In the past few years, 3D printing technology has experienced rapid growth. Not only does it change the best way we make goods, but it also expands the boundaries of design to make the impossible possible. The importance of this technology is self-evident, showing great potential and value in many fields, such as medicine, aviation and
development.
Among the many 3D printing consumables, TPU is the most commonly used among 3D printing consumables. This paper will deeply explore the basic knowledge of TPU, printing process, printing applications, etc. aiming to help readers to better use this flexible filament.
What is TPU in 3D printing?
The TPU, or thermoplastic polyurethane, is a thermoplastic elastomer (TPE). The TPU combines the high durability of plastic parts and the elasticity of rubber parts, making the TPU an ideal choice for applications that require repeated bending or compression. Due to its elasticity, the TPU is commonly used as a protective modifier for helmets, protective packaging, vibration-resistant products, and products such as washers or seals. The TPU also has excellent wear resistance, suitable for environments such as high friction or automotive interiors or cables and insulators. For these frequent oil industry applications, TPU oil resistance performance is also trustworthy.

Nature of TPU: advantages and disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| High abrasion, wear, oil, radiation resistance | Requires special manufacturing conditions through all methods |
| High elasticity | Some grades have short life cycles |
| Strength | Material cost is higher compared with some analogs (like PVC) |
| Good tactile properties | Requires water amount control before processed |
| Easily colored | Clear TPU yellows irreversibly |
| Compound and properties versatility | |
| Can be sterilized |
Common type of tpu 3d printing material
The common type of tpu 3d printing materialcan be classified from the following perspectives:
- Soft segment structure is divided into: polyester type, polyether type, polyolefin type.
- Hard segment structure: aromatic TPU, aliphatic TPU.
- With or without cross-linking: pure thermoplastic TPU, semi-thermoplastic TPU.
- Applications of finished products: special-shaped parts, pipes, films, adhesives, coatings, fibers.
TPU 3D Printing process
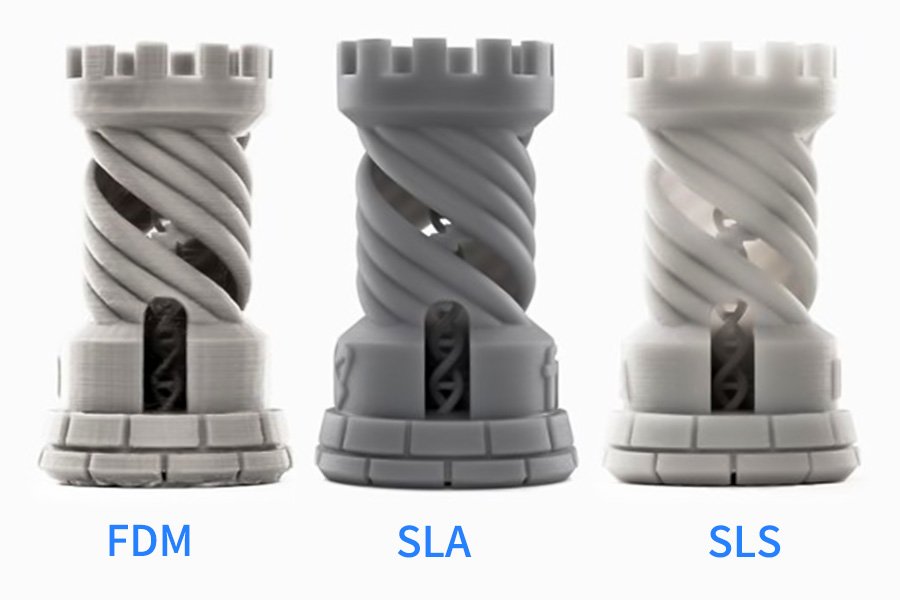
What are the FDM, SLA, and SLS?
- FDM (molten deposition molding): This printing technology involves building parts or prototypes using plastic wires extruded from the nozzle. The design range is very wide; you can use FDM to print complex geometries and simple housing and fixtures.
- SLA (three-dimensional light curing): is an additive manufacturing process in which the light source solidifies liquid resin into hardened plastic. SLA 3D Printing provides the fastest speed, the highest resolution and accuracy, the clearest details, and the smoother surface finish of all 3D printing technologies. Another major advantage of resin 3D printing is the diversity of available materials. Material manufacturers have created innovative SLA resin formulas with a wide range of optical, mechanical, and thermal properties that match standard, engineering, and industrial thermoplastics.
