In the field of metal processing, squeeze casting and high pressure die casting are two common process methods, each of which has unique process characteristics, application range and product characteristics. This article will delve into the differences between squeeze casting and high pressure die casting from multiple dimensions.
What Is Squeeze Casting?
Squeeze casting is a manufacturing technique that combines casting and forging. It’s also known as liquid metal forging. This technique involves injecting molten metal into a heated die, allowing it to begin solidifying, and then closing the upper die to form the mold chamber. Pressure from the upper die forces metal to completely fill the casting cavities which results in outstanding surface quality and minimal shrinkage. Aluminum and magnesium alloys are the most common metals for this procedure, but it can accept others as well. Vehicle parts are very often squeeze casting.
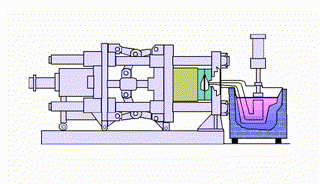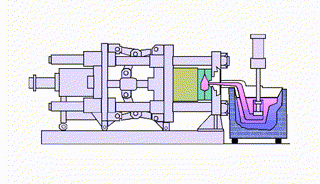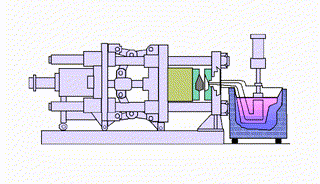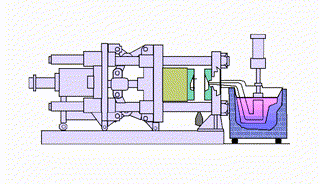
What types of squeeze casting are there?
There are two traditional types of squeeze casting process, each with its advantages, disadvantages and applications in part manufacturing. Here’s how each type of squeeze casting works:
direct squeeze casting
Direct squeeze casting technology or liquid metal forging utilizes a forging press. The technique involves pouring liquid metal into a preheated and lubricated mold. When the liquid metal begins to solidify, the upper mold or punch closes to create pressure (100MPa or more), allowing the liquid metal to fill the mold without air entrapment. The pressure is maintained until solidification occurs, and then the operator ejects the casting.
indirect squeeze casting
Indirect squeeze casting uses the same casting equipment as direct squeeze casting, but the process flow is different. The first step is to clean and refine the molten metal, which is then poured into a vertical or horizontal squeeze casting machine. The molten metal is then injected into the mold at a low speed (less than 0.5 m/s) through a thick gate, and then high pressure (55 MPa to 300 MPa) is applied until the liquid metal solidifies.
direct squeeze casting VS indirect squeeze casting
| Direct squeeze casting | Indirect squeeze casting |
|---|---|
| The pressure for preform penetration is provided directly to the melt in the direct squeeze casting method. | The melt is forced into the preform by a gate system in indirect squeeze casting. |
| There is no gate mechanism, direct squeeze casting tooling is relatively easy. | The tooling is more complicated, and a gating mechanism is present. |
| The existence of oxide residue in the composite is another difference. | The oxide residue in the composite is stopped by the gating system. |
| In most cases, this is done on a vertical machine (similar to a forging press). | Indirect squeeze casting , which uses both vertical and horizontal machines, is more analogous to traditional high-pressure die casting. |
What is High Pressure Die Casting?
High pressure die casting is a process whereby molten metal is fed into a die and solidified to obtain the desired component. The molten metal is forced, under high pressure (generally hydraulic pressure), within the die cavity and a powerful press secures it inside. Once solidification completes, removal of casting takes place by opening the die. Upon ejection of the final product, the die is locked again for the next production cycle. High pressure die casting tooling comprises two steel blocks that form the two ends of a die cavity that forms the desired object.
What types of high pressure die casting are there?
