In recent years, with the development of science and technology, environmental problems have become more and more prominent, and the production and application of environmentally friendly materials have received more and more attention. TPR material is thermoplastic rubber. Because of its excellent mechanical and thermal properties, it is an environmentally friendly material widely used in industrial production, automobiles, household appliances and other industries.
Next, we will analyze the definition, characteristics and applications of TPR materials in various fields in detail, hoping to provide readers with a more comprehensive and in-depth understanding.
What Is TPR Material?
TPR (Thermo-Plastic-Rubber material) is a thermoplastic rubber material. It is a thermoplastic soft rubber material with rubber elasticity that can be directly processed and molded (e.g., injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, etc.) without vulcanization.
TPR materials are based on thermoplastic styrene-butadiene rubber (e.g., SBS, SEBS), modified by adding resins (e.g., PP, PS), fillers, plasticizers, and other functional additives. In short, it is a recoverable, elastic, and malleable composite material. One of the main characteristics of TPR materials is their high fatigue strength, which allows them to withstand high bending stresses and long service life.
TPR, the term most users use for thermoplastic elastomers, refers to materials modified with styrene elastomers such as SBS and SEBS. TPR material suppliers refer to SBS-modified materials elastomer materials as TPR and SEBS-modified materials as TPE for ease of differentiation. But in fact, TPE is a broad concept that includes styrene elastomers, SEBS, SBS modified materials, but also TPU, TPV, TPEE, TPO, and other elastomeric materials.

How is TPR Material made?
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) is a material that combines the physical properties of plastic and rubber. It is made through a process called thermoplastic vulcanization (TPV). The process involves mixing two different polymers to create the desired TPR material.
The first polymer is usually an elastomer such as natural rubber, styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), nitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR), neoprene (CR), or chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM). The second polymer is usually a thermoplastic copolymer such as ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) or polypropylene (PP).
The two materials are mixed in an extruder and melted into one product. Once melted together and cooled to the desired temperature, the product can be formed into any shape required for the application.
1.Rubber injection molding
Rubber injection molding is a process in which molten plastic or thermoplastic rubber (TPR) material is injected into a mold to create parts with complex features. It is commonly used in the automotive and medical industries where precision and accuracy are required.
Depending on the project needs, this process can be done using automatic or manual machines. In this process, heated plastic is injected under pressure into a metal mold cavity to shape it into the desired part. After cooling, the molded parts are ejected from the mold and ready for use. Alternatively, TPR can be molded over a stiffer structure, such as an aluminum insert, to create soft grips and other resilient parts; this method is often called overmolding. With overmolding, two separate injection molds are required – one for the challenging part and one for the TPR assembly – which are joined together after cooling.
2.Extrusion
Extrusion is a manufacturing method used to produce parts with consistent cross-sections. It works by forcing molten plastic through a mold. The process helps in the manufacture of items such as tubes, rods and uniform shapes or cross-sectional profiles. The extrusion process can also create complex geometries such as hollow tubes and closed shapes. Due to its flexibility and durability, the extrusion process is widely used to produce thermoplastic rubber (TPR) materials, which are commonly used in medical devices, automotive parts, and consumer products.
3.Calenderin
Calendering refers to the main method of producing polymer material films and sheets. It passes the material close to the viscosity flow temperature through the gap of a series of parallel rollers rotating in opposite directions, so that it is squeezed and stretched into a shape with A sheet-like product of a certain thickness and width.
The molten and plasticized thermoplastic plastic passes through the gap between two or more parallel counter-rotating rollers, so that the melt is extruded, stretched and stretched by the rollers to become a continuous sheet product with certain specifications and quality requirements. Finally, it is processed Natural cooling molding method.
4.Blow molding
Blow molding is a popular production method, especially for items that require thin-walled structures and complex shapes. In the United States, blow molding technology has been widely used in automotive parts. This is a variation of injection molding technology in which air holds molten plastic to the inside surface of the mold. By controlling the temperature, the plastic is deformed and solidified to form a thin film material with a certain thickness. This technology can quickly and accurately create bottles, barrels, jars and other container parts. Since no excess material is produced in the product, a large amount of raw materials can be saved and energy consumption can be reduced. The result is a product that is both strong, lightweight and uniform in form.