- SLS (Selective laser sintering): an additive manufacturing (AM) technology that uses high power laser to burn small particles of polymer powder into a solid structure based on 3D model. The low cost, high productivity, and proven materials of each part make the technology ideal for a range of applications ranging from rapid prototyping to small batch, bridge, or custom manufacturing.

Printing speed and manufacturing time
- FDM: FDM is struggling with advanced design and complex options, which may slow down the printing process. Still, it is well suited for basic proof-of-concept models and simple parts.
- SLA: SLA printers can produce components with complex designs and complex functions more effectively than FDM printers. However, the production speed of 3D printing may actually be slower than the conventional production methods.
- SLS: SLS is suitable for complex geometries, including internal options and thin walls, and can effectively produce useful parts. Additive manufacturing can reduce lead times in cases of product growth and small batch manufacturing.
Comparing the three Pros and Cons of the three
| Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) | Stereolithography (SLA) | Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | |
| Pros | Fast | High accuracy | Strong, functional parts |
| Low-cost consumer machines and materials | Smooth surface finish | Design freedom | |
| Good Mechanical Strength & Durability | Large range of functional applications | No need for support structures | |
| Cons | Low accuracy | Sensitive to long exposure to UV light | Rough surface finish |
| Low details | Not best for outdoor use in direct sunlight | Limited material options | |
| Limited design compatibility | Limited Print Size | Lack of Color Options |
The three have different purposes
- FDM: FDM is suitable for a variety of ordinary thermoplastics, suitable for making simple parts and basic models.
- SLA: Due to its high decision-making and final quality, SLA is used in a wide range of industries, including engineering, product design, manufacturing, dentistry, pharmaceuticals, jewelry, and education.
- SLS: SLS is trusted for its ability to produce strong, practical components, and is adopted by engineers and manufacturers in different industries.
TPU 3D Preparation before printing
Before performing the TPU 3D printing, the following preparations are required:
1.Choose the suitable 3D printer
Ensure that the selected 3D printer supports the TPU material and has appropriate temperature and pressure settings to ensure proper melting and extrusion of the TPU material.
2.Prepare the TPU consumables
Select TPU consumables with reliable quality to ensure their compatibility with the printer. When storing TPU supplies, they should be placed in a dry and cool place to avoid direct sunlight and high temperature environment.
3.Clean printing platform
Before printing, ensure that the printing platform is clean and free of dirt and oil. This helps to ensure that the TPU material adheres smoothly to the platform during the printing process and reduces the risk of printing failure.
4.Set the print parameters
Set appropriate printing parameters according on the properties of the TPU material and the desired print model. This includes the printing speed, temperature, and high layers. Ensure that these parameters match the properties of the TPU material for optimal printing.
5.Preheat printer
Let the printer warm for some time to ensure that the nozzle and extruder reach the appropriate temperature. This helps ensure that the TPU material melts and extrsmoothly during printing.
6.Check model files
Before printing, check that the model file is correct. Ensure that the model file is not wrong or corrupted and is suitable for printing on the selected 3D printer.
TPU 3D Post-processing after the printing process
TPU is one of the most difficult FDM 3D printing materials to improve through the post-processing technology. Because of its ductility, it is not particularly well to techniques such as grinding, painting, or coating.
Remove the TPU print from the print bed
The TPU sticks more firmly to the print bed at higher temperatures, so the cooling of the print bed is easier to remove the print piece. The cooled bed may cause a slight contraction of the TPU print, which may help it fall off the bed on its own.
When manually removing TPU prints, flexible, thin and flat tools such as plastic scrapers or paint knives are recommended. The tool should slide gently and evenly under the print from the edge to the center. The flexibility of the TPU means that the print can be bent slightly to help it escape from the bed, but care must be taken not to deform it.
Bed adhesion method can also affect the difficulty of printing removal. For example, if glue sticks or hairgel are used on the bed before printing, it may be necessary to clean the bed with warm water and mild detergent to fully release the printing effect. In contrast, if flexible construction surfaces such as magnetic beds or removable spring steel plates are used, the curved surface.