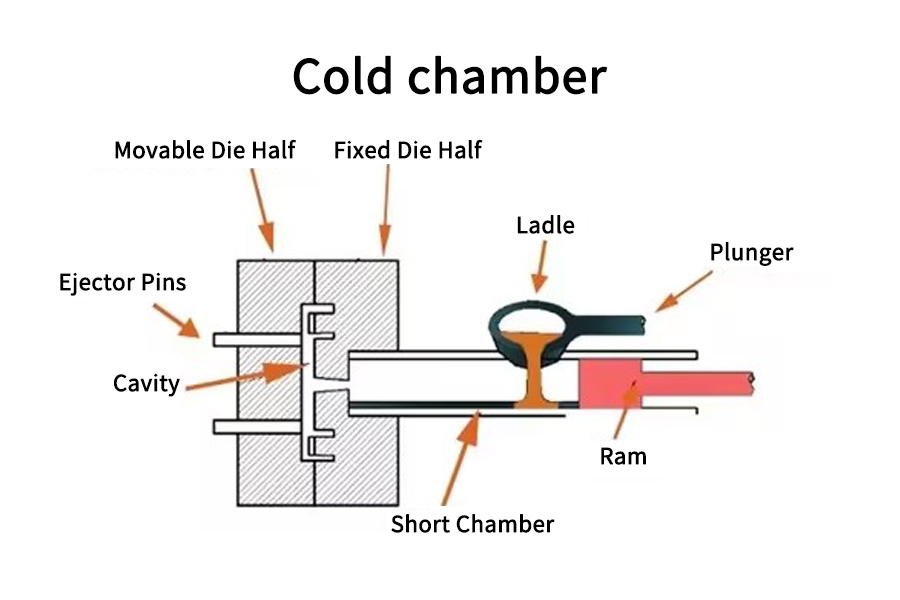
Cold chamber die casting is an ideal method for processing high melting point materials such as aluminum. It is a high-pressure die casting process in which molten metal is injected into the mold cavity through a cold chamber die casting machine.
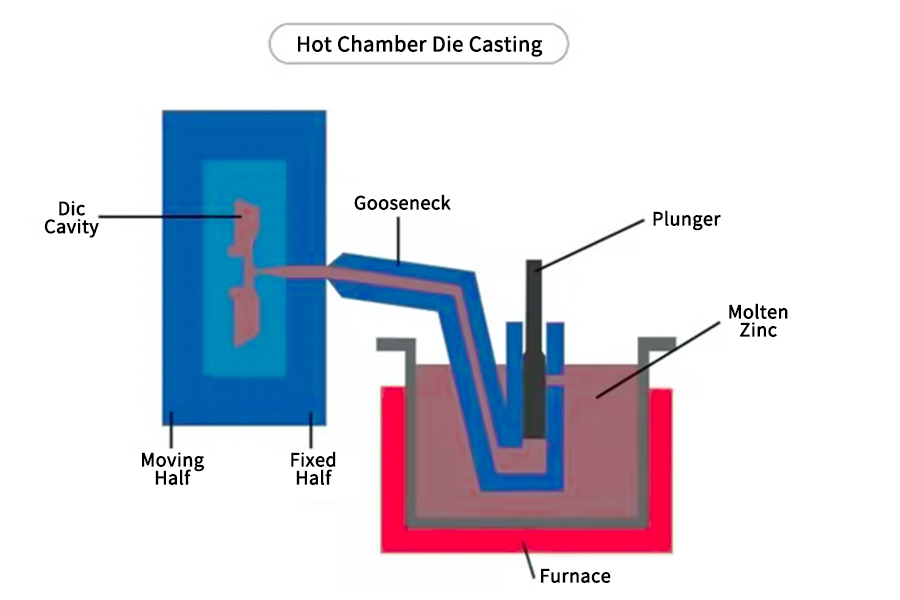
Unlike cold chamber die casting, the pressure chamber and gating system of hot chamber die casting are directly connected to the furnace, and the molten metal is always kept in a molten state. This method is suitable for metals with lower melting points, such as zinc alloys, magnesium alloys, etc. Because the molten metal always remains in a molten state, hot chamber die casting has higher production efficiency and better casting quality.
