A CNC vertical mill machine has cylindrical cutters oriented vertically on a spindle axis. That is particularly helpful for plunge cuts and drilling; these instruments are thought-about to be one of the best for diesinking purposes. With CNC expertise, the instruments in some vertical machining facilities might be manipulated on as much as 5 axes for the fabrication of customized shapes, slots, holes, and particulars in three-dimensional parts.
What’s CNC Vertical Milling?
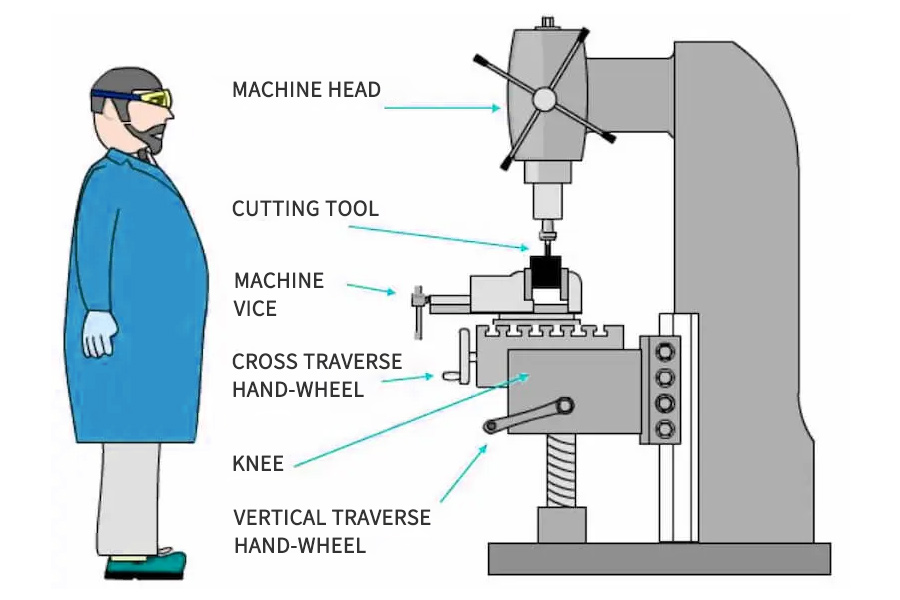
Vertical CNC milling refers to CNC milling operations that make the most of vertical milling machines. As urged by the title, the machines have vertically oriented tooling. This design makes them appropriate to be used in finish milling operations, which use instruments with enamel on the periphery and face.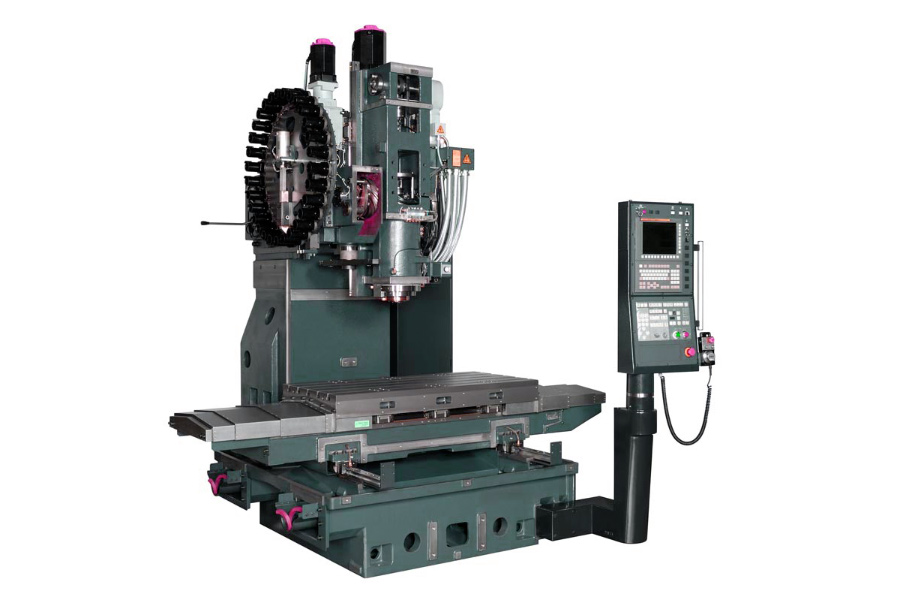
How does CNC Vertical Milling?
In a vertical milling machine, the spindle is aligned vertically and holds and rotates towards the stationary workpiece to take away materials from it. The spindle is fastened to the vertical axes, and the desk in a turret milling machine travels horizontally and vertically to the axes. This enables the machine to work in a vertical dimension, which is very versatile in manufacturing. The CNC program runs the automated instrument change system, pallet changer, instrument carousel, enclosures, and coolant methods. These options assist to boost the effectivity and precision of the milling process.