What are the advantages of TPR materials?
Thermoplastic rubber materials provide the following advantages:
- It can be recycled and effectively save energy. It is an ideal material to replace rubber and silica gel.
- Energy saving. Most thermoplastic elastomers do not need vulcanization or the vulcanization time is very short, the production efficiency is greatly improved and the forming cycle is short.
- Environmental protection, non-toxic and safe, with excellent coloring and soft touch. TPE materials do not introduce heavy metals and toxic phthalate plasticizers in the production process, which comply with ROHS, reach, EN71, PAHs and FDA environmental protection tests. It is a good material to replace PVC.
- The properties are relatively stable, with good temperature resistance (service temperature range – 50-100 ℃), aging resistance, chemical resistance and solvent resistance. Superior processing performance.
- It can be secondary injection molding, coated and bonded with PP, PE, PC, PS, ABS and other matrix materials, or formed separately.
- It has the characteristics of high elasticity of rubber and injection molding.

What are the disadvantages of TPR materials?
Although TPR materials offer many advantages, they also come with some disadvantages:
- Materials may become brittle or lose their flexibility outside the temperature range in which they are used.
- Has poorer elasticity and resilience properties than natural or synthetic rubber.
- Under fixed load conditions, there is a risk of creep or deformation over time, which may cause changes in the dimensions of the object.
- Ultraviolet (UV) protection is relatively weak, which poses a hidden danger in outdoor application scenarios.
- This can make overmolding or product assembly using adhesives more complicated due to poor adhesion to other materials.
What are the uses of TPR materials?
1.Automobile industry
- CVJ dust cover, steering gear cover, shock absorber cover, dust cover, etc.
- Automotive door and window seals, mechanical seals, wheels, etc.
- Car satellite antenna cable buckle, trunk lock assembly, door lock assembly, etc.
- Airbag cover, shock-absorbing chassis, chassis stone-resistant coating, etc.
2.Daily necessities industry
- Hand grips, toothbrush handles, bellows, telescopes, etc.
- Highly transparent replacement for silicone nipples, spoons, shower elastic parts, sanitary ware series, etc.
- Soft tablecloths, curtains, gift boxes, refrigerator boxes, anti-slip mats, etc.
2.Light industrial supplies and cultural and sports supplies
- Hand tools, power tools, gas masks, casters, etc.
- Various racket grips, bicycle, motorcycle grips, luggage and suitcase grips, etc.
- Pen cover rubber parts, diving equipment, mouse balls, chest protectors, mouthguards, etc.
- Sports equipment such as (golf, ski poles) rubber clubs, (tensioners) hoses, knee pads, etc.
3.Medical instruments
- Medical saline bottle stoppers, disposable syringe stoppers, ear cleaning balls, plasma bags, etc.
- Surgical gloves, medical protective clothing, medical sanitary rubber materials, etc.
4.Industrial manufacturing and construction industry
- Seals, conveyor belts, elevator slides, high-pressure washers, etc.
- Decorative membranes, decorative strips, bridge expansion joints, alternative PVC materials, etc.
5.Electronic product
- Cases, buttons, etc. for headphones, chargers, power banks, monitors, etc.
TPR materials are widely used in various industries due to their good elasticity and wear resistance, as well as environmental protection and processability. At the same time, the application of TPR materials is still expanding and deepening, meeting the needs of more fields.
What should you pay attention to when using TPR materials?
- Always wear protective gloves and safety glasses when handling TPR.
- Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and clothing.
- Keep TPR away from any sources of heat or open flames.
- Do not inhale the fumes from TPR.
- Make sure that all tools used to cut, shape or drill TPR are in good condition and are properly grounded.
- Clean up spilled TPR immediately, as it may cause slipping hazards.
