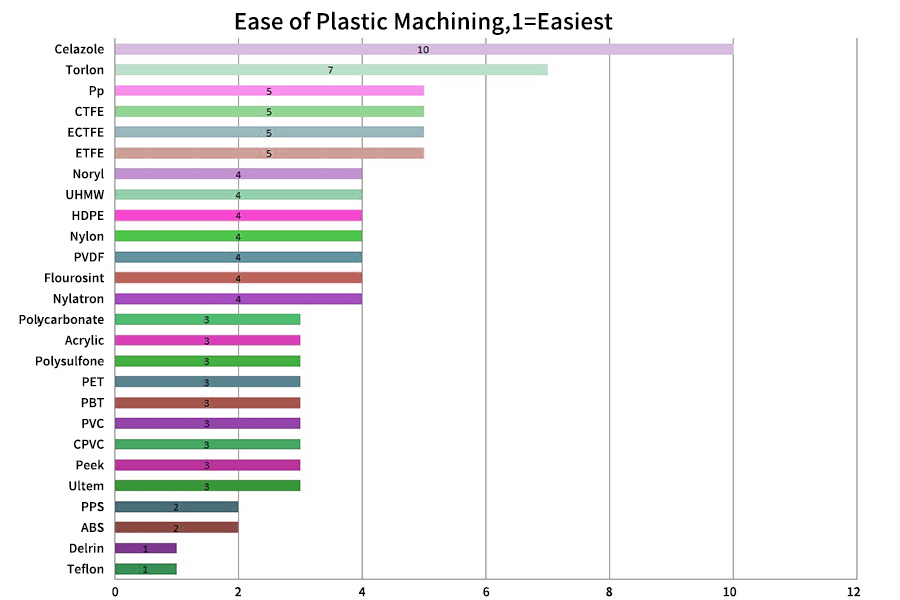
When it comes to machining plastics, a common misconception is that they are inferior to metalworking parts. In fact, computerized CNC machining services using plastics such as Kevlar or ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) can provide similar strength to weight ratios.machining is a general term for controlled subtraction manufacturing technology for the production of parts made of various materials. Today, many companies use CNC machining to improve the accuracy and accuracy of the final product.
Therefore, the use of plastic parts on the machine depends on the intended design application and tolerance. Do you know any of the supported plastic machining materials? This article focuses on the different engineering plastics suitable for your next custom machining project and introduces the types and properties of these machined plastics, plastic machining methods, and plastic machining plant options.
What is plastic machining?
Plastic machining is a way to manufacture precision plastic components in aerospace, automotive, electronics and other industries. This material reduction process removes the material from the plastic raw material to generate a finished product with a predetermined shape and size. This machining method actually covers many different machining processes and combines equipment such as cutting machinery, drill machines, grinders, lathes, milling machines, and other such tools. Computer numerical control machining is a common machining proces
Cutting
Generally, cutting operations generate some amount of heat, which can damage the plastic material. When cutting plastics, operators must take care to avoid causing thermal warping. With proper precautions, sawing is completely appropriate for cutting plastic sheets to a desired size and shape.
Turning
Plastic turning operations occur on a lathe, which rotates and manipulates the workpiece to allow the stationary cutting tool to cut and remove excess material as per the intended design.
Milling
While turning operations involve the rotation of the plastic workpiece, milling operations require the rotation of the cutting tool to remove chips of plastic from the stationary workpiece. Some milling techniques work better with plastics than others (such as down-milling), but the ideal choice depends on a number of factors.
Drilling
Drilling plastics can be risky, resulting in overheating or shearing if the proper drill isn’t selected. However, given the proper preparation and tools, a skilled technician can create both small and large diameter holes in a plastic product without damaging its structure.
Grinding
Grinding is similar to milling in that the process removes chips of plastic from the workpiece to alter its shape. The main difference is that milling uses intermittent cuts, whereas grinding continuously shears plastic from the product to achieve a smoother shape and surface finish.