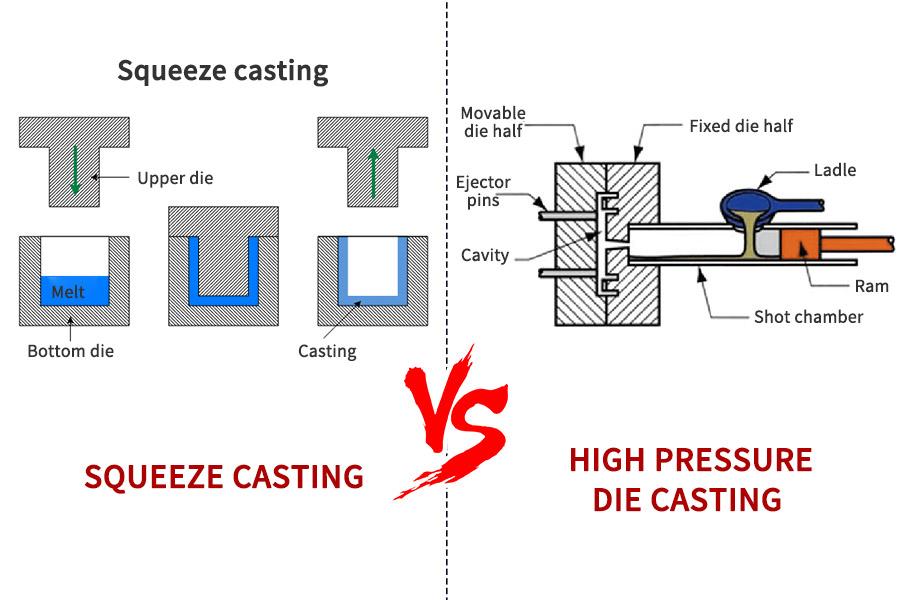
The working principle of squeeze casting and high pressure die casting
- Squeeze Casting: Liquid metal is introduced into a heated mold along with a preform made by powder metallurgy. Once the mold is filled, pressure is applied and the metal solidifies.
- High pressure die casting: A process in which metal is pressed into a mold at high pressure and high speed, and the solution is solidified. Its materials are non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum, magnesium, etc. which are suitable for producing high-quality small batch parts. The castings produced have high finish and precise dimensions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Squeeze Casting
Advantages of Squeeze Casting
- Offers a wider range of shapes and components than other manufacturing methods
- Little or no machining required after casting
- Low porosity
- good surface texture
- Fine microstructure with higher strength components
- No waste, 100% utilization rate
Disadvantages of Squeeze Casting
- It can be expensive as it requires specialized equipment and tools.
- Squeeze cast parts can require extensive machining to achieve precise tolerances.
- It is less adaptable to complex shapes than other casting methods.
Advantages and Disadvantages of high pressure die casting
Advantages of high pressure die casting
- high productivity:HPDC’s ability to quickly produce complex parts makes it ideal for high-volume production.The process involves injecting molten metal into precision molds at high speeds, thereby shortening cycle times and increasing productivity.
- Complex part geometries:HPDC allows the creation of complex part designs with tight dimensional tolerances.Complex shapes and thin-walled sections can be easily achieved, providing flexibility in product design.
- Excellent surface finish:HPDC produces parts with a smooth surface finish directly from the mold, reducing the need for secondary finishing operations.The process minimizes surface defects, resulting in high-quality components suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Tight dimensional tolerances:HPDC ensures parts have consistent dimensions, precise geometry and meet stringent quality requirements.Parts manufactured using HPDC exhibit minimal variation, making them suitable for components with tight fit tolerances.
- Material Versatility:HPDC can accommodate a wide range of metals and alloys, including aluminum, zinc and magnesium.This versatility enables manufacturers to select materials based on specific performance requirements and cost considerations.
Disadvantages of high pressure die casting
- High Initial Tooling Costs:Tooling for HPDC involves significant upfront investment, including the design and fabrication of complex molds.Initial setup costs may be prohibitive for small-scale production or low-volume applications.
- Limited Material Options:While HPDC offers material versatility, it is primarily suited for non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium.Limited availability of suitable materials may restrict the application of HPDC in certain industries or specialized applications.
- Porosity Issues:HPDC parts are prone to porosity defects, which can affect mechanical properties and structural integrity.Proper process control and optimization are necessary to minimize porosity and ensure part quality.
- Design Limitations:HPDC imposes design constraints, particularly in terms of draft angles, wall thickness, and parting lines.Design modifications may be required to accommodate the requirements of the casting process, leading to additional design iterations and costs.
- Environmental Considerations:HPDC involves the use of high-pressure machinery and melting furnaces, consuming energy and producing emissions.Sustainable practices such as recycling scrap metal and optimizing energy usage are essential to mitigate the environmental impact of HPDC.
Process comparison between squeeze casting and high pressure die casting
squeeze casting process
- Metal melting and purification: Heating selected metal materials above the melting point to change them from solid to liquid. During the metal melting process, purification processes such as degassing and slag removal are performed to remove gases and impurities in the molten metal and improve the purity and quality of the molten metal.
- Mold preparation: Check the integrity, cleanliness and dimensional accuracy of the mold, preheat the mold, and spray a layer of protective coating on the surface of the mold cavity to enhance the lubricity between the molten metal and the mold and prevent adhesion and wear.
- Pouring liquid or semi-solid metal: according to the production process requirements, pour the liquid or semi-solid metal into the mold cavity accurately and quickly.
