When creating brand-new items, accuracy, product compatibility, and time are crucial in the medical area. You need an approach that supports medical-grade products and produces quick results there. One technique that meets this criterion is vacuum casting.
This short article highlights using vacuum casting for clinical gadgets, discussing benefits, specific applications, and products ideal for making such medical products.
What’s Vacuum Casting?
Vacuum casting, a method for making plastic prototypes, utilizes a silicone mold and mildew to generate little batches of similar items. The name “vacuum molding” comes from the casting procedure under a vacuum, which removes air bubbles and ensures total mold and mildew fill with the molten substratum.
The procedure starts with producing a master mold using CNC machining or 3D Printing. After puttiPrintingmold in a barrel, workers load it with silicone. The silicone dries rapidly, causing a mold ideal for plastic or metal casting under vacuum cleaner problems.
One of the advantages of the process is its cost-effectiveness and time effectiveness compared to similar strategies, such as plastic shot molding. It’s excellent for making models.
Why Pick Vacuum Casting for Medical Device Production
The clinical field is susceptible, where materials are picked based on rigorous needs. The vacuum casting process helps fulfill those requirements.
Here are some reasons that you need to choose vacuum casting for rapid prototyping and medical device production:
Precision and Information Accuracy
Vacuum casting is preferred for its accuracy and precision. Nonetheless, that depends on precisely how precise your master mold is. Commonly, you can anticipate an accuracy of 0.05 mm with vacuum casting.
Material Flexibility
Medical tools generally use different sorts of plastics, each with specific attributes. The silicone molding technique sustains most of the commercially offered plastics and resins. This includes ABS, rubber, polypropylene, HDPE, polyamide, glass-filled nylon, polycarbonate, and PMMA (acrylic). That’s why it has a variety of applications simply in the clinical sector.
Cost-Effectiveness for Tiny Batches
In clinical tool production, the expense is essential when you’re in the growth stages. You don’t want to spend a whole lot on models and tests. Here, vacuum casting is much better than various other fast manufacturing techniques.
It has a low setup price; you only need a master mold, mildew, and material. The silicon itself is cheaper. In addition, one mold is enough to make up to 25 duplicates. And unlike other makers, you don’t have high-powered devices that take in considerable electrical power. So, on the whole, a low-operational price.
Speed of Production
The rate of manufacturing is also vital in the medical area. Scientists call for a process with a faster turnaround for testing theories in the quickest time feasible. Compared to techniques like injection molding with 2 to 3 weeks lead time, vacuum casting decreases this to 10 to 15 days.
Top Notch Surface Finish
Vacuum casting generates a high-grade surface area coating in clinical gadgets. The resin binds firmly with the silicon mold under a vacuum cleaner, duplicating the master mold’s surface area. Additionally, there’s an alternative to adding color pigments and accomplishing any surface area finish to the surface, be it glossy, matte, or any type of personalized structure.
Reduced Threat of Air Bubbles and Imperfections
Throughout spreading, air entrapped with liquified material can generate bubbles, devastating for items as they trigger imperfection. To avoid that, the whole spreading takes place under a vacuum cleaner. It eradicates bubble development and guarantees molten products get to every silicon mold and mildew edge.
Adaptability in Design Changes
In die casting, long-term metal molds make layout changes challenging and expensive. Nonetheless, silicon mold and mildew are cheaper and less complicated to prepare. After making a specific set, you can recreate or apologize in the mold layout with a bit of cost.
Capacity to Imitate Final Products
Vacuum casting imitates final products well. It makes use of numerous resins that simulate the properties of end products. That is why it’s rather prominent for creating and examining medical models.
Instances of Clinical Instruments Produced Utilizing Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting has applications throughout different fields, yet its role in the medical market is particularly remarkable. This strategy proves invaluable in situations needing specific replicas of human organs or complex parts of clinical machinery.
Below are some typical applications in the clinical field, in addition to specific instances of gadgets and vacuum cast parts:
| Application | Examples |
| Prosthetic Components | Customized prosthetic limbs |
| Surgical Models and Simulators | Organ models of the human body for surgical practices. |
| Medical Enclosures and Housings | Casings for ECG machines, defibrillators |
| Custom Orthotics and Braces | Ankle braces, custom shoe insoles |
| Hearing Aid Components | Earmolds, inner casings |
| Dental Devices | Dental impression trays, orthodontic retainers |
| Respiratory Therapy Devices | Parts for nebulizers, oxygen concentrator components |
| Surgical Instruments and Tools | Endoscopic tools, scalpel handles, clamps |
| Implant Prototypes | Hip and knee replacements, dental implants |
LongSheng Brings Your Medical Device to Life
Are you a researcher or item developer working on brand-new clinical gadgets? LongSheng provides an efficient option to bring your designs to life. We provide vacuum casting solutions for accurate, thorough clinical prototypes and small set production.