Support for removal and cleaning
After removing the print from the print bed, the first step is to remove any supporting structures that are printed with the model. Using the TPU, this can usually be done by hand due to the flexibility of the material. But a pliers or a beauty cutter can be used to remove hard-to-reach areas or more complex printing. Care should be taken in this process not to damage the print or to leave any residue from the supporting structure.
If drawing or leakage occurs during the printing process, you may need to clean up these defects using the same tools as the removal support.
TPU prints can usually be cleaned with warm water and mild soap, if desired. Soft brushes can be used to remove dirt or debris from the print.
level and smooth
TPU is known for its durability and resistance to multiple common solvents, making it difficult to smooth it out using the chemical methods used in other 3D printed materials. While this is usually a benefit, it means that any layer line or other defects in TPU printing cannot be easily smoothed out after printing.
A DIY solution for TPU smoothing is to use a hot-air gun that partially melts the surface of the printed part to form a uniform surface and reduce the layers. However, this approach is difficult to control and proceed precisely.
The pull on the model was processed
Drying the TPU wire before printing reduced the drawing on the printed parts, but this could not be eliminated completely, especially in models with long strokes. Therefore, if the model needs surface treatment, the removal of the drawing mold on the model. If you want to remove the drawing phenomenon from the model, you can choose to blow it out with the hot air generated by the hair dryer, or use the lighter flame to quickly burn the drawing area. If your printer doesn’t have these devices, you can heat the model with a small oven. However, be careful to hurt yourself and destroy the model.
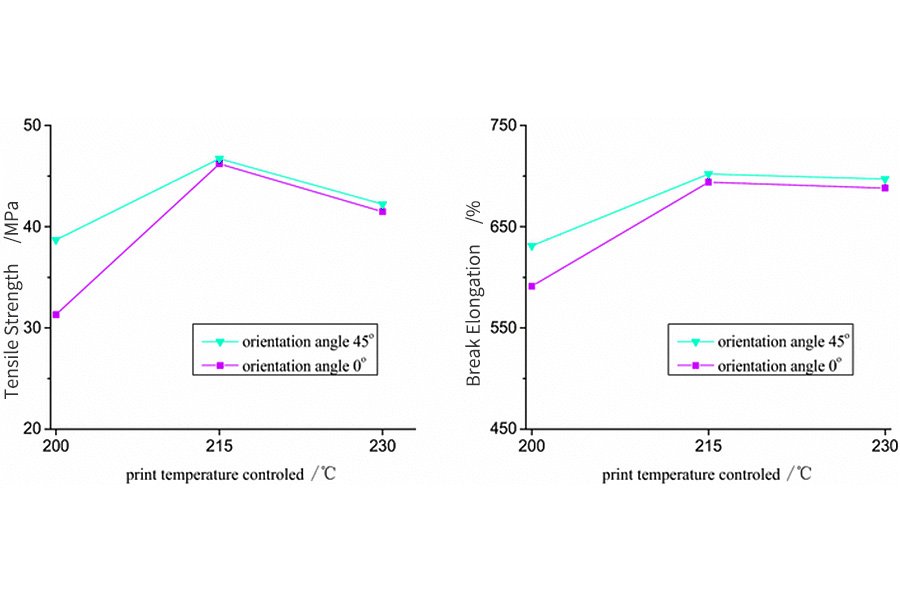
TPU 3D Print the parameter settings
When using TPU printing, it is critical to set the print parameters. This process includes setting the correct temperature for the nozzle and heating bed, adjusting the printing speed and retraction.
1.temperature
The temperature of the nozzle and heating bed plays a crucial role in ensuring the TPU filament melting and proper bonding. In general, the recommended nozzle temperature of a TPU is about 230℃. However, the exact temperature depends on the specific brand and type of the TPU filament used. Always recommend reference to the manufacturer’s guide for optimal temperature settings.
2.speed
Print speed is another important setting that needs to be adjusted when printing TPU parts.Due to the flexibility of TPU, printing is usually recommended to be slower than rigid materials such as PLA or ABS. TPU is usually to at 15 to 20 mm per second. A slower printing speed allows better control of consumables and help prevent problems such as drawing or leakage.