- Mold closing and pressure application: After the metal liquid pouring is completed, the mold is quickly closed, and high mechanical pressure is applied to the mold through a hydraulic press or other pressure equipment, so that the metal liquid fills and flows under pressure, and reaches the external shape of the part.
- Extrusion molding and pressure solidification: Under the action of pressure, the molten metal gradually fills the mold cavity and undergoes plastic deformation to form the required casting shape. Maintain pressure until the metal completely solidifies.
- Open the mold and eject the casting: After the metal is completely solidified, gradually release the pressure on the mold, separate the mold, and take out the casting.
- An ejection mechanism is used to eject the casting from the mold for subsequent processing.
- Follow-up processing: including gate and runner system removal, deburring, surface treatment, inspection and packaging.
High pressure die casting process
- Mold Making: During the mold making process, hardened steel molds are finely machined to create cavities in the desired finished shape and equipped with operating systems for injecting molten metal.
- Setting up the mold: The mold is installed above the die casting machine (DCM) and preheated. Increased throughput means the program is more efficient, as some settings may take more time.
- Melting the metal: Put the alloy used for parts into an electric furnace or gas furnace and wait until it melts into a liquid state
- Injecting metal: The molten alloy is injected into the mold at high strength. High pressure is used to ensure that the inside of the mold is completely filled and the entire mold is accurately replicated.
- Cooling the metal: Molten metal rapidly cools and solidifies into the mold shape, compensating for shrinkage with additional pressure.
- Ejection: The two halves of the mold are separated and the finished part is ejected using an ejector pin or ejector plate. Further finishing operations may be required.
- Recycling: Excess materials are cut and repurposed for use in the upcoming production cycle.
Application scope of squeeze casting and high pressure die casting
Applications of squeeze casting
Automobile industry
A common application of the casting process is in the automotive parts industry, where it is suitable for manufacturing high-quality automotive components such as brackets, nodes, chassis and frames. A common example is Porsche, which uses this process to manufacture engine parts.
army
Extrusion die casting is also suitable for manufacturing military weapons and heavy machinery. Using materials such as magnesium alloys, the squeeze casting process produces high-quality parts such as bombs, bevel gears, pipes, blades and discs.
ship parts
The casting process is also suitable for materials such as aluminum, which is used to make small turbine blades and ship propellers. Its compatibility with heat treatment methods such as annealing also makes it common here, as this can be used to improve component operation in marine environments.
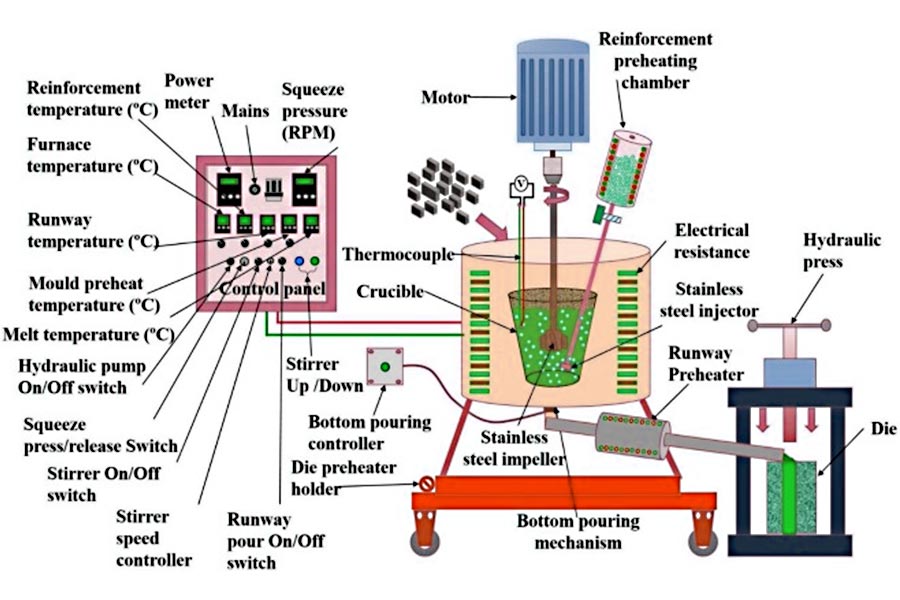
Applications of high pressure die casting
Automobile industry
High pressure die casting can produce various aluminum-magnesium automotive structural parts, such as engine blocks, transmission cases, oil pans, engine brackets, cross beams and other structural parts.