Considerations for Plastic Machining
Ensuring the success of a plastic machining project requires choosing construction materials and machining operations that are well-suited for each other. When planning a plastic machining project, some of the factors to consider are:
1.Plastic type
Different chemical compositions yield different physical characteristics, impacting everything from strength and chemical resistance to the cost of the material. When choosing a plastic material for a machined part, it is important to keep these properties in mind as they will influence how well the material withstands the stresses of manufacturing and the end product withstands the stresses of the intended application.
2.Thermal regulation
In general, plastics melt at substantially lower temperatures than metals. As such, proper heat regulation, including the use of coolants, is essential if a polymer is to withstand machining.
3.Process support
As plastics are less rigid than metals, the vibrations generated by the machining operations can more easily cause burrs, cracks, and chatter marks. Incorporating additional support structures during machining operations reduces the risk of damage to the end product.
4.Finishing options
Many companies employ finishing services to enhance the functional and aesthetic properties of a machined product. Some of the typical finishing processes are annealing, polishing, and coating.
Plastic machining application
Many industries have applied machining plastic parts. The process is ideal for manufacturing:
- Aerospace parts
- Analyze equipment parts
- Food processing parts
- Gas oil system components
- Healthcare equipment
- Marine parts and equipment
- semiconductor device
Characteristics of plastic machining
Differences in thermal performance
There are significant differences in the thermal properties of plastics and metals. The heating capacity of plastic is small and the thermal conductivity is poor, so in the process of mechanical processing, the heat generated by metal tools and plastic friction is mainly transmitted to the tool, and the surface temperature of plastic is easy to increase significantly, easy to local overheating, soft, discoloration and coking.
The thermal expansion coefficient of plastic is much higher than that of metal, about 1.5~20 times that of metal. Therefore, even if the temperature does not change much, the size of the plastic will produce a large change, which is unfavorable for the control of the dimensional accuracy of the product.
The elastic modulus is low
The elastic modulus of plastic is only 1 / 10~1 / 60 of the metal, which means that during the machining, the pressure applied by the fixture and tool leads to the torsion and deviation of the plastic products, which affects the tolerance of the parts.
Poor cutting performance
The hardness of plastic is low, easy to be pressed into the cutting blade, resulting in the increase of the cutting force, which may affect the quality of the processing surface.
Engineering plastics because of the long molecular chain and molecules contain a variety of functional groups, these functional groups are strong binding force, the requirements of processing technology is relatively high, relatively difficult to process.
The melting temperature is low
The melting temperature of plastic is usually low, so special attention is needed to control the temperature to avoid overheating leading to melting or burning of plastic.
The surface is prone to produce scratches
The surface hardness of plastic is low and easy to be cut by cutting tools. In the processing process, it is necessary to choose the appropriate cutting tools and cutting parameters to reduce the generation of scratches.
Short processing cycle
Compared with metal parts processing, the processing period of plastic parts is shorter. This is due to the variety of plastic processing methods, such as injection molding, blow molding, etc.these forming methods can quickly produce finished products, improve production efficiency.
The cost of materials is low
The cost of plastic materials is relatively low, and the molding process does not need heating, cooling and other complex steps, the cost is relatively controllable.
High molding accuracy
Plastic parts processing molding accuracy is high, not easy to appear metal parts prone to deformation, welding joints and other problems. The size, shape and surface smoothness of the formed parts can be well guaranteed.
What are the common machining plastics?
Today, many companies use computer numerical control (CNC) machining to improve the accuracy and accuracy of the final product.The choice of machitable plastics can affect the processing costs. Therefore, we have carefully listed the following CNC plastics and their Types , advantages and disadvantages, uses of common machining plastics in plastic CNC processing applications.