- Dispose of TPR properly in accordance with local regulations.
- Store TPR in a cool, dry place away from any sources of heat or open flames.
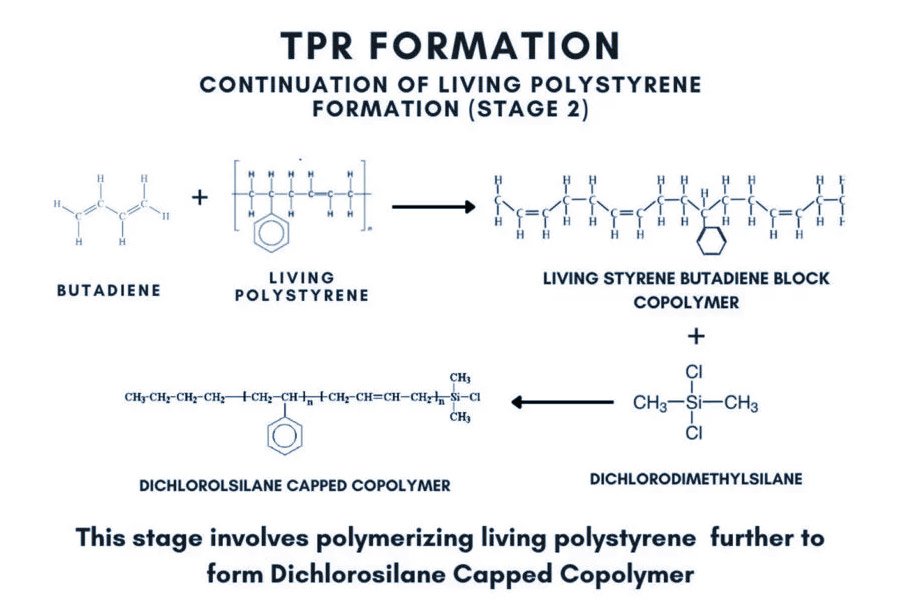
What are the properties of TPR materials?
Thermoplastic Rubber is a material that maintains both the characteristics of rubber and plastic. TPR material is a form of synthetic rubber, which means that it melts into a liquid when heated and becomes solid when cooled. Some of the Properties that TPR rubber and plastic materials provides, includes the following:
- High bending fatigue resistance
- good wear resistance
- Good dielectric properties
- Excellent resistance to weathering and chemicals
- High impact strength
- Elasticity similar to cross-linked rubber materials
- Available in a wide range of durometers, from 20 Shore O to 85 Shore D
- Wide temperature range: -30 degrees Celsius to 140 degrees Celsius (-22 degrees Fahrenheit to 284 degrees Fahrenheit)
- Combines the look, feel and elasticity of thermoset rubber with the processing capabilities of plastics
- recyclable
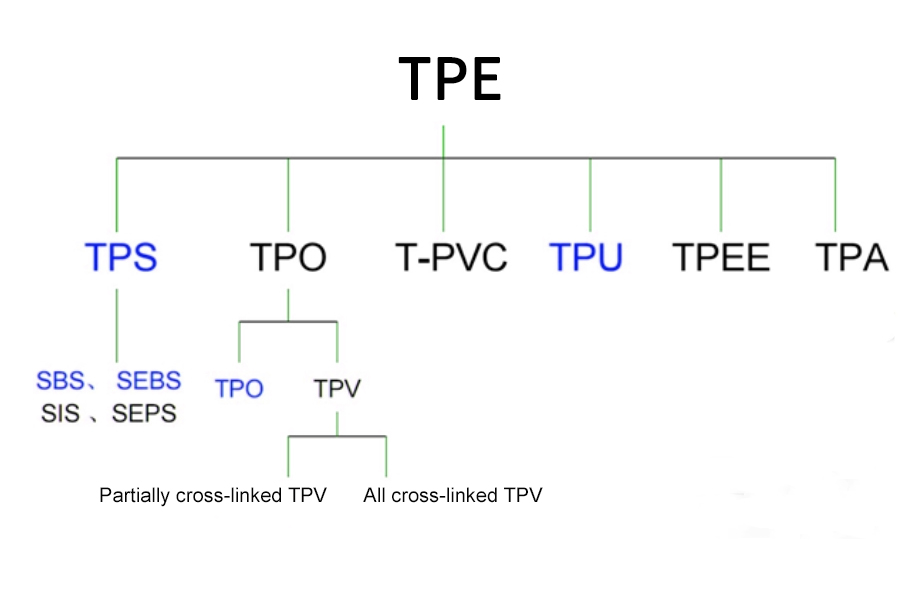
What Are The Different Types Of TPR Materials?