Medical industry
This is also a common technology used in the medical industry to produce lightweight surgical instruments. In addition, medical equipment and high volume imaging equipment, infusion pumps, etc. are also manufactured using high pressure die casting processes.
aerospace industry
The process is very popular in the aerospace industry due to its ability to manufacture complex and precise designs and automation. Aluminum, zinc and magnesium alloys are used to make engine components for aerospace applications.
What is the difference between squeeze casting and high pressure die casting?
| option | Squeeze Casting | high pressure die casting |
| Manufactured PartApplication | functional parts, such as engine cylinder blockwheel hub, piston, connecting rod, brake shoespneumatic or hydraulic valve body,etc | structural parts, such as vehicledoor frame, instrument panel.engine housing.etc |
| Raw Material | Most of metal alloys | Only casting alloys |
| Surface Finish &Heat Treatment | Much wider surface finish applications likeanodizing and heat treatment methods like solid.melt strengthening | limited surface finish like powercoating. Not able to applyanodizing. |
| Metallographic Structure | Typical crushing-grain texture as forging condition | Typical dendrite-shape texture ascast condition |
| SurfaceSmoothness | Extremely smooth surface like machining parts | Vicroscopic pores on surface. socalled “water streak texture” |
| Tensile Strength | 400-600Mpa | 200-300Mpa |
How to choose between squeeze casting and high pressure die casting?
Factors to consider based on product requirements:
- Complexity: High-pressure die casting is more suitable for manufacturing complex and precise parts. However, if machined properly, squeeze casting can also be used.
- Mechanical properties: If your main requirement is higher strength and ductility, squeeze casting is the best choice. However, if you can sacrifice usual strength or your product doesn’t require much ductility, you can conveniently use die casting.
- Yield: In mass production, high-pressure die-casting technology is considered the most ideal choice. Because of its high production efficiency and low cost, it has been widely used in industry. From another perspective, for small and medium-sized production, it is most appropriate to choose squeeze casting technology.
- Surface Finish: Regarding surface smoothness, high-pressure die casting is considered the most ideal post-processing method, while squeeze casting is a technology that requires a higher level of post-processing.
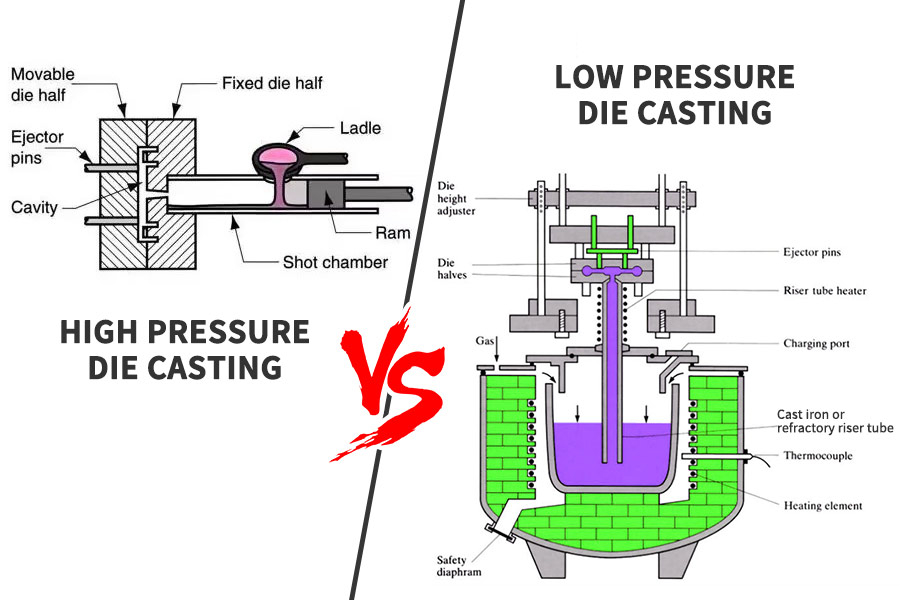
Industry-specific applications and recommendations:
- Automotive:die casting technology is considered the best option. From another perspective, for critical automotive components such as complex engine parts, the use of squeeze casting technology is the most ideal choice.
- Aerospace: squeeze casting technology is considered the technology of choice for manufacturing lightweight and high strength aerospace components. Because aluminum alloys have good plasticity and toughness, low pressure casting processes can be used to produce parts with complex shapes. However, when processing other non-complex components, high pressure die casting is often chosen.