1.Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a very common CNC machining plastic with impressive strength and impact resistance. It is the easiest plastic to CNC machine and is available in various grades on the thermoplastic market.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Strong mechanical properties | Low heat resistance |
| Excellent machinability/customization | Not suitable for food contact |
| Budget-friendly | Not UV stable |
Uses
- Hard hats
- Helmets
- Vacuum Cleaners
- Printers
- Musical Instruments
- Kitchen Utensils
2.Nylon (Polyamide)
Nylon or polyamide (PA) is a synthetic thermoplastic polymer with excellent thermal and mechanical properties. The nylon 66 grade is the commonly used polyamide for plastic CNC machining services.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Good chemical resistance | Prone to absorb moisture |
| Excellent wear resistance | Poor dimensional stability |
| Lightweight polymer | Limited heat resistance |
| Great shock absorption | Sensitive to UV radiation |
Uses
- Clothes
- Fishing lines
- Fishnets
- Conveyors
- Seatbelts
- Parachutes
- Camping gear

3.Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC is another easy-to-machine thermoplastic polymer suitable for plastic CNC machining. It is lightweight, and machined parts can withstand harsh environmental factors like sunlight.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Flame and chemical resistance | Produces harmful chlorine gas during recycling |
| Very durable | Limited heat resistance |
| Budget-friendly | |
| Electrical insulator |
Uses
- Building materials
- industrial products
- daily necessities
- pipeline
- wire and cable
- packaging film
4.Acetal Or Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Acetals are sometimes referred to as Delrin plastics or polyoxymethylene (POM). You can use them for plastic CNC machining applications that require fine machinability properties and low surface friction.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Can withstand harsh environmental conditions | Low compatibility with adhesives |
| Impact resistance | Flammable |
| Good aesthetics | Poor acid resistance |
Uses
- Seat belt parts
- Electronic Cigarettes
- Insulin pens
- Water meter
- Guitar picks

5.Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene (PE) is a common plastic CNC machining material known for its versatility. PE could exist as low-density polyethylene (LDPE) or high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Easily available and affordable | Not UV stable |
| Safe for industrial food packaging | Difficult to bond |
| High flexibility |
Uses
- Food packaging
- Bottles
- Pipes
- Trays
- Grocery bags
- Trash bags
- Insulations
- Toys
6.Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is also known by its common name Polypropene. It belongs to the thermoplastic polymer category. Its properties are a slight improvement to polythene.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It is not expensive | Low heat resistance |
| Excellent moisture resistance | Not UV stable |
| Durable and lightweight |
Uses
- Machine parts
- Flexible packaging
- Rigid packaging
- Tote bags
- Bottle caps
- Medical equipment

7.Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane (PU) is a polymer material formed by polyols and polyisocyanate by polycondensation reaction.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Physical performance is stable | Poor permeability |
| Strong durability | Not resistant to scratch |
| Good air permeability | Not environmental protection |
| Good sound insulation and heat insulation performance | Easy to age |
Uses
- 3D printer filament
- Automotive instrument panels
- Power tools
- Sports equipment
- Caster wheel
- Footwear
- Inflatable rafts
- Fire hoses
8.Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC)
Using CPVC plastics for CNC machining services is similar to conventional polyvinyl chloride (PVC) applications. However, CPVC makes up for the low thermal properties of PVC.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Same as PVCs | More expensive than ordinary PVCs |
| Higher temperature resistance | Slight environmental chlorine concerns |
Uses
- Cold water delivery system,
- Hot water pipes
- Plumbing
- Vents
9.Polysulfone (PSU)