Comparability between Conventional Milling and CNC Vertical Milling
Conventional milling and CNC vertical milling are two completely different strategies of steel slicing. Conventional milling primarily will depend on the ability and expertise of the operator, whereas CNC vertical milling depends on a pc numerical management system for exact slicing.Conventional Milling:
- Depends on the ability and expertise of the operator.
- Sometimes requires extra handbook operation and monitoring.
- For advanced part styles and sizes, a number of setups and changes could also be wanted.
- Normally much less environment friendly as handbook instrument adjustments and gear changes are wanted.
CNC Vertical Milling:
- Depends on a pc numerical management system for exact slicing.
- Can mechanically change instruments, lowering the necessity for handbook operation.
- Can full a number of operations directly, enhancing manufacturing effectivity.
- Can deal with advanced part styles and sizes, rising manufacturing flexibility.
Advantages of CNC Vertical Milling
Some great benefits of CNC vertical milling are primarily mirrored within the following points:- Excessive Precision: The precision of CNC vertical milling machines is usually greater than that of conventional milling machines as a result of they depend on a pc numerical management system for exact slicing.
- Excessive Effectivity: CNC vertical milling machines can mechanically change instruments and full a number of operations directly, tremendously enhancing manufacturing effectivity.
- Versatile Processing: CNC vertical milling machines can deal with advanced part styles and sizes, rising manufacturing flexibility.
Options of CNC Vertical Milling
CNC vertical milling machines are environment friendly and exact steel slicing gear, with the next predominant options:- Excessive Precision: CNC vertical milling machines depend on a pc numerical management system for exact slicing, so their precision is usually greater than that of conventional milling machines.
- Excessive Effectivity: CNC vertical milling machines can mechanically change instruments and full a number of operations directly, tremendously enhancing manufacturing effectivity.
- Flexibility: CNC vertical milling machines can deal with advanced part styles and sizes, rising manufacturing flexibility.
- Automation: CNC vertical milling machines have computerized instrument altering and computerized measurement capabilities, which may scale back handbook operations, enhance manufacturing effectivity, and product high quality.
- Programmable: CNC vertical milling machines can function in response to preset applications, enabling them to carry out advanced slicing operations akin to spirals, curves, and three-dimensional cuts.
Variations between Vertical Milling and Horizontal Milling
| Options | Vertical Milling | Horizontal Milling |
|---|---|---|
| Spindle Orientation | The spindle is vertical to the worktable, with the instrument on high | The spindle is parallel to the worktable, with the instrument on the aspect |
| Cutting Methodology | The instrument rotates, the workpiece is fastened | The workpiece rotates, the instrument is fastened |
| Processing Vary | Appropriate for machining planes, grooves, gears, and many others. | Appropriate for machining elongated parts, massive gears, spiral grooves, and many others. |
| Footprint | Usually smaller, appropriate for small factories | Usually bigger, requiring extra space |
| Worth | Usually cheaper | Usually costlier |
| Flexibility | Appropriate for small batch and diversified manufacturing | Appropriate for mass manufacturing |
Variations between Vertical Milling and 5-Axis Milling
| Options | Vertical Milling | 5-Axis Milling |
|---|---|---|
| Spindle Orientation | The spindle is vertical to the worktable | The spindle can rotate in a number of instructions |
| Cutting Methodology | Sometimes can transfer and minimize on two axes (X and Y) | Can transfer and minimize on 5 axes (X, Y, Z, and two rotational axes) |
| Processing Vary | Appropriate for machining comparatively easy parts like planes, grooves, gears, and many others. | Able to advanced slicing operations like spirals, curves, and three-dimensional cuts, appropriate for machining advanced parts and molds |
| Tools Value and Operation Complexity | Comparatively decrease | Comparatively greater |
| Flexibility and Precision | Appropriate for machining easy parts | Larger machining flexibility and precision |
CNC vertical milling software
- Automotive Manufacturing: Used for machining automotive parts, akin to engine parts, brake system parts, and many others.
- Aerospace: Used for machining aerospace parts, akin to turbine blades, aviation engine parts, and many others.
- Mould Manufacturing: Used for machining numerous molds, akin to plastic molds, die-casting molds, and many others.
- Mechanical Manufacturing: Used for machining numerous mechanical parts, akin to gears, bearings, and many others.
- Electronics Trade: Used for machining parts of digital gear, akin to circuit boards, connectors, and many others.
- Medical Units: Used for machining medical machine parts, akin to synthetic joints, dental implants, and many others.