3.Retraction
Retraction is the mechanism in a 3D printer, which pulls the filament backwards into the extruder as a means of preventing the oozing of the melted filament. This feature is very useful with rigid filaments like PLA and ABS, however, with TPU filaments, retractions can be challenging and can result in clogging. That’s why it is highly advisable to disable retraction to prevent stretching and compressing of the flexible filament in the nozzle.
Why is TPU so hard to print?
TPU constitutes a material with obvious limitations in the field of 3D printing. The soft and flexible yarn are easier to print than the stiffer materials.
TPU printing technology is more challenging than plastic, but by following this advice, it can significantly improve the chances of most TPU 3D printers successfully completing the printing task:
- Avoid the TPU printing speed is too fast
- Use the appropriate spray nozzle
- Adjust for the temperature and retraction
- The recommended print rate is set to 5-30 mm / second,
- The feed speed should be kept slow and uniform
- Negative tolerance shall be used in each part
- Avoid using rafts
Comparison between TPU and PLA
| TPU | PLA | |
| Print temperature | 225–235℃ | 180–230°C |
| Print bed temperature | unheated | not heated or 60–80 °C |
| Tensile strength | 20–55 MPa | 50 MPa |
| Flexibility | high | low |
| Durability | medium | medium |
TPU vs PLA: Which One to Choose?
When faced with the choice of TPU and PLA, 3D printer users are faced with an obvious fact: TPU is a flexible filament, while PLA is a very rigid filament. But there are other factors to consider.
When faced with the choice of TPU and PLA, 3D printer users are faced with an obvious fact: TPU is a flexible filament, while PLA is a very rigid filament. But there are other factors to consider.Of course, you may be making parts that do not require a particularly high level or flexibility or stiffness. In this case, you may consider other important factors, such as heat resistance: the TPU requires a higher extruder temperature, but the TPU part maintains its shape and function even at high temperatures. At the same time, PLA components will begin to soften around 60 C and therefore only be useful at low or room temperatures.Among 3D printed materials, PLA and TPU are commonly used choices. The PLA components begin to soften at around 60 C, so they are mainly suitable for the environment at low temperature or room temperature. The PLA has a higher tensile strength compared to the TPU, although the TPU is more durable. On the other hand, TPU printing has better wear resistance. The choice of PLA or TPU depends on the cost and the specific printing requirements.
I hope that through the above introduction can help you to better choose their own 3D printing materials.
TPU 3D Print applications
The traditional manufacturing of TPU parts has proven workflows that remain ideal for mass production of rubber products. However, the 3D printed TPU is a good alternative in many cases, including the need for speed or ease of use, rapid prototyping, on-demand manufacturing aids, and customized applications. Starting with a design process that requires rapid prototyping to a final design using parts (or even mass-customized consumer goods), the 3D printed TPU can make workflows faster and more efficient without sacrificing mechanical performance or fidelity.
Fast prototype production
3D printing with TPU enables companies to prototype in their own premises, thereby reducing delivery times and reducing costs previously charged by a service agency or machine shop.
Small batch and custom garment products
In the sports, fashion and wearable technology industries, providing personalized choices is crucial for brands seeking more market share. The costs associated with the tools make small batch or one-time production almost impossible until 3D printing technology opens the door.
medical treatment
With its superior durability and toughness, the 3D-printed TPU is ideal for prosthetics, orthotics, patient-specific appliances, and medical equipment. By combining the high tear strength and break elongation of rubber material with the design freedom and durability of SLS 3D printing, end-use parts that can be flexible and robust in 3D printing.
automobileindustrial circleautomobile
The TPU can be used for shock absorbers in automotive and aerospace testing, as well as fixtures for industrial processes such as thermoforming unique shape parts. In automotive factories, large robotic systems operate on a gantry that must be bent and rotated. Custom cushions and soft shells can help these machines avoid friction and extend their service life.
Manufacturing additives
The TPU addresses one problem facing many manufacturers: how to prevent their multi-million-dollar manufacturing technology from experiencing too much wear and tear. Soft touch manufacturing aids can help extend the life of heavy machinery by cushioning certain shocks or providing perfectly shaped fixtures. When the seal or gasket is torn after years of reuse, the operator can immediately print the replacement and get the line to resume within hours, rather than waiting days or weeks to get new parts. Increasing material capability is more insurance for manufacturers —— it can protect them from damaged parts or faulty machine parts that they have not foreseen. The more mechanical properties they can rely on internally, the more they can avoid supply chain delays and high repair costs from OEMs. With rubber 3D printed parts, it is now possible to repair or replace a new subset of equipment components on demand. Avoid factory production or process closures can save thousands of dollars a day.