Polysulfone (PSU) is a semi-transparent, high-performance thermoplastic polymer with high mechanical strength in machined parts design. In addition, PSU plastics on CNC machines can withstand high temperatures and are suitable for biomedical applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Good chemical and heat resistance | PSU plastics can be expensive |
| Dimensional stability | Sensitive to UV radiation |
| Electrical insulators | Poorer machinability than close alternatives |
Uses
- Waste water recovery systems
- Hemodialysis systems
- Gas separation
- Food and beverage equipment
10.Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS)
The PPS plastic is an alternative engineering thermoplastic with thermally stable properties up to about 425°F. It is a perfect fit for precision CNC machining plastics projects that require dimensional stability.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Excellent chemical resistance | Not UV stable |
| Good heat resistance | Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) is not cheap |
| Low moisture absorption |
Uses
- Coal boiler filter fabric
- Film capacitors
- Gaskets
- Specialty membranes
- Packing

11.Polycarbonate (PC)
Customers interested in custom machined parts design that is transparent and durable should consider polycarbonate (PC) plastic parts in their next computer numerical controlled machining projects.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Easy-to-machine plastics | Highly susceptible to scratches |
| Great for transparent applications like windows | Low chemical resistance |
| Excellent strength-to-weight ratio |
Uses
- Safety glass
- Bulletproof glass
- Room divider
- Electronics
- Construction
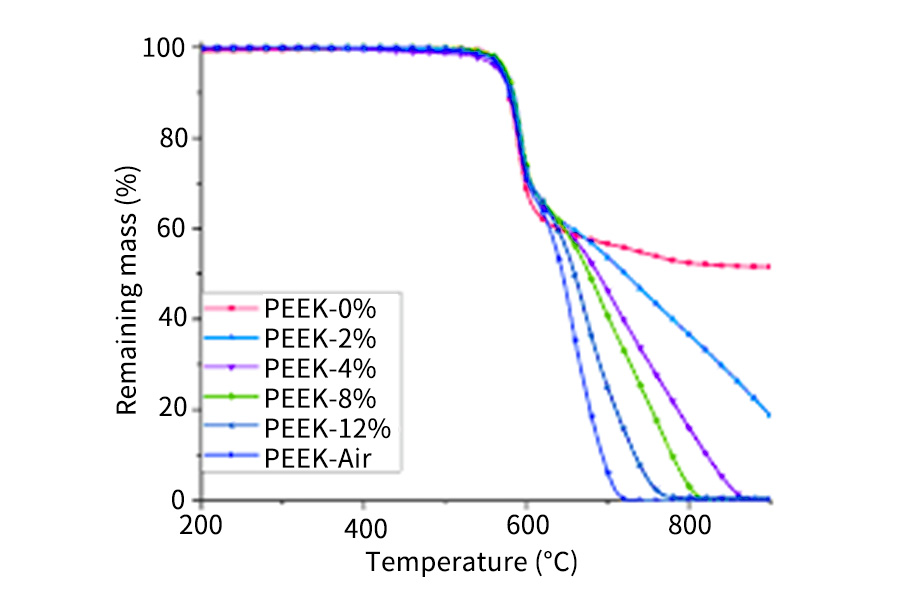
12.Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
PEEK is a very popular CNC machining thermoplastic. It is colorless in pure form. Its melting point is 343 °C, which makes it good for high-temperature applications. Operating temperatures of many PEEK subtypes easily go up to 250 °C.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Resistant to thermal degradation | Expensive |
| Good operating temperature | Degrades in UV light |
| Chemical resistant | Does not biodegrade |
| Good mechanical properties |
Uses
- Water pumps
- Aerospace parts
- Medical implants
- Bearings
13.Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is in the subclass of polyester plastic materials. It is the major constituent of packaging in the food and beverage industries. It is a hygienic, water-resistant, and lightweight material. It is also one of the easy-to-machine plastics used in plastic CNC machining projects.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Transparent material | Limited heat resistance |
| Highly recyclable | Not ideal for extreme weather |
| PET plastic is not expensive | |
| Good chemical resistance |
Uses
- Water bottles
- Jars
- Rope
- Automotive parts
- Protective packaging
14.Carbon Fiber (CF)
Carbon fiber is basically Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers (CFRP). It has thin strands of carbon fiber added to a base plastic for improved properties. It is classified as a composite material.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Extremely strong plastic | Expensive |
| Lightweight | Conducts heat |
| High rigidity | Poor electrical insulation |
| High strength-to-weight ratio |
Uses
- Aerospace
- Machine tool spindles
- Robotic arms
- Power transmission shafts
15.Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
PTFE is a synthetic polymer derivative of tetrafluoroethylene. Its trademark name is Teflon®, and it is best for non-stick CNC applications in medical equipment or artificial body parts.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Non-stick | Costly |
| Heat resistance | Difficult to mass produce |
| Cold resistance | Deforms under pressure |
| Comes in a coating form | It cannot be welded |
Uses
- Non-stick cookware
- Abrasion-resistant coating on automobiles
- Coating surgical equipment
16.Polysiloxane (Silicone)
Polysiloxane is a colorless, rubber-like substance also called Silicone. It is used for many plastic CNC machining applications in electronics, household, electrical, automobile, and aviation manufacturing industries.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Non-toxic and biocompatible | Silicone is not cheap |
| High flexibility and elasticity | Some silicone grades have low tensile strength |
| Can withstand temperatures between 150°F and 550°F | |
| UV stable |
Uses
- Lubricants
- Sealants
- Adhesives
- Thermal insulation
- Electrical insulation