- Consumer Electronics: High pressure die casting technology is the most popular die casting method for manufacturing high precision electronic components. It is difficult to obtain high dimensional accuracy and high quality components using traditional stamping processes on low pressure die casting machines. In contrast, squeeze casting technology is suitable for products with relatively low complexity.
Choose Longsheng as your trustworthy partner
LongSheng Steel is certainly one of China’s high aluminum and zinc die casting manufacturing service suppliers. Along with casting, we additionally present prototyping, tooling, machining, and floor ending providers. We use essentially the most superior expertise for die-casting manufacturing. Our CNC machining service runs with one of the best expertise and a decade-long skilled engineers and employees. We provide one of the best cost-saving and technical machining design and manufacturing solutions you may ask for. Here’s a record of our CNC machining capabilities:
- Our CNC milling store incorporates 5-axis CNC machines that are extremely exact. These machines are able to offering tolerance as much as 0.005mm.
- We now have speedy CNC fixture expertise that ensures quicker machining and on-time supply for our purchasers.
- Our machining service is just not just for casting parts but additionally for a lot of sorts of plastics and chrome steel parts.
- From superior CNC lathes and EDM machines to floor grinders and wire slicing machines, we’ve got every little thing you want for machining in our machine store.
The machined casting process is just not the ultimate job for a casting half. Floor ending can also be an vital a part of casting manufacturing. Holding that in thoughts, we offer surface finishing providers like anodizing, powder coating, chrome plating, moist portray, and many others. So you may see that LongSheng Steel supplies the whole resolution to die casting manufacturing. We offer providers in China and likewise internationally. Contact us to have one of the best die casting manufacturing service from China.

Summary
When choosing between high pressure die casting vs. squeeze casting, a thorough and comprehensive evaluation of the specifications and workability of the project you are involved in is essential. Whether it’s efficient speeds in die casting or superior material properties in squeeze casting, each method has its own unique advantages and limitations. But when deciding between these two casting methods, you should constantly weigh multiple factors, including industry guidelines, the specific specifications of the product, its quantity, and its complexity.Visit our Instant Quote Engine to get a free, no-obligation quote in minutes.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. LongSheng makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through LongSheng’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please contact to our for more information.
Team LongSheng
This article was written by various LongSheng contributors. LongSheng is a leading resource on manufacturing with CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, injection molding,metal stamping and more.
FAQs
Which one is cheaper, squeeze casting or high pressure die casting?
In terms of cost, which one is lower is not absolute, but needs to be considered comprehensively based on specific circumstances. If the production scale is large, there are high requirements for production efficiency, and a certain scrap rate and defective product processing costs can be accepted, then high-pressure die casting may be a better choice; if there are high requirements for product quality and you want to reduce the scrap rate and the cost of handling defective products and subsequent processing costs, then squeeze casting may be more advantageous.
What is the difference between high and low pressure die casting?
The pressure range of low pressure casting is between 0.08-0.15 MPa, while the pressure range of high pressure casting is between 30-70 MPa. The highlights of low pressure casting are average and the casting cycle is slow. On the contrary, the highlight of high pressure casting is that the casting cycle is faster. Products produced by high pressure castings have waviness and good surface finish. In addition, low pressure castings do not produce waviness inside the castings, but their surface finish is average.
What is the difference between squeeze casting and high pressure casting?
Squeeze casting and high pressure casting are both metal casting processes, but they differ in the application of pressure. Squeeze casting exerts a lot of pressure, but it is considered low to medium pressure compared to high-pressure die casting. HPDC can produce higher quality and more complex parts.
What are the extrusion die casting parameters?
① Casting temperature: The starting point is usually 6-55 degrees Celsius higher than the liquid temperature. But the temperature will vary depending on the alloy and geometry.②Extrusion pressure: Usually the pressure level is about 70 to 140MPa.③Tool temperature: The range is usually between 190 and 315 degrees Celsius.④Lubrication: For common casting metals such as aluminum, copper and magnesium, any high-quality colloidal graphite can be used as a spray lubricant. Satisfactory results can be obtained by applying lubricant to the hot mold before the casting process.⑤ Time delay: This is the measurement of the actual time between the metal pouring and the press piston starting to pressurize the metal in the mold cavity.⑥ Extrusion pressure holding time: For castings weighing about 9 kg, a range between 30 and 120 seconds is considered appropriate.



Pingback: From Fuel Nozzle Microholes to Turbine Vane Casting – The Machining Arms Race in Aerospace