TPU 3D Technical challenges and solutions of printing
Although TPU 3 D printing technology has obvious advantages and very wide application prospects, it also faces some technical challenges in the practical application process. Here are some of the common TPU 3D printing technology challenges and their possible solutions:
Technical challenges
1.Precision problem:
Due to the viscosity and elasticity of TPU materials, problems such as interlayer stripping and warping deformation may occur in the printing process, resulting in reduced printing accuracy.
2.Material cost:
Good-quality TPU materials have a relatively high viscosity, which may limit their application in certain fields.
3.Printing speed:
TPU may be slower compared to some other 3D printing materials, especially when printing large and complex parts.
4.Printer adaptability:
Not all 3D printers are suitable for printing TPU materials, requiring a specific print head and temperature control system.
solution
1.Improved printing accuracy
By adjusting the printing speed, nozzle temperature, hot bed temperature and other parameters, reduce the warping deformation and interlayer stripping problems. Use a closed printing environment to introduce a post-processing process.
2.Material cost reduction
Reduce the cost of TPU materials by improving the material formulation and production process. Recycling and reuse the waste generated during the printing process to reduce material consumption.
3.Printing speed increase
Adopt multi-nozzle, multiple heat source and other design to improve the printing speed. Improve the , reduce the empty travel and invalid motion in the printing process, and improve the printing efficiency.
4.Improve the printer adaptability
A special print head and temperature control system are designed for the characteristics of the TPU material. Upgrade the hardware and software of the printer to make it better adapt to the printing requirements of TPU materials.
TPU 3D Future prospects of printing
The future outlook of TPU 3D printing is full of opportunities and challenges. Through technological innovation, application expansion, environmental protection and sustainable development, digital and intelligent, education and popularization efforts, we can expect TPU 3D printing to play a greater role in the future and bring more innovation and convenience to various industries and fields.
Conclusion
The importance of TPU in 3D printing is mainly reflected in its unique material characteristics and design flexibility, which can meet a variety of complex and special needs. At the same time, the application advantages of TPU include high elasticity, wear and weather resistance, biocompatibility, lightweight, environmental sustainability and rapid prototyping, so that TPU 3D printing technology has a wide range of application prospects in many fields.
When selecting 3D printing consumables, consider the physical and chemical characteristics of the fabric, price, printing problems, and half-specific use. Although these are normal indicators, the specific choices may vary depending on the specific formulation of the fabric, the printing situation, and half of the specific needs.
Longsheng can provide professional advice and high-quality 3D printing companies according to your special needs. Whether you need prototypes, dedicated parts, or creative work, they can meet your needs!
FAQs
Is TPU better than PLA?
Both TPU and PLA are commonly used 3D printed materials, each of which has different characteristics and advantages, so it is not possible simply to say that TPU is better than PLA or vice versa. Choosing either a TPU or a PLA depends on the specific application requirements. TPU is a better choice to make parts with elasticity, flexibility and high mechanical strength, and PLA is environmentally friendly and easy to print.
Is TPU safe for human skin?
The TPU is usually safe for human skin. TPU is a new environmentally friendly material, safe, non-toxic, recyclable and recyclable with a wide range of applications. However, although TPU itself is safe for human skin, some chemicals may be used during its production, which may have negative effects on the health of workers. Therefore, appropriate safety measures need to be taken in the manufacturing process to avoid workers’ exposure to these harmful substances.
How to improve the surface quality of the TPU print?
Surface quality is improved by fine-tuning the retraction settings to reduce wire drawing, using overhanging support structures, and selecting lower layer heights to reduce the visibility of each layer. It is also important to maintain the optimal print temperature of the TPU, usually around 230 °C.
Can I use both TPU and PLA in the same print?
Yes, if your 3D printer supports multi-material printing, you can use both materials in the same print. This enables you to leverage the properties of both materials in a single object.
Resource
Performance comparison of the 3D



Pingback: Is TPE or TPU better?