17.Poly Paraphenylene Terephthalamide (Kevlar)
Poly Paraphenylene Terephthalamide usually goes by its common names kevlar and twaron. It is one of the most popular aromatic polyamides globally. It is a synthetic fiber developed by DuPont. Its physical properties are comparable to or even better than metals and alloys.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Lightweight | It is expensive |
| Good tensile strength | Difficult machinability |
| Abrasion resistance | Absorbs moisture |
| Dimensional stability |
Uses
- Racing tires
- Bicycle tires
- Bulletproof vests
- Armor
18.Polyethersulfone (PES)
PES plastic is available in blocks, sheets, and rods. It is also sometimes referred as PESU. These plastics have great physical properties and temperature handling. The color of PES is reddish brown with good transparency.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Good dimensional stability | Rough surface |
| Good temperature handling | Hydrophobic |
| Can withstand high temperatures for extended periods | Membrane fouling |
| High mechanical strength | |
| Rigidity | |
| Hydrolysis resistant |
Uses
- Dialyzer membranes
- Surgical theater luminary
- Infusion equipment
- Sterilization boxes
19.Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE)
TPE is also sometimes termed as Thermoplastic Rubber. It is a mix of different polymers, often plastic and rubber. TPE is different from conventional elastomers, which is thermosetting in nature. However, the thermoplastic properties of TPE allow the application of many different manufacturing methods.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Good elongation | Below-average heat resistance |
| Returns to original shape after elongation | Significant degradation in physical properties with temperature rise |
| Long service life | |
| Higher physical range than alternative plastics |
Uses
- Cables and wires
- Toys
- Automotive parts
- Shoes
- Sports equipment
- Consumer goods
The method of plastic machining
Cutting
- Turning: Plastic is cut with a rotating tool to obtain the desired shape and size.
- Milling: Rotary cutting using multi-edged tools, often used to machine flat surfaces, grooves, and contours.
- Drilling: Use a drill to make holes in the plastic.
- Tapping: Using a tap to create internal threads based on the drilled hole.
- Thread turning: Processing external threads on the plastic surface.
Sawing and shearing
- Sawing: Cutting plastic using a saw blade or saw blade.
- Shearing: The plastic is sheared and separated through the relative movement of the upper and lower blades.
Die cutting and punching
- Die Cutting: Using a die to punch the desired shape out of plastic.
- Punching: Punching holes in plastic.
Modification processing
- Filing: Used to smooth plastic products and sheets and remove burrs and waste edges.
- Drum burnishing: Place the product, diamond-shaped wood blocks and mold materials into a hexagonal drum, and remove the waste edges and sprue residues through rotation.
- Grinding: Use a grinding wheel or abrasive belt to remove the waste edges and sprue residues of molded products, smooth the surface or modify the size.
- Polishing: Use a rotating cloth wheel with abrasive material or glossy paste attached to the surface to polish the surface of plastic products.
Surface coating and decoration
- Dissolution brightening: Dip thermoplastic products in soluble organic solvents, and then dip them in insoluble solvents to remove the surface solvent, thereby increasing the surface gloss.
- Transparent coating: Spray the resin solution directly onto the surface of the product to form a transparent coating.
- Color decoration: Adding colorful patterns or patterns to the surface of plastic products through heat embossing, silk printing, printing, etc.
Joining processing
- Bonding: Using adhesives to join plastic parts to other materials.
- Welding: Joining plastic parts together by melting them with heat.
- Mechanical joining: The use of mechanical force to join plastic parts to each other or to parts of other materials.
Plastic machining plant selection
Each plastic machining plant provides a unique set of processing skills, so it is necessary to find a factory specializing in key aspects of the project. Suitable factories should not only produce quality products, but should also be able to deliver the products on time. In addition, they should promptly respond to your inquiries and optimize your experience.