TPR materials come in a variety of different forms, including:
※Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE): This flexible, durable material is often used for parts and components that require flexibility and strength.
※Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): This is a more rigid material often used for parts and components requiring a higher level of durability.
※Thermoplastic Copolyester (TPC): This is a more flexible material often used for components requiring flexibility and strength.
※Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV): This is a more rigid material often used for components requiring a higher level of durability.
How to distinguish between TPE, TPR, TPV and TPU?
The types we come into contact with include TPE, TPR, TPU, and TPV. Do you find it confusing? Let’s teach you how to distinguish these four materials:
TPE
First of all, TPE has such a meaning, which is the general name of all thermoplastic elastomers, including TPR, TPU, TPV, TPEE, TPO, TPAE, etc. The Chinese name is Thermo-Plastic Elastomer.Usually users or what we call TPE often refer to SEBS-based blended modified thermoplastic elastomers. The TPE hardness range of the SEBS system is 0~95A, and it is transparent or natural particles. The combustion flame is yellow, yellow or yellow, the smoke is light, and it has an aromatic smell. but In fact, when users encounter TPE, they should choose the appropriate TPE type according to their specific requirements, and should not subjectively understand the TPE of a specific SEBS system.
TPR
TPR, this is the name of users in Taiwan and even Asia. The earliest people used SBS to synthetically modify it to make rubber, but this rubber is thermoplastic, which means “thermoplastic rubber” in English, or TPR for short. Later, the blend-modified high-performance material SEBS appeared in the SBS family. In order to distinguish it from the SBS-modified TPR, the manufacturer called it TPE. However, many users (especially in Taiwan and Asia) still use the name TPR and do not pay much attention to the difference between SEBS and SBS materials. In fact, there are performance differences between the TPE (TPR) of the SEBS and SBS systems. TPR (according to the above analysis, in a sense, SEBS TBS is used as the material) appears as transparent or white particles with a hardness of 0~95A.
TPV
TPV is a dynamic vulcanization elastomer blended with PP and EPDM. TPV can be regarded as a type of TPO, but its special dynamic vulcanization system gives it excellent comprehensive properties (TPV has better solvent resistance, high temperature resistance and mechanical strength than TPE and TPR of the TBS system) . TPV is currently the most successful and widely used rubber-plastic blend elastomer, so TPV is listed separately. The application of TPV in the automotive industry will be favored by the industry. When TPV burns, it has the petroleum smell of polypropylene PP, and its appearance is yellow or light yellow particles, usually 50~100A.
TPU
TPU, thermoplastic polyurethane. It is made by mixing MDI containing NCO functional group and POLYOL and 1.4BG containing OH functional group. It has good elasticity, good physical properties and various mechanical strengths. Therefore, it is widely used in processes such as injection molding, extrusion, calendering and dissolving into solution resin. It is a plastic material often used by plastic manufacturers, and its products cover various aspects such as industrial use and civilian necessities. TPU has transparent particles in appearance and a hardness of 65A~80D. There is a special smell and hissing sound when burning.
| Comparison of the thermoplastic elastomer properties | |||||
| property | EPDM+PP-X | styrene classTPE/TPR | TPU | ||
| TPV | TPO | SBS | SEBS | ||
| tensile strength | average | good | good | good | excellent |
| compression set (100℃,168h) | excellent | good | average | average | average |
| end-use temperature (℃) | -60-135 | -40-125 | -20-80 | -30-110 | -30-120 |
| air ageing(100℃、720h) | excellent | good | poor | average | poor |
| oil resistivity | excellent | average | poor | average | average |
| Acid and alkali resistance | excellent | average | poor | average | average |
| processing technic | excellent | excellent | excellent | excellent | poor |
What are the differences between TPR and TPE?