Our spreading services are backed by ISO 13485 and ISO 9001:2015 qualifications, which indicates every item we make satisfies the highest requirements of medical tool production.
Our knowledgeable design group can help you pick the most effective manufacturing method, whether shot molding for significant volumes, 3D Printing for complicaPrintinges, or CPrintingning for precision parts.
Obtain trusted, quality-focused production for your medical tools today!
Materials for Vacuum Casting Medical Devices
As mentioned, the medical field generally utilizes various plastics for device production. Some prominent material options are:
Rubber
Rubber is famous for its adaptable nature. It can be conveniently built into complicated forms. Additionally, it’s low-cost and can be reused.
T0387 (clear rubber) and UPX800 are rubber-like products commercially utilized for vacuum casting. They are fantastic for making elastic prototypes.
ABS
ABS has a low melting thickness, which makes it difficult to work with throughout casting. After setting, it dramatically affects stamina, durability, and chemical resistance. Furthermore, it’s dimensionally stable so that the abdominal components won’t warp gradually. Its variations, PU8260 and PU8263, have superb flame resistance and are perfect for making high-strength elements.
Polypropylene( PP) and HDPE
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic, which implies it’s an exceptional candidate for vacuum casting. Additionally, it’s lightweight and warmth resistant. A material with similar properties is HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene). Nonetheless, it is inflexible compared to PP.
Polyamide
Polyamide also has excellent strength but is very flexible and resilient, regardless of that. Chemical resistance is another significant attribute. It is suitable for high-temperature applications.
Glass Filled Nylon
Enhancing glass fibers to nylon substantially raises its strength. It additionally shows improved wear and thermal resistance. It is best for internal moving parts that undergo friction and wear.
Polycarbonate (PC).
The computer is widely known for its resilience, lightweight nature, and outstanding dimensional security. It is solid and durable and can be conveniently built into intricate forms. UP6160 and PX510 are frequently used for polyurethane casting.
PMMA (Acrylic).
PMMA, typically called acrylic, is a clear plastic known for its toughness and shatter resistance. It is high-quality, making it ideal for applications calling for openness. PMMA’s usual grades are X522HT, PX5210, and PX5210H.
Filled up ABS.
Filled-up ABS combines abdominal with other materials to boost properties like resilience and warmth resistance.
Below is a quick summary of the mechanical properties of vacuum casting materials.
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Flexural Rigidity(MPa) | Hardness(Shore D) |
| Rubber | 15 – 40 | — | 95 (Shore A) |
| ABS | 60 – 84 | 1.2 – 2.5 | 80 – 100 |
| PP | 20 – 50 | 0.6 – 1.3 | 70– 85 |
| HDPE | 21 – 30 | 0.5 – 1.6 | 60 – 75 |
| Polyamide | 50 – 80 | 1 – 3.2 | 64 – 72 |
| Glass Filled Nylon | 90 – 120 | 1.75 – 2 | 58 – 75 |
| Polycarbonate | 60 – 70 | 1.5 – 2.3 | 85 – 90 |
| PMMA | 65 – 75 | 2 – 2.2 | 83 – 99 |
Alternatives of Vacuum Casting for Medical Devices
Besides utilizing vacuum casting for the clinical industry, alternate fast prototyping procedures exist to execute the same work:
Injection molded
Injection molding resembles the vacuum cleaner molding process in that a mold and mildew tooth cavity aids in making items. In this case, a liquified product is infused right into a permanent metal tooth cavity under high pressure, where it strengthens and attains the shape of the tooth cavity. It’s even more exact and used for the high-quantity production of clinical gadgets.
3D Printing.