Here are some factors to consider when choosing a plastic machining partner:
Material availability and expertise
When making plastic products, different machining plants focus on providing different materials. Be able to handle the material you need and offer multiple options.It is also important to check whether the company is proficient in material selection. Most mature and reliable factories have established good relations with their raw material suppliers. This will accelerate the satisfaction of specific requirements, such as design tolerances, heat resistance, and permeability.Your plastic machining partner should be able to help you select the right material for your application.
Equipment and manufacturing capacity
Ensure that the factory is equipped with cutting-edge machinery and equipment to manufacture reliable and high-performance plastic products. It would also be advantageous if they optimize the production methods and techniques for the materials you need.Quality is always the focus; therefore, you should check the products and ask about the processes to ensure that they meet global standards and your requirements.
Design and engineering teams’ capabilities
Ask whether the company’s design and engineering team has ever been involved in similar projects in the past. This will help you determine if they are qualified to handle your project. If they have not yet participated in similar projects but are still willing to cooperate, please verify that they have the necessary skills and knowledge.
Production capacity and additional services
Whether you need prototypes, small-scale production, or mass production, the plastic machining you choose must be able to suit the size of your project. For example, working with factories that provide a wide range of project development and implementation services would be ideal.
Standards and certifications
When selecting a plastic product manufacturing partner, it is essential to determine whether suppliers comply to acceptable criteria. They should be familiar with ISO standards.
price
Price is always a factor to consider when evaluating items. Many factors can affect the final price of a product, including raw materials, manufacturing processes, and total production. The total project costs should also consider the expertise, responsiveness, and additional services provided by the manufacturer. Finally, look at the solutions that the factory provides, because given the backend labor and other savings, their recommended finished product may actually reduce the total cost of ownership.
Longsheng: your plastic machining partner
As an international high-end OEM / ODM manufacturer, Longsheng has nearly 20 years of development experience.We are committed to providing quality products to our customers that can only be achieved through knowledge and technical expertise.We also have a ISO 9001:2015 certified quality assurance program and have advanced equipment and an experienced team to ensure quality from design to production.
Furthermore, all design and tool work was done internally, allowing us to establish strict control over all projects while reducing lead times.Our experts can help you produce high quality plastic products that meet your requirements! Please contact us for more information about our services and solutions.

conclusion
most common plastic materials can be mechanically processed, but need to be considered in the selection and use according to the specific material properties and processing requirements. In the plastic machining, we need to pay attention to the selection of appropriate cutting tools, processing parameters and processing technology, to ensure a good processing effect.
FAQs
How much does plastic machining cost?
Plastic machining cost is a complex and changeable concept, which needs to be calculated according to the specific machining requirements, materials, process, quantity and other factors. If you need an accurate quotation, it is recommended to contact Longsheng directly for a detailed consultation.
What are the plastic machining methods?
Plastic processing is the general term of various processes that convert synthetic resin or plastic into plastic products. The main methods include but are not limited to injection molding, extrusion molding, blowing molding, plastic film molding, calendering molding, hot molding, plastic absorption molding, foam molding, composite molding. Each plastic processing method has its specific application scenarios and advantages, according to the specific needs and design of the product, you can choose the most suitable processing method. At the same time, different processing methods will also affect the cost, quality and production efficiency of products.
What is the most solid plastic in plastic machining?
Nylon 66 (PA66), polycarbonate (PC), polybenzene sulfide (PPS) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) are all considered relatively robust plastic materials in plastic machining. However, each material has its own unique physical and chemical properties, so in practical applications, the most appropriate material should be selected according to the specific needs and the use environment.
How to reduce plastic machining costs?
①Choose plastic materials that meet the design requirements of the part and are less expensive. This helps reduce the overall cost of parts. ② Simplify part design to reduce complexity and processing time. The simple design is not only cost-effective but also easier to manufacture with high precision. ③Bulk discounts are available for ordering larger quantities of parts. Bulk ordering is a cost-effective way to reduce overall machining costs. ④ Consider relaxing tolerance requirements to reduce processing time and cost. However, balancing cost and required accuracy is critical. ⑤ Optimize the machining process and reduce the time required to process each part. Reducing machining time can result in significant cost savings without compromising part quality.
Resource
Effect of Recycled Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Plastic Material on Moldability
Effect of extrusion and compression moulding on the thermal properties of nylon