Although thermoplastic rubber (TPR) and thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) belong to the same family of thermoplastic elastomers, they have some significant differences in composition, properties and applications. Understanding these differences is critical to choosing the material that best suits your specific needs.
| Difference | Elaborate |
| Composition | TPR is specially formulated to contain thermoplastic and rubber components, giving it more rubbery properties. TPE, on the other hand, is typically a blend of two or more components, including a thermoplastic polymer and an elastomeric phase. This ingredient allows for fine-tuning of properties such as hardness, flexibility and chemical resistance. |
| Hardness range | One significant difference between TPR and TPE is the range of hardness they can achieve. TPR typically has a narrower hardness range, often providing a softer, more rubbery hardness level. TPEs, on the other hand, can be formulated to cover a wider range of hardnesses, from very soft and pliable materials, such as gel-like materials, to harder, more rigid materials. |
| Processing Properties | While TPR is still thermoplastic, its processing requirements may be slightly different due to its different rubber composition. They may require higher processing temperatures and specific processing techniques to achieve optimal results. Known for its excellent processing properties, TPE can be easily molded, extruded or blown using traditional thermoplastic processing techniques. They can be processed efficiently at lower temperatures, thus saving energy. |
| Characteristics and Performance | TPE and TPR may differ in overall characteristics and performance. TPR, with its higher rubber content, tends to have enhanced elasticity, resilience and impact resistance, which can be beneficial in certain applications. TPEs typically offer a balanced combination of elasticity, flexibility and processability. Depending on the specific formulation, they can provide good chemical resistance, UV stability and weather resistance. |
| Applications | TPE and TPR are suitable for use in a variety of industries; however, due to their different characteristics, specific applications may vary. TPR has more rubber-like properties and is commonly used in shoe soles, grips, handles, and other applications that require greater elasticity and impact resistance. TPE is commonly used in automotive parts, consumer products, cables, medical equipment, and more. |
TPR vs. PVC
Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) are used in a variety of manufacturing contexts, but TPR offers superior flexibility and safety, which makes it more desirable in many applications.
Property comparison
| Property | TPR | PVC |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, can be adjusted | Rigid and less flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to many chemicals | Good resistance, but can be compromised |
| Safety | Phthalate-free, safer for consumer products | Often contains phthalates, which are risky |
Applications and Uses
TPR is extensively utilized in products requiring direct contact and flexibility:
- Medical devices such as flexible tubing and face masks
- Automotive interior components that require soft touch and durability
- Footwear components like insoles and outer soles
PVC is primarily used in settings where structural stability is key:
- Plumbing pipes and fittings due to its rigidity and durability
- Electrical cable insulation for its non-conductive properties
- Outdoor furniture as it withstands weather and UV exposure
Cost
While TPR might be more expensive than PVC, it offers significant advantages in flexibility, safety, and environmental resistance that justify the higher cost. PVC, while less costly, poses risks with its use of phthalates and offers less versatility in applications requiring flexibility and safety.

TPR vs. Silicone
Property comparison
| Property | TPR | Silicone |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, suitable for up to moderate temperatures | Excellent, can withstand high temperatures |
| Abrasion Resistance | Superior abrasion resistance | Less abrasion resistant |
| Load-Bearing Capacity | High, suitable for dynamic loads | Moderate, better for static loads |
Applications and Uses
TPR is advantageous in applications requiring durability under physical stress:
- Automotive belts and hoses subject to dynamic stress
- Vibration dampening components in machinery
- High-wear floor mats and industrial flooring
Silicone is indispensable in heat-critical applications:
- High-temperature gaskets and seals in automotive and aerospace
- Protective cooking gloves and silicone bakeware
- Medical implants and prosthetics that require biocompatibility and temperature resilience
Cost
TPR often provides a more cost-effective solution for applications requiring durability and versatility, especially when considering long-term usage and performance needs. Silicone, though ideal for specialized applications, typically incurs higher costs due to its unique properties and manufacturing processes.