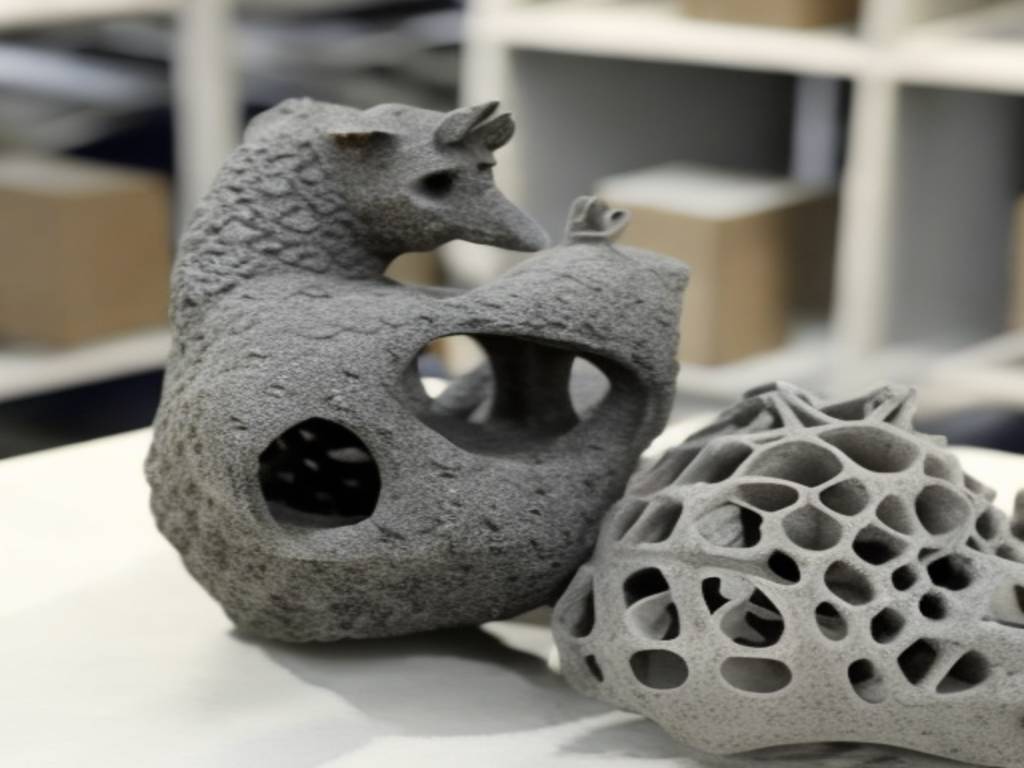

3D Printing is an additive process that develops layer by layer from electPrintingsigns. It offers high customization and adaptability, making it perfect for prototyping and creating intricate geometries. Nonetheless, the surface finish is not as good as that of other processes.
CNC Machining.
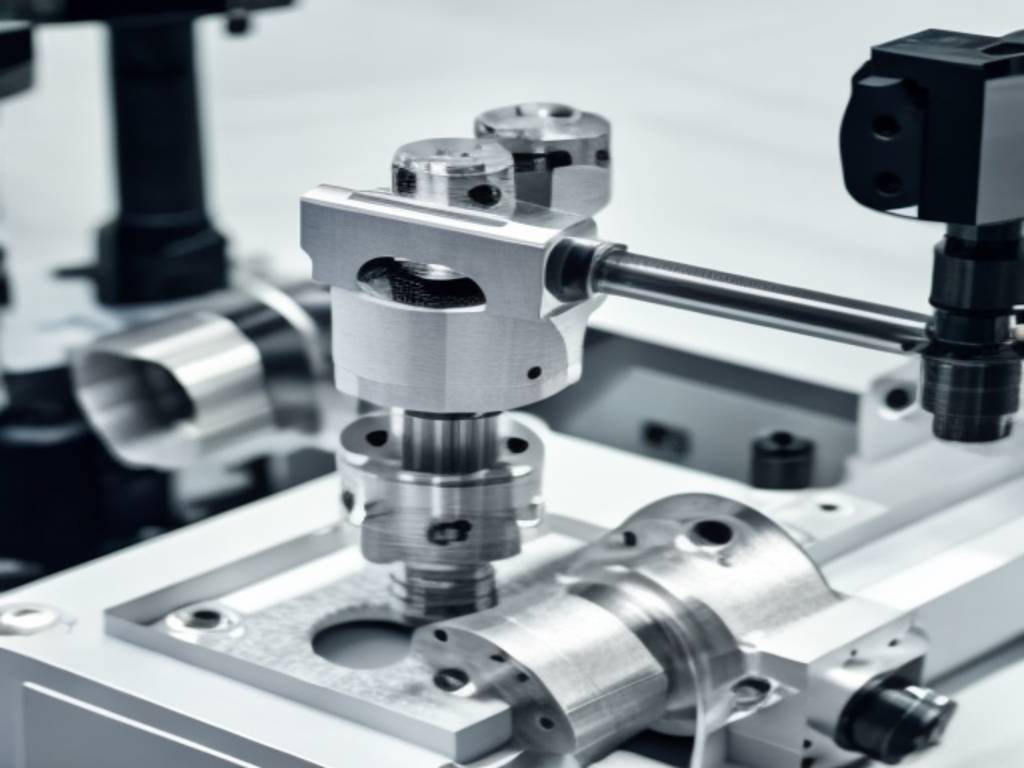

CNC (Computer System Numeric Control) machining entails deducting material from a solid block and using various reducing tools to achieve the desired form. CNC machining is significantly more closely related to precision and accuracy than all other procedures. It is appropriate for prototyping, but costs are relatively high compared to other procedures.
Conclusion
Vacuum Casting is a cost-efficient method for rapidly generating clinical devices. With its ability to mold a range of medical-grade materials, vacuum casting has substantial applications in the clinical gadget industry. The approach functions effortlessly, whether making prosthetic arms or legs, oral implants, or rapid prototyping.


