tin Bronze-QSN-6-6-3 | – |
| – | Stainless Steel-17-4PH | Mold Steel-SKD11 | Beryllium copper-C17200 | – |
Metal Spring Selection Guide
1.material selection
(1)Steel spring
Advantages: It has high strength and elastic modulus, and can withstand large stress and deformation.
Common materials:
High carbon steel: Harder, wear-resistant, and elastic. It is suitable for occasions with large loads and small deformation requirements.
Alloy steel: moderate hardness, good toughness, good corrosion resistance, suitable for medium load and large deformation occasions.
Stainless steel: good corrosion resistance, beautiful appearance, suitable for occasions with high environmental hygiene and appearance requirements.
(2)Copper spring
- Advantages: good electrical and thermal conductivity, good elasticity, good corrosion resistance, small internal stress and long service life.
- Applicable scenarios: springs in electrical connectors and electronic products.
(3)Aluminum spring
- Advantages: light weight and good corrosion resistance.
- Applicable scenarios: springs in automobiles, aviation, aerospace and other industrial fields.
(4)Titanium alloy spring
- Advantages: high strength, low density, good corrosion resistance.
- Applicable scenarios: High-load, high-temperature occasions in aviation, aerospace and other industrial fields.
2.shape and structure
- Spring shape: Choose coil springs, tension springs, compression springs, etc. according to the usage scenario.
- Spring structure: including diameter, number of turns, wire diameter and other parameters, which need to be selected based on load-bearing capacity and deformation characteristics.
3.Size parameters
- Spring diameter: affects torsional stiffness and load carrying capacity.
- Spring length: affects the amount of elongation and compression.
- Spring wire diameter: affects bending resistance and load-bearing capacity.
4.Performance parameters
- Carrying capacity: needs to meet actual usage needs.
- Deformation characteristics: optimized according to usage requirements.
- Fatigue life: ensure that the spring is stable and reliable during long-term use.
Why choose LongSheng metalspring manufacturing company?
We have advanced metal spring manufacturing setup and perfect inspection equipment to meet your various needs, we offer only the best metal spring manufacturing services and the ability to refine that even more. So if you are looking to have parts turned in with a high level of accuracy and need parts made right the first time, you have come to the right place.You can always get more competitive pricing at higher quantities. We also offer DFM, first article inspection (FAI) reporting, and material certifications.Longsheng Metal Spring Manufacturers:
- Instant Pricing
- Free DFM analysis
- Parts as Fast as 1 day
- Tight Tolerances
- ISO 9001 Certificated
- ISO 14001 Certificated
- IATF 16949 Certificated

The metal springs we often process now include compression springs, extension metal springs, torsional metal springs, and custom metal springs, which are often used in various industries such as automobile hardware parts, Electrical equipment, Electronic products, Medical equipment, Gym equipment parts, Industrial equipment, Mechanical parts, Office equipment, Children’s toys, Etc.Our spring manufacturing company has been open for many years and is known for producing high quality springs that meet or exceed industry standards. We use the latest technology and employ skilled technicians to ensure that our springs are precisely designed and manufactured to meet the customer’s exact specifications.
FAQs
Why are springs made from metal?
The physical properties of metal materials, such as elasticity and ductility, make them ideal materials for spring manufacturing. The elasticity of the metal material allows the spring to deform and release the force after being stressed, while the ductility ensures that the spring can be stretched or compressed without breaking under the force. Together, these properties make metal the material of choice for making springs.
What are steel springs used for?
Steel springs are often used in the field of spring manufacturing due to their good elasticity and ductility. For example, various types of springs, such as compression springs, torsion springs, tension springs, etc., can be manufactured using steel springs. The elasticity and corrosion resistance of steel springs make it an indispensable material in the field of machinery manufacturing. In machinery manufacturing, steel springs can be used to manufacture machine tools, vibrators, compressors, automobile parts, etc. In the construction field, steel springs can be used to manufacture door and window springs and door hinges. Steel springs are also used in electronic products, such as contact springs and connector springs.
What is the temperature resistance range of metal springs?
Piano wire: The recommended operating temperature range is 0~40℃.304 stainless steel: The recommended operating temperature range is -10~100℃.SUS613: Recommended to be used below 300℃.
What are the possible reasons for spring breakage during use?
①Fatigue fracture: Fatigue damage caused by long-term use.②Environmental damage: such as hydrogen embrittlement or stress corrosion cracking.③Overload rupture: The load-bearing limit of the spring is exceeded.