Conclusion
TPR material is a versatile and cost-effective plastic material that has been used in various industries for decades. As technology advances and new materials are developed, TPR materials will continue to be a viable option for many products and applications in the future.
Soon, TPR materials will continue to be used in many current applications, such as kitchenware, automotive parts, and medical devices. As research continues to push the boundaries of materials science, new TPR formulations may be developed that are stronger, more durable, and more cost-effective than current formulations. In addition to new formulations, new processes and production techniques can be developed to produce TPR materials faster and more efficiently. This results in cost savings and faster turnaround times for customers.

Finally, TPR materials may have new and innovative uses. For example, TPR materials can be used in 3D printing applications or as a replacement for metal parts in industrial equipment. As technology develops, TPR materials may become more versatile and cost-effective in many industries.
If you have additional questions or would like to learn more about this topic, please feel free to contact our team. Longsheng specializes in prototype parts manufacturing and provides comprehensive services to meet your prototype design and production needs. Feel free to contact us for a free quote.
FAQs
Is TPR safe?
Yes, TPR is considered safe and is commonly used in products that come into direct contact with the human body, such as medical devices and children’s toys. It does not contain harmful substances such as latex, phthalates and heavy metals, and meets international safety standards.
Is TPR waterproof?
Yes, Thermoplastic rubber, like most thermoplastics, is waterproof. It is mainly used in products used for outdoor activity (mainly for waterproof soles in footwear). Soles made of thermoplastic rubber not only provide a good grip on slippery roads but are also lightweight with a rough texture.
Is TPR waterproof?
It is impossible to simply say which one is better, TPR or PVC. Instead, you need to choose based on specific application scenarios and needs. Both are relatively environmentally friendly materials, but TPR meets many standards and performs well in environmental testing. TPR does not require vulcanization and can be directly processed and formed, while PVC needs to be made into products through thermal processing, injection molding and other methods. TPR excels in softness, comfort and reflective properties, while PVC has excellent corrosion resistance, heat resistance, flame retardancy and mechanical properties. Choosing TPR or PVC mainly depends on the specific application scenarios and needs. For example, if a material that is soft, comfortable and easy to process is required, TPR may be a better choice, whereas if a material with excellent corrosion resistance and electrical insulation properties is required, PVC is more suitable.
What Makes TPR Material Used For Shoe Soles So Popular?
TPR material is popular for shoe soles because it provides the thermoplastic properties necessary for easy molding and design, alongside the desirable characteristics of rubber, such as flexibility, durability, and slip resistance. This combination makes TPR an ideal material for producing comfortable, durable, and aesthetically pleasing shoe soles.
Is TPR rubber or plastic?
TPR is neither pure rubber nor pure plastic. It is a thermoplastic elastomer material that combines rubber elasticity and plastic processing properties. This material combines the advantages of rubber and plastic to provide flexible and efficient solutions for a variety of applications.



Pingback: What Advantages Does TPR Material Offer? - geeksmagazine
Pingback: Latex vs. Other Elastic Membranes - Latex Membranes Specialist
It is remarkable, very valuable information
Thank you for your support, each article is written by ourselves, we will update the article every day, you can subscription LS, wish you a happy day.
I am really inspired with your writing talents and also with the format in your blog.
Is that this a paid subject matter or did you customize it yourself?
Either way keep up the nice high quality writing, it’s
uncommon to peer a nice weblog like this one these days.
Blaze AI!
Thank you for your support, each article is written by ourselves, we will update the article every day, you can subscription LS, wish you a happy day.